 W
WThe almond moth or tropical warehouse moth is a small, stored-product pest. Almond moths infest flour, bran, oats, and other grains, as well as dried fruits. It belongs to the family of snout moths (Pyralidae), and more specifically to the tribe Phycitini of the huge snout moth subfamily Phycitinae. This species may be confused with the related Indian mealmoth or the Mediterranean flour moth, which are also common pantry pests in the same subfamily.
 W
WThe American cockroach is the largest species of common cockroach, and often considered a pest. In certain regions of the U.S. it is colloquially known as the waterbug, though it is not a true waterbug since it is not aquatic. It is also known as the ship cockroach, kakerlac, and Bombay canary. It is often misidentified as a palmetto bug.
 W
WMezium americanum, the American spider beetle or black spider beetle, is a species of beetle in the subfamily Ptininae, the spider beetles. These are sometimes mistaken for spiders or mites because of their rounded abdomens and long legs. It has a cosmopolitan distribution, but it is an exotic species in Australia.
 W
WAnthrenus flavipes is a species of beetle in the family Dermestidae known by the common name furniture carpet beetle. It has a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring throughout the world, being most active in warmer climates. It is a pest that damages household materials such as textiles.
 W
WThe Argentine ant, formerly Iridomyrmex humilis, is an ant native to northern Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia and southern Brazil. It is an invasive species that has been established in many Mediterranean climate areas, inadvertently introduced by humans to many places, including South Africa, New Zealand, Japan, Easter Island, Australia, Europe, Hawaii, and the continental United States.
 W
WThe banded sugar ant, also known as the sugar ant, is a species of ant native to Australia. A member of the genus Camponotus in the subfamily Formicinae, it was described by German entomologist Wilhelm Ferdinand Erichson in 1842. Its common name refers to the ant's liking for sugar and sweet food, as well as the distinctive orange-brown band that wraps around its gaster.
 W
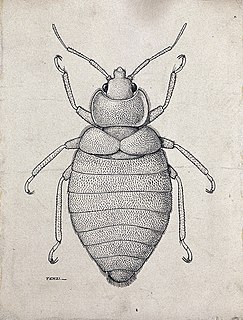
WBed bugs are insects from the genus Cimex that feed on human blood, usually at night. Their bites can result in a number of health impacts including skin rashes, psychological effects, and allergic symptoms. Bed bug bites may lead to skin changes ranging from small areas of redness to prominent blisters. Symptoms may take between minutes to days to appear and itchiness is generally present. Some individuals may feel tired or have a fever. Typically, uncovered areas of the body are affected. Their bites are not known to transmit any infectious disease. Complications may rarely include areas of dead skin or vasculitis.
 W
WCamponotus pennsylvanicus, or the black carpenter ant, is one of the largest and most common species of carpenter ant native to the central and eastern United States as well as eastern Canada.
 W
WThe black-headed sugar ant, also known as the brown sugar ant, is a species of Formicinae ant endemic to Australia. Found throughout most states, the species is a member of the genus Camponotus, a cosmopolitan genus of ants commonly known as carpenter ants. It was formally described and named by British entomologist Frederick Smith in 1858. These ants are characterised by their black head, reddish-brown mesosoma and black gaster, which can change in colour.
 W
WThe Asian cockroach, is a species of cockroach that was first described in 1981 from insects collected on Okinawa Island, Japan. It is a small species of cockroach, and typically are 1.3 to 1.6 cm long and is tan to dark brown in colour with dark parallel stripes on the back of their head. It is commonly mistaken with the German cockroach for their similar appearance. It is commonly found in the United States in and around houses.
 W
WThe boxelder bug is a North American species of true bug. It is found primarily on boxelder trees, as well as maple and ash trees. The adults are about 12.5 millimetres (0.49 in) long with a dark brown or black colouration, relieved by red wing veins and markings on the abdomen; nymphs are bright red. This species recently invaded Chile, thus becoming an invasive species.
 W
WCamponotus nearcticus, commonly named smaller carpenter ant is a relatively small carpenter ant. Its appearance is similar of that to Lasius niger, commonly named the black garden ant. The ant is a household pest.
 W
WCimex hemipterus, known as the tropical bed bug, is a species of bedbugs within the cimicidae family that primarily resides in tropical climates. However, it has been reported that this species can live in more temperate climates along with the closely related bed bug species C. lectularius. C. hemipterus is a hematophagous, obligate parasite of humans. This means that it requires blood meals from their human hosts in order to survive. When bitten, humans experience itchiness, wheals, and lesions around the affected areas on the skin. This species typically resides in human domiciles within cracks, crevices, or mattresses, and are more prevalent in developing countries. Like other bed bugs, C. hemipterus is primarily active during the night time.
