 W
WAchnanthales is an order of diatoms.
 W
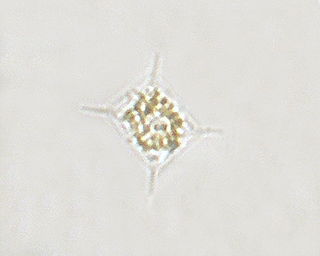
WActinocyclus is a genus of diatoms in the family Hemidiscaceae.
 W
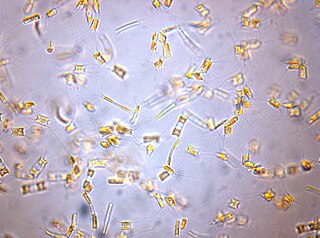
WAttheya decora is a species of diatoms in the genus Attheya. Type material was collected from Cresswell sands, Northumberland by Mr. Atthey.
 W
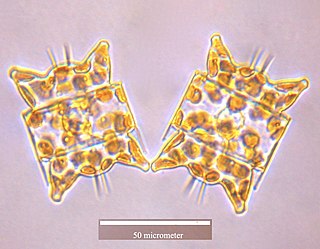
WAttheya longicornis is a species of diatoms in the genus Attheya. Type material was collected from Penberth, Cornwall in England.
 W
WBacillaria paxillifer is a diatom species in the family Bacillariaceae.
 W
WBacillariaceae is a family of diatoms in the phylum Heterokontophyta, the only family in the order Bacillariales. Some species of genera such as Nitzchia are found in halophilic environments; for example, in the seasonally flooded Makgadikgadi Pans in Botswana.
 W
WBacteriastrum delicatulum is a diatom in the genus Bacteriastrum.
 W
WBiddulphiaceae is a family of diatom in the order Biddulphiales. The Biddulphiaceae are distinguished from the Eupodiscaceae by their pseudocelli, where the Eupodiscaceae have fully developed ocelli. Both families commonly inhabit the littoral zone of the ocean, close to the shore. Sixteen species of Biddulphiaceae are found on the west coast of India.
 W
WBiddulphiophycidae or Biddulphiineae is a grouping of Centrales. In some taxonomic schemes Centrales or Centric diatoms are named Coscinodiscophyceae and may have different naming of suborders and families.
 W
WCampylodiscus is a genus of diatoms in the family Surirellaceae.
 W
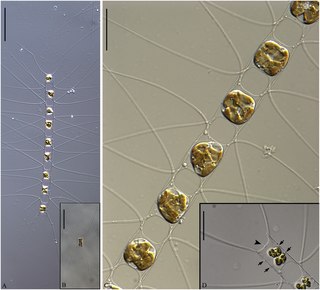
WChaetoceros diadema is a diatom in the genus Chaetoceros. The easiest way to identify this species is by finding the very characteristic diadem-like resting spores.
 W
WChaetoceros elegans is a species of diatom in the family Chaetocerotaceae. According to Li, 2017, the type locality is Dapeng Bay, Guangdong Province, P. R. China.
 W
WChaetoceros furcellatus is an Arctic neritic diatom in the genus Chaetoceros. The easiest way to identify this species is by finding the very characteristic resting spores. C. furcellatus is a common and important species in the Barents sea.
 W
WCocconeis is a genus of diatoms. Members of the genus are elliptically shaped diatoms.
 W
WCoscinodiscaceae is a diatom family in the order Coscinodiscales.
 W
WCoscinodiscophycidae or Coscinodiscineae is a grouping of Coscinodiscophyceae, previously known as "Centrales", a paraphyletic order of centric diatoms, a major group of algae and one of the most common members of the phytoplankton.
 W
WThe Cymbellaceae are a diatom family in the order Cymbellales.
 W
WThe Cymbellales are a diatom order in the class Bacillariophyceae. They include the following families:Anomoeoneidaceae Cymbellaceae Gomphonemataceae Rhoicospheniaceae
 W
WEunotia is a genus of diatoms. They are fresh water diatoms, specifically common in lakes, and they are also common in fossil records, although their siliceous wall design may have been lost and they appear plane, an example is Eunotia tetradon.
 W
WEunotiaceae is a family of diatoms in the order Eunotiales that includes the following genera:Actinella F.W. Lewis, 1864 Amphicampa (C.G. Ehrenberg) J. Ralfs in A. Pritchard, 1861 Amphorotia G.M. Williams & G. Reid, 2006 Burliganiella C.E.Wetzel & Kociolek Bicudoa C.E.Wetzel, Lange-Bertalot & L.Ector, 2012 Colliculoamphora D.M. Williams & G. Reid, 2006 † Desmogonium C.G. Ehrenberg in R. Schomburgk, 1848 Eunotia C.G. Ehrenberg, 1837 Eunotioforma J.P.Kociolek & A.L.Burliga, 2013 Euodia J.W. Bailey ex J. Ralfs in A. Pritchard, 1861 Perinotia D. Metzeltin & H. Lange-Bertalot, 2007 Semiorbis R. Patrick in R. Patrick & C.W. Reimer, 1966 Temachium Wallroth, 1833
 W
WEunotiales is an order of diatoms.
