 W
WAmoeba proteus , of which Chaos diffluens is one of many synonyms, is a large amoeba related to another genus of giant amoebae, Chaos. It can be bought at science supply stores.
 W
WAnosteira is an extinct genus of carettochelyid turtle from the Eocene to the Oligocene of Asia and North America.
 W
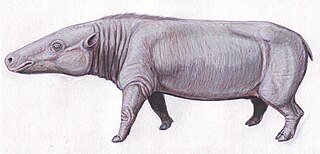
WAnthracotheriidae is a paraphyletic family of extinct, hippopotamus-like artiodactyl ungulates related to hippopotamuses and whales. The oldest genus, Elomeryx, first appeared during the middle Eocene in Asia. They thrived in Africa and Eurasia, with a few species ultimately entering North America during the Oligocene. They died out in Europe and Africa during the Miocene, possibly due to a combination of climatic changes and competition with other artiodactyls, including pigs and true hippopotamuses. The youngest genus, Merycopotamus, died out in Asia during the late Pliocene. The family is named after the first genus discovered, Anthracotherium, which means "coal beast", as the first fossils of it were found in Paleogene-aged coal beds in France. Fossil remains of the anthracothere genus were discovered by the Harvard University and Geological Survey of Pakistan joint research project (Y-GSP) in the well-dated middle and late Miocene deposits of the Pothohar Plateau in northern Pakistan.
 W
WAntrodemus is a dubious genus of theropod dinosaur from the Kimmeridgian-Tithonian age Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation of Middle Park, Colorado. It contains one species, Antrodemus valens, first described and named as a species of Poekilopleuron by Joseph Leidy in 1870.
 W
WThe short-faced bear is an extinct bear genus that inhabited North America during the Pleistocene epoch from about 1.8 Mya until 11,000 years ago. It was the most common tremarctine bear in North America and many of its fossils have been found in the La Brea tar pits in southern California. There are two recognized species: the lesser short-faced bear and the giant short-faced bear, with the latter considered to be one of the largest known terrestrial mammalian carnivores that has ever existed. It has been hypothesized that their extinction coincides with the Younger Dryas period of global cooling commencing around 10,900 BC.
 W
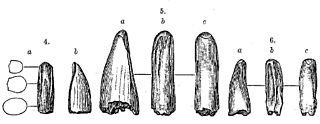
WAublysodon is a genus of carnivorous dinosaurs known only from the Judith River Formation in Montana, which has been dated to the late Campanian age of the late Cretaceous period. The only currently recognized species, Aublysodon mirandus, was named by paleontologist Joseph Leidy in 1868. It is now considered dubious, because the type specimen consists only of an isolated premaxillary (front) tooth. Although this specimen is now lost, similar teeth have been found in many US states, western Canada, and Asia. These teeth almost certainly belong to juvenile tyrannosaurine tyrannosaurids, but most have not been identified to species level. However, it is likely that the type tooth belongs to one of the species in the genus Daspletosaurus, which was present in contemporary formations, and which matches specific details of the original tooth. The synapomorphies alleged to distinguish the Aublysodontinae, especially lack of serrations on premaxillary teeth could have been caused by tooth wear in life, postmortem abrasion, or digestion. Most other "aublysodontine"-type teeth may be from ontogenetic stages or sexual morphs of other tyrannosaurids.
 W
WBison antiquus, the antique or ancient bison, is an extinct species of bison that lived in Late Pleistocene North America until around 10,000 years ago. It was one of the most common large herbivores on the North American continent during the late Pleistocene, and is a direct ancestor of the living American bison along with Bison occidentalis.
 W
WBootherium is an extinct bovid genus from the middle to late Pleistocene of North America which contains a single species, Bootherium bombifrons. Vernacular names for Bootherium include Harlan's muskox, woodox, woodland muskox, helmeted muskox, or bonnet-headed muskox. Bootherium was one of the most widely distributed muskox species in North America during the Pleistocene era. It is most closely related to the modern muskox, from which it diverged around 3 million years ago, it is possibly synonymous with Euceratherium, although this is uncertain.
 W
WCamelops is an extinct genus of camels that lived in North and Central America, ranging from Alaska to Honduras, from the middle Pliocene to the end of the Pleistocene. It is more closely related to the Old World dromedary and bactrian and wild bactrian camels than the New World guanaco and vicuña, and alpaca and llama, making it a true camel of the Camelini tribe. Its name is derived from the Ancient Greek κάμηλος and ὄψ, i.e. "camel-face".