 W
WCockroaches are insects of the order Blattodea, which also includes termites. About 30 cockroach species out of 4,600 are associated with human habitats. About five species are well known as pests.
 W
WThe confused flour beetle, a type of darkling beetle known as a flour beetle, is a common pest insect known for attacking and infesting stored flour and grain. They are one of the most common and most destructive insect pests for grain and other food products stored in silos, warehouses, grocery stores, and homes.
 W
WThe deathwatch beetle is a species of woodboring beetle that sometimes infests the structural timbers of old buildings. The adult beetle is brown and measures on average 7 mm (0.3 in) long. Eggs are laid in dark crevices in old wood inside buildings, trees, and inside tunnels left behind by previous larvae. The larvae bore into the timber, feeding for up to ten years before pupating, and later emerging from the wood as adult beetles. Timber that has been damp and is affected by fungal decay is soft enough for the larvae to chew through. They obtain sufficient nourishment by using a number of enzymes present in their gut to digest the cellulose and hemicellulose in the wood.
 W
WThe destructive or dark flour beetle, one of the species of darkling beetle known generally as flour beetles, is a common pest insect known for attacking and infesting stored flour and grain.
 W
WEphestia elutella, the cacao moth, tobacco moth or warehouse moth, is a small moth of the family Pyralidae. It is probably native to Europe, but has been transported widely, even to Australia. A subspecies is E. e. pterogrisella.
 W
WForelius pruinosus, commonly known as the high noon ant, is a species of ant in the genus Forelius. Described by Roger in 1863, the species is endemic to North America.
 W
WForficula auricularia, the common earwig or European earwig, is an omnivorous insect in the family Forficulidae. The European earwig survives in a variety of environments and is a common household insect in North America. The name earwig comes from the appearance of the hindwings, which are unique and distinctive among insects, and resemble a human ear when unfolded; the species name of the common earwig, auricularia, is a specific reference to this feature. They are considered a household pest because of their tendency to invade crevices in homes and consume pantry foods, and may act either as a pest or as a beneficial species depending on the circumstances.
 W
WThe German cockroach is a small species of cockroach, typically about 1.1 to 1.6 cm long. In colour it varies from tan to almost black, and it has two dark, roughly parallel, streaks on the pronotum running anteroposteriorly from behind the head to the base of the wings. Although B. germanica has wings, it can barely fly, although it may glide when disturbed. Of the few species of cockroach that are domestic pests, it probably is the most widely troublesome example. It is very closely related to the Asian cockroach, and to the casual observer, the two appear nearly identical and may be mistaken for each other. However, the Asian cockroach is attracted to light and can fly like a moth, while the German cockroach cannot.
 W
WThe golden spider beetle, Niptus hololeucus, is a species of spider beetle in the family Ptinidae.
 W
WThe housefly is a fly of the suborder Cyclorrhapha. It is believed to have evolved in the Cenozoic Era, possibly in the Middle East, and has spread all over the world as a commensal of humans. It is the most common fly species found in houses. Adults are gray to black, with four dark, longitudinal lines on the thorax, slightly hairy bodies, and a single pair of membranous wings. They have red eyes, set farther apart in the slightly larger female.
 W
WHylotrupes is a monotypic genus of woodboring beetles in the family Cerambycidae, the longhorn beetles. The sole species, Hylotrupes bajulus, is known by several common names, including house longhorn beetle, old house borer, and European house borer. It is the only genus in the tribe Hylotrupini.
 W
WIncisitermes minor is a species of termite in the family Kalotermitidae known commonly as the western drywood termite. It is native to western North America, including the western United States and northern Mexico. It has been found in many other parts of the United States, all the way to the East Coast. It has been reported from Toronto. It has been introduced to Hawaii. It has been noted in China and it is not uncommon in Japan. This is an economically important pest of wooden structures, including houses. In California and Arizona alone its economic impact is estimated to be about $250 million per year.
 W
WThe Indianmeal moth, also spelled as Indian meal moth and Indian-meal moth, is a pyraloid moth of the family Pyralidae. Alternative common names are weevil moth, pantry moth, flour moth or grain moth. The almond moth and the raisin moth are commonly confused with the Indian-meal moth due to similar food sources and appearance. The species was named after being noted for feeding on Indian-meal or cornmeal and it does not occur natively in India as the aberrant usage of Indian meal moth would suggest. It is also not to be confused with the Mediterranean flour moth, another common pest of stored grains.
