 W
WAmata perixanthia is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by George Hampson in 1898. It is found in Taiwan, Tibet and eastern China.
 W
WAmolops gerbillus is a species of frog found in Asia. It is native to northern and northeastern India, Tibet (China), and Myanmar, and possibly to Bhutan and Nepal. Its common names include Yembung sucker frog and gerbil stream frog. It is a semi-aquatic frog occurring in hill streams.
 W
WAreas galactina is a moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Jan van der Hoeven in 1840. It is found in China, Taiwan, the north-western Himalayas, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Indochina, the Philippines, Indonesia and Sundaland.
 W
WAthyma opalina, the Himalayan sergeant, is a species of nymphalid butterfly found in tropical and subtropical Asia.
 W
WBassarona durga, the blue duke, is a species of nymphalid butterfly found in the Himalayas.
 W
WBhutanitis thaidina, commonly known as the Chinese three-tailed swallowtail, is a rare species of butterfly in the family Papilionidae.
 W
WThorold's deer is a threatened species of deer found in grassland, shrubland, and forest at high altitudes in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. It is also known as the white-lipped deer for the white patches around its muzzle.
 W
WDichagyris juldussi is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in western China, western Tibet and Turkestan.
 W
WDuttaphrynus himalayanus, also known as the Himalaya toad, Himalayan toad, Himalayan broad-skulled toad, and Günther's high altitude toad, is a species of toad that is widely distributed throughout the Himalayan mountains. The Yunnanese populations are sometimes considered a separate species, Duttaphrynus cyphosus.
 W
WThe false osman is an Asian cyprinid freshwater fish living in the highlands of Afghanistan, southwestern China, Iran, northern India, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan and Tajikistan. Young individuals and small adults live in shallow streams and pools, while large adults inhabit the main river and lakes. It grows to 34 cm (13 in) in total length.
 W
WThe goa, also known as the Tibetan gazelle, is a species of antelope that inhabits the Tibetan plateau.
 W
WHodgson's giant flying squirrel is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae. This large flying squirrel lives in Himalayan forests in Asia. Like other flying squirrels, it is nocturnal and able to glide long distances between trees by spreading out its patagium, skin between its limbs.
 W
WJapalura tricarinata is a species of agamid lizard endemic to Asia.
 W
WKurixalus naso is a species of frog in the family Rhacophoridae. It is found in northeastern India, Tibet, and Myanmar. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, subtropical or tropical moist shrubland, subtropical or tropical seasonally wet or flooded lowland grassland, and intermittent freshwater marshes. It is threatened by habitat loss.
 W
WLycodon fasciatus, commonly known as the banded wolf snake, is a species of colubrid snake.
 W
WThe Turkestan lynx is a subspecies of Eurasian lynx native to Central Asia. It is also known as Central Asian lynx, Tibetan lynx or Himalayan lynx. It is widespread from west in Central Asia, from South Asia to China and Mongolia. There are 27,000 mature individuals in China as of 2013. It is proposed for the Turkestan lynx to be listed as Vulnerable in Uzbekistan.
 W
WThe northern pig-tailed macaque is a species of macaque in the family Cercopithecidae. It is found in Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam. Traditionally, M. leonina was considered a subspecies of the southern pig-tailed macaque, but is now classified as individual species.
 W
WThe Tibetan macaque, also known as the Chinese stump-tailed macaque or Milne-Edwards' macaque, is a macaque species found from eastern Tibet east to Guangdong and north to Shaanxi in China. It has also been reported from northeastern India. This species lives in subtropical forests at elevations from 800 to 2,500 m above sea level.
 W
WMangina argus, the crotalaria podborer, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Vincenz Kollar in 1847. It is found in south-east Asia, including Zhejiang, Fujian, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Guangdong, Yunnan, Taiwan, Hunan, from southern India to Kashmir, the Himalayas, Nepal, Bhutan and Sri Lanka.
 W
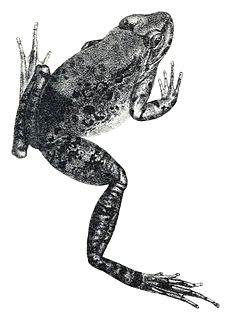
WNanorana blanfordii is a species of frog in the family Dicroglossidae. It is found in northeastern India, southern Tibet (China), and eastern Nepal, and likely in the adjacent western Bhutan. The specific name blanfordii honours William Thomas Blandford, a British geologist and zoologist.
 W
WNanorana conaensis is a species of frog in the family Dicroglossidae. Its name refers to its type locality, Mama in Cona County in Tibet. Note that while large parts of Cona County are located within Arunachal Pradesh in the area that is controlled by India but claimed by China, Mama is on the Tibetan side of the border. It has recently been reported also from Bhutan. Its natural habitats are subtropical moist montane forest, high-altitude shrubland, and rivers.
 W
WNanorana liebigii, also known as Sikkim paa frog, Liebig's paa frog, Liebig's frog, and spiny-armed frog, is a species of frog in the family Dicroglossidae. It is found in the Himalayas, specifically in Bhutan, southern Tibet (China), northern India, and Nepal. The specific name liebigii honours a certain "Dr von Liebig Jr.", likely referring to Justus von Liebig, German botanist and chemist.
 W
WThe northern frog, or the Rotung oriental frog is a species of frog in the family Dicroglossidae. It is found in Bangladesh, Bhutan, northeastern India, Tibet, Nepal, and western Myanmar.
 W
WPhilautus kempii is a species of frog in the family Rhacophoridae. It is known with certainty from its type locality, Upper Rotung in Arunachal Pradesh, Northeast India, in the area also claimed by China. It is also reported from Arunachal Pradesh in general as well as from extreme eastern Tibet; these might represent another species. Very little is known about this species, and even its taxonomic validity remains uncertain.