 W
WThe dire wolf is an extinct canine. It is one of the most famous prehistoric carnivores in North America, along with its extinct competitor Smilodon. The dire wolf lived in the Americas and eastern Asia during the Late Pleistocene and Early Holocene epochs. The species was named in 1858, four years after the first specimen had been found. Two subspecies are recognized: Aenocyon dirus guildayi and Aenocyon dirus dirus. The largest collection of its fossils has been obtained from the Rancho La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles.
 W
WChisternon is a genus of baenid cryptodiran turtles from the Eocene of North America.
 W
WThe pygmy hippopotamus is a small hippopotamid which is native to the forests and swamps of West Africa, primarily in Liberia, with small populations in Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Ivory Coast. It has been extirpated from Nigeria.
 W
WCimoliasaurus was a plesiosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of New Jersey. It grew from 13 to 25 ft long.
 W
WCimolichthys is an extinct genus of 1.5- to 2.0-meter-long nektonic predatory aulopiformid fish.
 W
WDimetrodon borealis, formerly known as Bathygnathus borealis, is an extinct species of pelycosaur-grade synapsid that lived about 270 million years ago (Ma) in the Early Permian. A partial maxilla or upper jaw bone from Prince Edward Island in Canada is the only known fossil of Bathygnathus. The maxilla was discovered around 1845 during the course of a well excavation in Spring Brook in the New London area and its significance was recognized by geologists John William Dawson and Joseph Leidy. It was originally described by Leidy in 1854 as the lower jaw of a dinosaur, making it the first purported dinosaur to have been found in Canada, and the second to have been found in all of North America. The bone was later identified as that of a pelycosaur. Although its current classification as a sphenacodontid synapsid was not recognized until after the discovery of its more famous relative Dimetrodonin the 1870s, Bathygnathus is notable for being the first discovered sphenacodontid. A 2015 study by the researchers from U of T Mississauga, Carleton University and the Royal Ontario Museum reclassified the species into the genus Dimetrodon.
 W
WDiplotomodon is a dubious genus of theropod dinosaur, from New Jersey. It was possibly a member of the Tyrannosauroidea, the clade that also contains Tyrannosaurus.
 W
WHadrosaurus is a genus of hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaurs that lived in North America during the Late Cretaceous Period in what is now the Woodbury Formation about 80 million to 78 million years ago. The holotype specimen was found in fluvial marine sedimentation, meaning that the corpse of the animal was transported by a river and washed out to sea.
 W
WHeleopera is a genus of Amoebozoa. It includes the following species.Heleopera sphagni Heleopera rosea Heleopera sylvatica Heleopera petricola
 W
WHypohippus is an extinct genus of three-toed horse, which lived 17–11 million years ago. It was the size of a pony at 1.8 meters long. and fossils of it have been found in Nebraska, Colorado, and Montana.
 W
WHyracodon is an extinct genus of perissodactyl mammal.
 W
WMegacerops is an extinct genus of the prehistoric odd-toed ungulate family Brontotheriidae, an extinct group of rhinoceros-like browsers related to horses. It was endemic to North America during the Late Eocene epoch, existing for approximately 4.1 million years.
 W
WMegalocnus is a genus of extinct giant ground sloths that were found on Cuba and Hispaniola. They were among the largest of the Caribbean ground sloths, with individuals estimated to have weighed up to 90 kg (200 lb) when alive. Two species have been described, M. rodens of Cuba, and M. zile of Hispaniola. Their relatives include other Caribbean ground sloths, such as Acratocnus, Mesocnus, Miocnus, Neocnus, Parocnus, and Paulocnus. M. zile is currently thought to be a junior synonym of Parocnus serus.
 W
WMerychyus is an extinct genus of oreodont of the family Merycoidodontidae, endemic to North America. It lived during the Miocene, 20.4—10.3 mya, existing for approximately 10 million years. Fossils are widespread through the central and western United States.
 W
WMylohyus is an extinct genus of peccary found in North and Central America. It evolved in the Pliocene and its extinction is probably as recent as 9,000 years ago. It would have been familiar with early humans.
