 W
WThe Atka mackerel is a mackerel in the family Hexagrammidae. Atka mackerel are common to the northern Pacific ocean, and are one of only two members of the genus Pleurogrammus - the other being the Arabesque greenling. The Atka mackerel was named for Atka Island, the largest island of the Andreanof islands, a branch of the Aleutians.
 W
WThe bicolored false moray, bicoloured false moray, false moray, or bicolor eel, Chlopsis bicolor, is an eel in the family Chlopsidae. It was described by Constantine Samuel Rafinesque in 1810. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from throughout the eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including southern Florida, USA; Mexico, southern Brazil, eastern Morocco, Mauritania, and the northern Mediterranean. It typically dwells at a depth of 80–365 m. Males can reach a maximum total length of 42 cm.
 W
WThe big-scale sand smelt is a species of fish in the family Atherinidae. It is a euryhaline amphidromous fish, up to 20 cm in length.
 W
WThe blackmouth catshark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, common in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean from Iceland to Senegal, including the Mediterranean Sea. It is typically found over the continental slope at depths of 150–1,400 m (490–4,590 ft), on or near muddy bottoms. The youngest sharks generally inhabit shallower water than the older juveniles and adults. This slim-bodied species is characterized by the black interior of its mouth, a marbled pattern of pale-edged brownish saddles or blotches along its back and tail, and a prominent saw-toothed crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the upper edge of its caudal fin. It reaches lengths of 50–79 cm (20–31 in), with sharks in the Atlantic growing larger than those in the Mediterranean.
 W
WThe bluegill is a species of freshwater fish sometimes referred to as "bream", "brim", "sunny", or "copper nose". It is a member of the sunfish family Centrarchidae of the order Perciformes. It is native to North America and lives in streams, rivers, lakes, and ponds. It is commonly found east of the Rockies. It usually hides around, and inside, old tree stumps and other underwater structures. It can live in either deep or very shallow water, and will often move from one to the other depending on the time of day or season. Bluegills also like to find shelter among aquatic plants and in the shade of trees along banks.
 W
WThe blunt-snouted clingfish is a species of clingfish found along the Mediterranean Sea coasts from Syria to Spain. This species grows to a length of 5 centimetres (2.0 in) TL. The blunt-nosed clingfish is a little known species of shallow water along the littoral of the northern Mediterranean from Alicante to northern Israel. It can survive out of the water and occurs only among intertidal pebbles and sand.
 W
WThe bullet tuna, Auxis rochei, is a species of tuna, in the family Scombridae, found circumglobally in tropical oceans, including the Mediterranean Sea, in open surface waters to depths of 50 m (164 ft). The population of bullet tuna in the western Pacific was classified as a subspecies of A. rochei, A. rochei eudorax, but some authorities regard this as a valid species Auxis eudorax. Its maximum length is 50 centimetres (20 in).
 W
WCentracanthus cirrus, also known as the curled picarel, is a species of picarel native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It has been found at depths down to 1,000 metres (3,300 ft). This species grows to a length of 34 centimetres (13 in) TL though usually not exceeding 12 centimetres (4.7 in). This species is of minor importance to local commercial fisheries. This species is the only known member of its genus.
 W
WCentrolabrus melanocercus, the black-tailed wrasse, is a species of marine ray-finned fish from the wrasse family Labridae which is found in the Mediterranean Sea and the Sea of Marmara. This species was formally described in 1810 as Lutjanus melanocercus by Antoine Risso with the type locality given as Saint Hospice near Villefranche-sur-Mer on the Mediterranean coast of France. This species was regarded as a member of the genus Symphodus but meristic and behavioural data placed it closer to the rock cook than the sexually dimorphic paternal nesting fishes in Symphodus. This species prefers areas with rocks or eelgrass at depths from 1 to 25 m. It can reach 14 cm (5.5 in) in total length, though most do not exceed 11 cm (4.3 in).
 W
WClinitrachus argentatus, the Cline, is a species of clinid found in shallow waters of the eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea. This species feeds primarily on benthic invertebrates. This species is currently the only known member of its genus.
 W
WEpigonus telescopus, the black cardinal fish, is a species of deepwater cardinalfish found in most temperate oceans worldwide, at depths of between 75 and 1,200 metres though mostly between 300 and 800 metres. It can reach a length of 75 centimetres (30 in) TL though most specimens do not exceed 55 centimetres (22 in) TL. It has been reported that this species can reach an age of 104 years.