 W
WPhrynocephalus theobaldi is a species of lizard in the family Agamidae. The species is endemic to Asia.
 W
WThe Himalayan pika is a species of small mammal in the pika family (Ochotonidae). It is found at high altitudes in remote areas of Tibet and possibly also in Nepal. The IUCN has listed this species as being of "least concern".
 W
WThe Moupin pika, also known as Ribetischer Pika, Moupin-Pika, Pika del Tibet, and Manipuri pika, is a species of mammal in the pika family, Ochotonidae. It has many subspecies, some of which may be distinct species. Its summer pelage is dark russet-brown with some light spots on the dorsal side, and ochraceous buff tinged on the belly. In winter it is lighter, with buff to dull brown dorsal pelage. A generalist herbivore, it is found in the mountains of the eastern Tibetan Plateau in China, Bhutan, India (Sikkim), and northern Myanmar. Both the International Union for Conservation of Nature Red List of Endangered Species and the Red List of China's Vertebrates classify it as a species of least concern; although one subspecies may be endangered.
 W
WRaorchestes andersoni is a species of frog in the family Rhacophoridae. It is found in northeast India, northern Myanmar, and Tibet and Yunnan, China. The common names Anderson's bubble-nest frog, Anderson's bush frog and tuberculed small treefrog have been coined for it.
 W
WRhacophorus rhodopus is a species of frog in the moss frog family (Rhacophoridae). It occurs in south-eastern Asia, from India to southern China, and south to Malaysia. Previously unknown from Laos, it has now been found in Phongsali Province and at Luang Prabang. Its taxonomy is disputed.
 W
WScorpiops atomatus is a species of scorpion in the Euscorpiidae family, first found in Tibet and Yunnan, China.
 W
WScorpiops pococki is a species of scorpion in the Euscorpiidae family, first found in Tibet and Yunnan, China.
 W
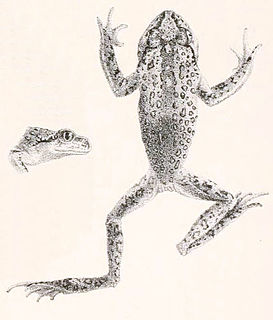
WScutiger boulengeri is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in Nepal, India (Sikkim) and western China. A healthy population has been found at an elevation of 5,270 m (17,290 ft) in one of the lakes in the Gurudongmar Lake complex in Sikkimese Himalaya. This is one of the highest elevations where amphibians have ever been recorded.
 W
WScutiger sikimmensis is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in northeastern India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Tibet. Many common names have been coined for this species: Sikkim lazy toad, Sikimmese pelobatid toad, Sikkim high altitude toad, Sikkim spade foot frog, Blyth's short-limbed frog, and Sikkim snow toad. It is very common in the high altitudes of Sikkimese Himalaya.
 W
WScutiger spinosus is a species of toad in the family Megophryidae. It is found in Medog County, Tibet (China) and in Tawang district, Arunachal Pradesh (India). Prior to its description in 2016, it was confused with Scutiger nyingchiensis. Common name spiny lazy toad has been coined for it.
 W
WSpilosoma erythrozona is a moth in the family Erebidae. It was described by Vincenz Kollar in 1844. It is found in China, eastern Afghanistan and Himalayas.
 W
WSwinhoe's striped squirrel is a small species of rodent in the family Sciuridae known scientifically as Tamiops swinhoei. This species is found mostly in China and Southeast Asia. Their diet consists of mostly seeds, fruits, nuts and ginger nectar. Like most squirrels they live in forest areas with mountains, usually in groups. They have litters that average in size of 3.25 offspring.
 W
WThe Mishmi takin is an endangered goat-antelope native to India, Myanmar and the People's Republic of China. It is a subspecies of takin.
 W
WTheloderma moloch is a species of frog in the family Rhacophoridae. It is found in northeastern India and adjacent Tibet, China, possibly wider. Taxonomic placement of this taxon has been a source of much debate, possibly because of wrong tissue was used for it in a molecular study—with ramifications for the taxonomy of whole Theloderma and its sister taxon Nyctixalus.
 W
WThe Tibetan stone loach is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Nemacheilidae. The specific name is sometimes spelled stoliczkae but the original spelling used by Steindachner is stoličkai. It is found in southern and central Asia.
 W
WThe Tian Shan dhole, also known as the Siberian dhole, western Asiatic dhole, or northern dhole is a subspecies of dhole native to the Altai and Tian Shan mountain ranges, and possibly Pamir and Kashmir.
 W
WTrachischium tenuiceps, also known as the yellowbelly worm-eating snake, is a species of colubrid snake found in South Asia and Tibet.
 W
WThe white-cheeked macaque is a species of macaque found only in Mêdog County in southeastern Tibet and Arunachal Pradesh in northeastern India. The white-cheeked macaque lives in forest habitats, from tropical forests to primary and secondary evergreen broad-leaved forests and mixed broadleaf-conifer forests. The species was first described by its discoverers, Chinese primatologists Cheng Li, Chao Zhao, and Peng-Fei Fan, in the American Journal of Primatology in 2015. It is one of twenty-three extant species in the genus Macaca, and the most recent to be formally described to science. While the species' exact conservation status has not yet been determined, it is likely threatened by poaching, deforestation, and increased human development of its habitat, much like the other primates which inhabit the area.
 W
WThe domestic yak is a long-haired domesticated cattle found throughout the Himalayan region of the Indian subcontinent, the Tibetan Plateau, Northern Myanmar, Yunnan, Sichuan and as far north as Mongolia and Siberia. It is descended from the wild yak.
 W
WYpthima sakra, the Himalayan five-ring, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae native to Asia.