 W
WNotharctus is a genus of adapiform primate that lived in North America and Europe during the late to middle Eocene.
 W
WOntocetus is an extinct genus of walrus, an aquatic carnivoran of the family Odobenidae, endemic to coastal regions of the southern North Sea and the southeastern coastal regions of the U.S. during the Miocene-Pleistocene. It lived from 13.6 mya—300,000 years ago, existing for approximately 13.3 million years.
 W
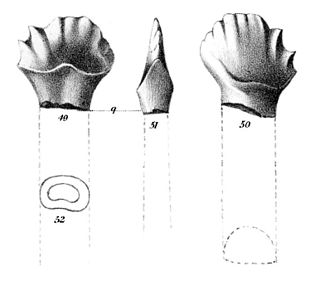
WPalaeocastor is an extinct genus of beavers that lived in the North American Badlands during the late Oligocene period to early Miocene. Palaeocastor was much smaller than modern beavers. There are several species including Palaeocastor fossor, Palaeocastor magnus, Palaeocastor wahlerti, and Palaeocastor peninsulatus.
 W
WPalaeoscincus is a dubious genus of ankylosaurian dinosaur based on teeth from the mid-late Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Judith River Formation of Montana. Like several other dinosaur genera named by Joseph Leidy, it is an historically important genus with a convoluted taxonomy that has been all but abandoned by modern dinosaur paleontologists. Because of its wide use in the early 20th century, it was somewhat well known to the general public, often through illustrations of an animal with the armor of Edmontonia and the tail club of an ankylosaurid.
 W
WThe American lion, also known as the "North American lion", or "American cave lion", is an extinct pantherine cat that lived in North America during the Pleistocene epoch and the early Holocene epoch, about 340,000 to 11,000 years ago. Its fossils have been excavated from Alaska to Mexico. Genetic analysis has shown that the American lion and the Late Pleistocene Eurasian cave lion are sister lineages. It was about 25% larger than the modern lion, making it one of the largest known felids.
 W
WParahippus, is an extinct equid, a relative of modern horses, asses and zebras. It was very similar to Miohippus, but slightly larger, at around 1 metre tall, at the withers.
 W
WPatriofelis was a large, cat-like oxyaenid of middle Eocene in North America. It was around 1.2 to 1.8 metres long, not including the tail, and weighed about 40–90 kg, making it around the same size as a modern cougar. It had short legs with broad feet, suggesting that it may have been a poor runner, but a quite good swimmer. As its close relative Oxyaena was a reasonably good climber, it is possible Patriofelis could climb as well. It is found in particular in the Bridger Basin of southwestern Wyoming and at John Day Fossil Beds National Monument, in the U.S. state of Oregon.
 W
WPectinatella magnifica, the magnificent bryozoan, is a member of the Bryozoa phylum, in the order Plumatellida. It is a colony of organisms that bind together; these colonies can sometimes be 60 centimeters in diameter. These organisms can be found mostly in North America with some in Europe. They are often found attached to objects, but can be found free floating as well. They form a translucent body with many star-like blooms along the outside. The density of the organism is similar to that of gelatin, and is easily breakable into smaller chunks.
 W
WPeritresius is an extinct genus of sea turtle from the Late Cretaceous deposits in the US Eastern Seaboard.
 W
WPiratosaurus is a dubious genus of plesiosaur possibly belonging to the Polycotylidae that is known exclusively from the type species P. plicatus, named and described by Joseph Leidy in 1865. It is known only from the holotype, USNM V 1000, a tooth, discovered in Late Cretaceous-aged rocks in the Red River basin of Manitoba; at least one researcher erroneously assumed it was found in Minnesota.
 W
WPoebrotherium is an extinct genus of camelid, endemic to North America. They lived from the Eocene to Miocene epochs, 46.3—13.6 mya, existing for approximately 32 million years.
 W
WProcamelus is an extinct genus of camel endemic to North America. It lived from the Middle to Late Miocene 16.0—5.3 mya, existing for approximately 11 million years. The name is derived from the Greek πρό, meaning "before" or denoting priority of order, and κάμελος ("camel"), thus meaning "fore-camel", "early camel" or "predecessor camel".
 W
WProtohippus is an extinct three-toed genus of horse. It was roughly the size of a modern donkey. Fossil evidence suggests that it lived during the Late Miocene, from about 13.6 Ma to 5.3 Ma.