 W
WThe five-spotted wrasse is a species of wrasse native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean from Spain to Morocco and through the coastal waters of the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea. This species inhabits rocky areas usually within beds of eelgrass at depths from 1 to 30 m. It can reach 17 cm (6.7 in) in standard length, though usually not more than 12 cm (4.7 in). This species is sought by local peoples as a food fish and can also be found in the aquarium trade.
 W
WGadella maraldi, the gadella or morid cod, is a species of fish in the family Moridae from the warmer waters of the north eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
 W
WThe golden goby is a species of goby from the family Gobiidae endemic to the Mediterranean Sea. It prefers areas with rocky substrates at depths of from 5 to 80 metres with plentiful growth of algae and gorgonians. This species can reach a length of 10 centimetres (3.9 in) TL. It can also be found in the aquarium trade. Gobius xanthocephalus is the name that is applied to the populations of similar gobies in the eastern Atlantic and western Mediterraean which were previously considered to be G. auratus.
 W
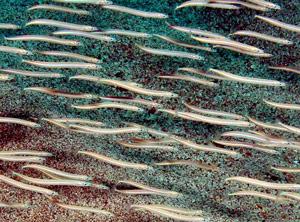
WThe golden grey mullet is a fish in the family Mugilidae.
 W
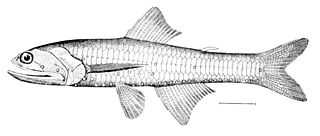
WGymnammodytes cicerelus, also known as Mediterranean sand eel, sonso in Catalan, and barrinaire or enfú in Menorca, is a fish in the family Ammodytidae. It is the only species of this family in the Mediterranean Sea. It is a species from the family Ammodytidae, the sandlances or sandeels.
 W
WLampanyctus crocodilus, the jewel lanternfish, is a lanternfish of the family Myctophidae, found in west Mediterranean Sea and north Atlantic Ocean. Bathypelagic between 400 and 2000 m.
 W
WHexagrammos decagrammus, the kelp greenling, is a species of greenling that occurs in rocky nearshore areas of the northern Pacific especially around British Columbia and Alaska, and is common on kelp beds and on sand bottoms. They feed on crustaceans, polychaete worms, brittle stars, mollusks, and small fishes. The young are food for large predators such as lingcod and halibut. Unique to this species is its mating ritual, where males attempt to inseminate eggs in the nests of other males. This phenomenon can be explained with condition dependent mating decisions.
 W
WThe leaping mullet is a species of fish in the family Mugilidae. It is found in coastal waters and estuaries in the northeast Atlantic, ranging from Morocco to France, and including the Mediterranean and Black Sea. It has been introduced to the Caspian Sea.
 W
WLepadogaster candolii, common name Connemarra clingfish, is a species of fish in the genus Lepadogaster. It occurs in the Eastern Atlantic from the British Isles south to Madeira and the Canary Islands and into the western Mediterranean and the Black Sea. The specific name candolii honours the Swiss botanist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle (1778-1841) and has various spellings: candolii, candolei, candollei, and decandollii, but only the first one is correct. Some workers have found that L. candolii is not closely related to the other two species in the genus Lepadogaster and have proposed the placing of this species in the revived monotypic genus Mirbelia Canestrini, 1864, at least until more definitive taxonomic studies can be undertaken.
 W
WThe four-spot megrim is a species of flatfish in the family Scophthalmidae. It is found a depths between 7 and 800 m in the northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean. It can be separated from its close relative, the megrim or whiff, by the dark spots towards the rear of the fins. It reaches a length of 40 cm (16 in).
 W
WLesueur's goby is a species of goby native to the Eastern Atlantic Ocean near the coasts of the Canary Islands and Morocco as well as in the Mediterranean Sea. This species occurs at depths down to 230 metres (750 ft) through most of its range, though the population in the Ionian Sea are found much deeper, at depths of from 322 to 337 metres. This species can reach a length of 5 centimetres (2.0 in) TL. This species can also be found in the aquarium trade The specific name honours the French naturalist Charles Alexandre Lesueur (1778-1846).
 W
WThe lined seahorse, northern seahorse or spotted seahorse, is a species of fish that belongs to the family Syngnathidae. H. erectus is a diurnal species with an approximate length of 15 cm and lifespan of one to four years. The H. erectus species can be found in myriad colors, from greys and blacks to reds, greens, and oranges. The lined seahorse lives in the western Atlantic Ocean as far north as Canada and as far south as the Caribbean, Mexico, and Venezuela. It swims in an erect position and uses its dorsal and pectoral fins for guidance while swimming.