 W
WIridomyrmex, or the rainbow ant is a genus of ant first described by Austrian entomologist Gustav Mayr in 1862. He placed it in the subfamily Dolichoderinae of the family Formicidae. There are 79 described species and five fossil species. Most of these ants are native to Australia; others are found in Asia and Oceania, and they have been introduced to Brazil, New Zealand and the United Arab Emirates. Fossil species are known from China, France and the United States.
 W
WThe jack jumper ant, also known as the jack jumper, jumping jack, hopper ant, or jumper ant, is a species of venomous ant native to Australia. Most frequently found in Tasmania and southeast mainland Australia, it is a member of the genus Myrmecia, subfamily Myrmeciinae, and was formally described and named by British entomologist Frederick Smith in 1858. This species is known for its ability to jump long distances. These ants are large; workers and males are about the same size: 12 to 14 mm for workers, and 11 to 12 mm for males. The queen measures roughly 14 to 16 mm long and is similar in appearance to workers, whereas males are identifiable by their perceptibly smaller mandibles.
 W
WThe meat ant, also known as the gravel ant or southern meat ant, is a species of ant endemic to Australia. A member of the genus Iridomyrmex in the subfamily Dolichoderinae, it was described by British entomologist Frederick Smith in 1858. The meat ant is associated with many common names due to its appearance, nest-building behaviour and abundance, of which its specific name, purpureus, refers to its coloured appearance. It is among the best-known species of ant found throughout Australia; it occurs in almost all states and territories except for Tasmania. Its enormous distribution, aggression and ecological importance have made this ant a dominant species.
 W
WThe Mediterranean flour moth or mill moth is a moth of the family Pyralidae. It is a common pest of cereal grains, especially flour. This moth is found throughout the world, especially in countries with temperate climates. It prefers warm temperatures for more rapid development, but it can survive a wide range of temperatures.
 W
WMoths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species.
 W
WMusca is a genus of flies. It includes Musca domestica, as well as Musca autumnalis. It is part of the family Muscidae.
 W
WOchetellus glaber is a species of ant native to Australia. A member of the genus Ochetellus in the subfamily Dolichoderinae, it was described by Austrian entomologist Gustav Mayr in 1862. Aside from Australia, O. glaber has been introduced to a number of countries, including China, India, Japan, New Zealand, the Philippines and the United States, where it has established itself in Hawaii and Florida. It has been found on Lord Howe Island, New Caledonia, Norfolk Island, Réunion and the Solomon Islands. Compared with other ants, O. glaber is a small species, with workers measuring 2–3 mm (0.079–0.118 in). Males are the smallest at 1.6 mm (0.063 in), while the queens measure 5.2–5.5 mm (0.20–0.22 in). The ant's colour ranges from brown to black.
 W
WThe oriental cockroach, also known as the waterbug or black beetle, is a large species of cockroach, adult males being 18–29 mm (0.71–1.14 in) and adult females being 20–27 mm (0.79–1.06 in). It is dark brown or black in color and has a glossy body. The female has a somewhat different appearance from the male, appearing to be wingless at a casual glance, but is brachypterous, having non-functional wings just below her head. She has a wider body than the male. The male has long wings, which cover three quarters of the abdomen and are brown in color, and has a narrower body. Both of them are flightless. The female oriental cockroach looks somewhat similar to the Florida woods cockroach and may be mistaken for it. Originally endemic to the Crimean Peninsula and the region around the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, its distribution is now cosmopolitan.
 W
WPowderpost beetles are a group of seventy species of woodboring beetles classified in the insect subfamily Lyctinae. These beetles, along with spider beetles, death watch beetles, common furniture beetles, skin beetles, and others, make up the superfamily Bostrichoidea. While most woodborers have a large prothorax, powderpost beetles do not, making their heads more visible. In addition to this, their antennae have two-jointed clubs. They are considered pests and attack deciduous trees, over time reducing the wood to a powdery dust. The damage caused by longhorn beetles is often confused with that of powderpost beetles, but the two groups are unrelated. The larvae of the Cerambycidae are white, straight and generally flat-headed, whereas those of the Bostrichidae are white and C-shaped.
 W
WPtinus tectus, often called the Australian spider beetle, is a species of beetle in the genus Ptinus of the family Ptinidae, or family Anobiidae, subfamily Ptininae. It is a cosmopolitan species. It is a pest of stored foods and museum specimens.
 W
WThe tawny crazy ant or Rasberry crazy ant, Nylanderia fulva, is an ant originating from South America. Like the longhorn crazy ant, this species is called "crazy ant" because of its quick, unpredictable movements. It is sometimes called the "Rasberry crazy ant" in Texas after the exterminator Tom Rasberry, who noticed that the ants were increasing in numbers in 2002. Scientists have reorganised the genera taxonomy within this clade of ants, and now it is identified as Nylanderia fulva.