 W
WSaniwa is an extinct genus of varanid lizard that lived about 48 million years ago during the Eocene epoch. It is known from well-preserved fossils found in the Bridger and Green River Formations of Wyoming. The type species S. ensidens was described in 1870 as the first fossil lizard known from North America. Several other species have since been added, but their validity is uncertain. It is a close relative of Varanus, the genus that includes monitor lizards.
 W
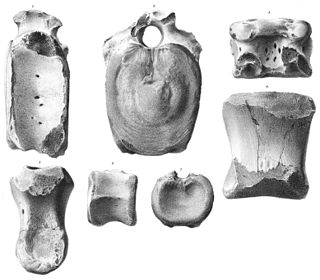
WStylemys is the first fossil genus of dry land tortoise belonging to the order Testudines discovered in the United States. The genus lived in temperate to subtropical areas of North America, Europe, and Asia, based on fossil distribution. The genus was first described in 1851 by Joseph Leidy. The tortoise was common in the prehistoric Badlands, especially Nebraska and South Dakota. The species has also been found in the formations in and around Badlands National Park. Fossil fragments have also been found in the Palm Park Formation of New Mexico.
 W
WThespesius is a dubious genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur from the late Maastrichtian-age Upper Cretaceous Lance Formation of South Dakota.
 W
WThoracosaurus is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph which existed during the Late Cretaceous and Early Paleocene. The animal had traditionally been thought to be related to the modern false gharial, largely because the nasal bones contact the premaxillae. Phylogenetic work starting in the 1990s instead supported affinities within Gavialoidea exclusive of such forms, although a 2018 tip dating study simultaneously using morphological, molecular, and stratigraphic data suggests that it might have been a non-crocodylian eusuchian. The genus contains the species Thoracosaurus neocesariensis in North America and what is either Thoracosaurus isorhynchus or T. macrorhynchus; a recent review argues that T. macrorhynchus is a junior synonym of T. isorhynchus, but it is unclear whether the type of T. isorhynchus allows differentiation of European and North American Thoracosaurus; if not, then T. isorhynchus would be a nomen dubium. A number of species have been referred to this genus, but most are dubious.
 W
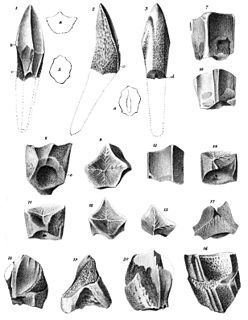
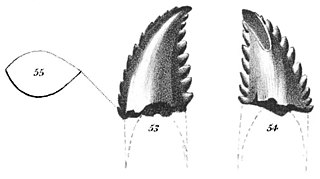
WTrachodon is a dubious genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur based on teeth from the Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Judith River Formation of Montana, U.S. It is a historically important genus with a convoluted taxonomy that has been all but abandoned by modern dinosaur paleontologists.
 W
WTroodon is a former wastebasket taxon and a potentially dubious genus of relatively small, bird-like dinosaurs known definitively from the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period. It includes at least one species, Troodon formosus, known from Montana. Discovered in October 1855, T. formosus was among the first dinosaurs found in North America, although it was thought to be a lizard until 1877. Several well-known troodontid specimens from the Dinosaur Park Formation in Alberta were once believed to be members of this genus. However, recent analyses in 2017 have found the genus to be undiagnostic and referred some of these specimens to the genus Stenonychosaurus and others to the genus Latenivenatrix.
 W
WUintatherium is an extinct genus of herbivorous mammal that lived during the Eocene epoch. Two species are currently recognized: U. anceps from the United States during the Early to Middle Eocene and U. insperatus of Middle to Late Eocene China.
 W
WXiphactinus is an extinct genus of large predatory marine bony fish that lived during the Late Cretaceous. When alive, the fish would have resembled a gargantuan, fanged tarpon. The species Portheus molossus described by Cope is a junior synonym of X. audax. Skeletal remains of Xiphactinus have come from the Carlile Shale and Greenhorn Limestone of Kansas, and Cretaceous formations all over the East Coast in the United States, as well as Europe, Australia, the Kanguk and Ashville Formations of Canada, La Luna Formation of Venezuela and the Salamanca Formation in Argentina.