 W
WThe little gulper shark is a small, deepwater dogfish of the family Centrophoridae.
 W
WThe little tunny is the most common tuna in the Atlantic Ocean. It is found in warm temperate and tropical waters of the Atlantic and the Mediterranean; in the western Atlantic, it ranges from Brazil to the New England states. It is found regularly in offshore and inshore waters, and is classified as a highly migratory species by UNCLOS. Occurring in large schools and weighing up to 36 lb, it is one of the smaller members of the tuna family (Scombridae).
 W
WThe louvar or luvar is a species of perciform fish, the only extant species in the genus Luvarus and family Luvaridae. It is closely related to the surgeonfish. The juvenile form has a pair of spines near the base of the tail, like the surgeonfish, though they are lost in the adult.
 W
WThe marbled electric ray is a species of electric ray in the family Torpedinidae found in the coastal waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean from the North Sea to South Africa. This benthic fish inhabits rocky reefs, seagrass beds, and sandy and muddy flats in shallow to moderately deep waters. It can survive in environments with very little dissolved oxygen, such as tidal pools. The marbled electric ray has a nearly circular pectoral fin disc and a muscular tail that bears two dorsal fins of nearly equal size and a large caudal fin. It can be identified by the long, finger-like projections on the rims of its spiracles, as well as by its dark brown mottled color pattern, though some individuals are plain-colored. Males and females typically reach 36–38 cm (14–15 in) and 55–61 cm (22–24 in) long respectively.
 W
WPomatoschistus marmoratus, the marbled goby, is a species of goby native to the eastern Atlantic from the Bay of Biscay down around the Iberian Peninsula through the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov. It is also found in the Suez Canal in Egypt. It occurs in marine and brackish waters on sandy substrates in shallow waters, typically down to 20 m (66 ft), but occasionally to 70 m (230 ft) in the winter. It can reach a length of 8 cm (3.1 in) TL though most do not exceed 5 centimetres (2.0 in) TL.
 W
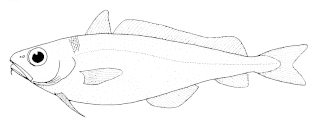
WThe Mediterranean spearfish is a species of marlin native to the Mediterranean Sea where it is particularly common around Italy, although there is a probable record of one caught off Madeira. It is an open-water fish, being found within 200 metres (660 ft) of the surface. This species can reach a length of 240 centimetres (94 in) TL. The heaviest recorded specimen weighed in at 70 kilograms (150 lb) This species is of minor importance to commercial fisheries.
 W
WMora moro, the common mora, is a deep-sea fish, the only species in the genus Mora. It is found worldwide in temperate seas, at depths of between 300 and 2,500 m. Its length is up to about 80 cm. Other names in English include goodly-eyed cod, googly-eyed cod, and ribaldo.
 W
WMyctophum punctatum is a species of mesopelagic fish in the family Myctophidae. Its common name is spotted lanternfish, sometimes spelled spotted lanterfish. It is found in the Northern Atlantic and in the Mediterranean at depths down to 1000m. It is one of the dominant species in midwater assemblages near the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
 W
WThe Pacific cod, Gadus macrocephalus, is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Gadidae. It is a bottom-dwelling fish found in the northern Pacific Ocean, mainly on the continental shelf and upper slopes, to depths of about 900 m (3,000 ft). It can grow to a length of a meter or so and is found in large schools. It is an important commercial food species and is also known as gray cod or grey cod, and grayfish or greyfish. Fishing for this species is regulated with quotas being allotted for hook and line fishing, pots, and bottom trawls.
 W
WSalaria pavo, the peacock blenny, is a species of combtooth blenny found in the eastern Atlantic coast from France to Morocco; also in the Mediterranean and Black seas. This species has colonised the northern Red Sea by anti-Lessepsian migration through the Suez Canal. The peacock blenny reaches a length of 13 centimetres (5.1 in) TL.
 W
WThe red-black triplefin is a species of fish in the family Tripterygiidae, the threefin blennies. It is widespread in the d the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea. In the Black Sea it occurs off the coasts of the Crimea and Ukraine.
 W
WHexagrammos lagocephalus is a colorful marine fish with the common name rock greenling in the greenling family. It is sometimes known as fringed greenling and erroneously as the red rock trout.
 W
WThe saffron cod (Eleginus gracilis) is a commercially harvested fish closely related to true cods. It is dark grey-green to brown, with spots on its sides and pale towards the belly. It may grow to 60 cm and weigh up to 1.3 kg.