 W
WThe red flour beetle is a species of beetle in the family Tenebrionidae, the darkling beetles. It is a worldwide pest of stored products, particularly food grains, and a model organism for ethological and food safety research.
 W
WThe red imported fire ant, also known as the fire ant or RIFA, is a species of ant native to South America. A member of the genus Solenopsis in the subfamily Myrmicinae, it was described by Swiss entomologist Felix Santschi as a variant in 1916. Its current specific name invicta was given to the ant in 1972 as a separate species. However, the variant and species were the same ant, and the name was preserved due to its wide use. Though South American in origin, the red imported fire ant has been accidentally introduced in Australia, New Zealand, several Asian and Caribbean countries, and the United States. The red imported fire ant is polymorphic, as workers appear in different shapes and sizes. The ant's colours are red and somewhat yellowish with a brown or black gaster, but males are completely black. Red imported fire ants are dominant in altered areas and live in a wide variety of habitats. They can be found in rain forests, disturbed areas, deserts, grasslands, alongside roads and buildings, and in electrical equipment. Colonies form large mounds constructed from soil with no visible entrances because foraging tunnels are built and workers emerge far away from the nest.
 W
WThe silverfish is a species of small, primitive, wingless insect in the order Zygentoma. Its common name derives from the animal's silvery light grey colour, combined with the fish-like appearance of its movements. The scientific name indicates that the silverfish's diet consists of carbohydrates such as sugar or starches. While the common name silverfish is used throughout the global literature to refer to various species of Zygentoma, the Entomological Society of America restricts use of the term solely for Lepisma saccharinum.
 W
WTechnomyrmex albipes, commonly known as the white-footed ant, is a species of ant first described in 1861 from Sulawesi, Indonesia by the British entomologist Frederick Smith. Invasive pest ants in Florida, previously identified as T. albipes, have now been separated as Technomyrmex difficilis, both forming part of a species complex with a worldwide distribution.
 W
WTermites are eusocial insects that are classified at the taxonomic rank of infraorder Isoptera, or as epifamily Termitoidae within the order Blattodea. Termites were once classified in a separate order from cockroaches, but recent phylogenetic studies indicate that they evolved from cockroaches, as they are the sister group to wood eating cockroaches of the genus Cryptocercus. Previous estimates suggested the divergence took place during the Jurassic or Triassic. More recent estimates suggest they have an origin during the Late Jurassic, with the first fossil records in the Early Cretaceous. About 3,106 species are currently described, with a few hundred more left to be described. Although these insects are often called "white ants", they are not ants, and are not closely related to ants.
 W
WThylodrias is a monotypic genus of beetles in the family Dermestidae containing the single species Thylodrias contractus, known commonly as the odd beetle and tissue paper beetle. It is native to Asia and is a widespread introduced species in North America. It can be a pest at times.
 W
WTineidae is a family of moths in the order Lepidoptera described by Pierre André Latreille in 1810. Collectively, they are known as fungus moths or tineid moths. The family contains considerably more than 3,000 species in more than 300 genera. Most of the tineid moths are small or medium-sized, with wings held roofwise over the body when at rest. They are particularly common in the Palaearctic, but many occur elsewhere, and some are found very widely as introduced species.
 W
WTineola bisselliella, known as the common clothes moth, webbing clothes moth, or simply clothing moth, is a species of fungus moth. It is the type species of its genus Tineola and was first described by Arvid David Hummel in 1823. The specific name is commonly misspelled biselliella – for example by G. A. W. Herrich-Schäffer, when he established Tineola in 1853.
 W
WTrichomyrmex destructor is a species of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae. Its common names include destructive trailing ant or Singapore ant. It is a pest species in urban areas, known for causing costly damage to structures, vehicles, and electronic devices with its chewing activity. In 2015, the species was moved from the genus Monomorium to the revised genus Trichomyrmex.
 W
WThe Turkestan cockroach, also known as the rusty red cockroach, red runner cockroach or simply rusty red, red runner, or lat, is a primarily outdoor-dwelling cockroach native to an area from northern Africa to Central Asia. Adults measure around 3 cm (1.2 in) in length. Adult males are a brownish orange or red, are slender, and have long, yellowish wings which allow it to attract females and to glide. Adult females are dark brown to black, with cream-colored markings on the shield and a cream-colored stripe edging its wings; they are broader than males, and have short vestigial wings. Nymphs are brown in front, black on the rear, and are wingless.