 W
WSalmo cettii, or the Mediterranean trout, is a species of trout, a freshwater fish in the family Salmonidae. It lives in the Mediterranean region in Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily, and on the Italian mainland in the Magra drainage and further south. It is a nonmigratory fish which lives in streams and in karstic resurgences. It is smaller than 40 cm (16 in) in length. It is sometimes referred to Salmo trutta macrostigma, which depending on concept is either a more widespread Mediterranean taxon, or a taxon endemic to Algeria.
 W
WThe sand sole is a fish species in the family Soleidae. It is a marine, subtropical, demersal fish, up to 40 centimetres (16 in) long.
 W
WThe sand tiger shark, grey nurse shark, spotted ragged-tooth shark or blue-nurse sand tiger, is a species of shark that inhabits subtropical and temperate waters worldwide. It inhabits the continental shelf, from sandy shorelines and submerged reefs to a depth of around 191 m (627 ft). They dwell in the waters of Japan, Australia, South Africa, the Mediterranean and the east coasts of North and South America. Despite its name, it is not related to the tiger shark Galeocerdo cuvier.
 W
WThe scale-rayed wrasse, Acantholabrus palloni, is a species of wrasse native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean where it occurs from Norway to Gabon and in the Mediterranean Sea and the Adriatic Sea. This species can be found on reefs at depths of from 30 to 500 m. It can reach a length of 25 cm (9.8 in). It is a commercially important food fish. It is currently the only known member of its genus.
 W
WThe shortfin mako shark, also known as the blue pointer or bonito shark, is a large mackerel shark. It is commonly referred to as the mako shark, as is the longfin mako shark. The shortfin mako can reach a size of 4 m (13 ft) in length. The species is classified as Endangered by the IUCN.
 W
WSmall red scorpionfish is a venomous Scorpionfish, common in marine subtropical waters. It is widespread in the Eastern Atlantic from the Bay of Biscay to Senegal, Madeira, Azores and the Canary Islands, including the Mediterranean and the Black Sea.
 W
WThe smalleye squaretail, Tetragonurus cuvieri, is a squaretail of the genus Tetragonurus found in all tropical and temperate oceans of the world, at depths up to 800 m. Its length is 20 to 70 cm.
 W
WThe smalltooth sand tiger or bumpytail ragged-tooth is a species of mackerel shark in the family Odontaspididae, with a patchy but worldwide distribution in tropical and warm temperate waters. They usually inhabit deepwater rocky habitats, though they are occasionally encountered in shallow water, and have been known to return to the same location year after year. This rare species is often mistaken for the much more common grey nurse shark, from which it can be distinguished by its first dorsal fin, which is larger than the second and placed further forward. It grows to at least 4.1 m (13.5 ft) in length.
 W
WThe solenette or yellow sole, Buglossidium luteum, is a species of flatfish in the family Soleidae, and the only member of its genus. It is characterized by its small size, low-slung semi-circular mouth, and regularly placed dark fin rays. A common and widespread species, it is native to sandy bottoms in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It is of little commercial value.
 W
WThe spotted pipefish, Nerophis maculatus, is a species of Pipefishes, found in the Eastern Atlantic: Portugal and Azores, Mediterranean Sea, especially numerous in its western part and the Adriatic Sea. Ovoviviparous, marine subtropical coastal fish up to 15 centimetres (5.9 in) maximal length. It is inhabits rocky sites of coast, also in aquatic plants and algae, at depth up to 50 metres (160 ft).
 W
WThresher sharks are large lamniform sharks of the family Alopiidae found in all temperate and tropical oceans of the world; the family contains three extant species, all within the genus Alopias.
 W
WTrachyrincus scabrus, the roughsnout grenadier or Mediterranean longsnout grenadier, is a species of bathydemersal marine fish from the subfamily Trachyrincinae, part of the family Macrouridae. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean.
 W
WAphia minuta, the transparent goby, is a species of the goby native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean where it can be found from Trondheim, Norway to Morocco. It is also found in the Mediterranean, Black Sea and the Sea of Azov. It is a pelagic species, inhabiting inshore waters and estuaries. It can be found at depths of from the surface to 97 metres (318 ft), though it is usually found at 5 to 80 metres, over sandy and muddy bottoms and also in eelgrass beds. This species can reach a length of 7.9 centimetres (3.1 in) TL. It is an important species to local commercial fisheries. It is currently the only known member of its genus.