 W
WFragilariophyceae is a group of pennate diatoms lacking a raphe.
 W
WGomphoneis is a genus of diatoms in the family Gomphonemataceae.
 W
WNavicula is a genus of boat-shaped diatom algae, comprising over 1,200 species. Navicula is Latin for "small ship", and also a term in English for a boat-shaped incense-holder.
 W
WNavicula stesvicensis is a species of algae in the genus Navicula which has been isolated from the Danube river.
 W
WNaviculaceae is a diatom family in the order Naviculales.
 W
WThe Naviculales are an order of diatoms.
 W
WNitzschia is a common pennate marine diatom. In the scientific literature, this genus, named after Christian Ludwig Nitzsch, is sometimes termed Nitzchia, and it has many species described, which all have a similar morphology.
 W
WOdontella is a genus of marine diatoms. It contains the following species:Odontella aurita (Lyngbye) C. A. Agardh Odontella calamus (Brun & Tempère) H. J. Schrader Odontella cornuta (J. Brun) H. J. Schrader Odontella granulata (Roper) R. Ross Odontella hastata (Greville) J. Fenner ex D. M. Williams Odontella litigiosa (Van Heurck) Hoban Odontella longicruris (Greville) Hoban Odontella mobiliensis (J. W. Bailey) Grunow Odontella regia (Schultze) Simonsen Odontella rhombus Odontella septentrionalis H. J. Schrader Odontella sinensis (Greville) Grunow Odontella weissflogii (Janisch) Grunow
 W
WOdontella aurita is a diatom and the type species of genus Odontella. The easiest way to identify this species is by recognizing the very distinct shape of the cells belonging to this genus. Odontella aurita is cultivated industrially for human consumption due to its ability to produce up to 28% of its total lipids as Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), a long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA). PUFAs such as EPA are known to provide a variety of health benefits in humans, and are commonly obtained by fish oil. However, with the increasing concern of over-exploited fisheries, microalgae are a promising source of PUFAs as they can be grown year-round and their fatty acid profile and content are easily manipulated by growth conditions.
 W
WOscillaria is a genus of filamentous diatoms.
 W
WRhizosoleniophycidae or Rhizosoleniineae is a grouping of centric diatoms.
 W
WSkeletonema is a genus of diatoms in the family Skeletonemataceae. It is the type genus of its family. The genus Skeletonema was established by R.K. Greville in 1865 for a single species, S. barbadense, found in the Barbados deposit [Jung 2009]. These diatoms are photosynthetic organisms, meaning they obtain carbon dioxide from their surrounding environment and produce oxygen along with other byproducts. Reproduce sexually and asexually [Guiry 2011]. Skeletonema belong to the morphological category referred to as centric diatoms. These are classified by having valves with radial symmetry and the cells lack significant motility [Horner 2002]. Skeletonema are cylindrical shaped with a silica frustule. Cells are joined by long marginal processes to form a filament [Horner 2002]. Their length ranges from 2-61 micrometers, with a diameter ranging from 2-21 micrometers [Hasle 1997]. They are found typically in the neritic zone of the ocean and are highly populous in coastal systems [Jung 2009]. The genus is considered cosmopolitan, showing a wide range of tolerance for salinity and temperature [Hasle 1973]. For example, they have been found in various aquatic environments such as brackish or freshwater. Skeletonema are found worldwide excluding Antarctic waters [Hevia-Orube 2016]. Some harmful effects these diatoms may have on an ecosystem are attributed to large blooming events which may cause hypoxic events in coastal systems. Additionally, they are known to cause water discoloration [Kraberg 2010].
 W
WSkeletonemataceae is a family of diatoms in the order Thalassiosirales. There is currently only one known genera in this family of diatoms known as Skeletonema as reported from diatom.org. Being from the thalassiosirales order means that skeletonemataceae are centric diatoms.
 W
WSurirella is a genus of diatoms in the family Surirellaceae.
 W
WSurirellaceae is a family of diatoms in the order Surirellales.
 W
WSurirellales is an order of diatoms.
 W
WTabellaria is a genus of freshwater diatoms (Bacillariophyta). They are cuboid in shape, and the frustules are attached at the corners so that the colonies assume a zigzag shape.
 W
WTerpsinoë is a genus of diatom. Species include T. americana, T. javanicum, and T. musica.
 W
WThalassiosira is a genus of centric diatoms, comprising over 100 marine and freshwater species. It is a diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotes that make up a vital part of marine and freshwater ecosystems, in which they are key primary producers and essential for carbon cycling
 W
WThalassiosira pseudonana is a species of marine centric diatoms. It was chosen as the first eukaryotic marine phytoplankton for whole genome sequencing. T. pseudonana was selected for this study because it is a model for diatom physiology studies, belongs to a genus widely distributed throughout the world's oceans, and has a relatively small genome at 34 mega base pairs. Scientists are researching on diatom light absorption, using the marine diatom of Thalassiosira. The diatom requires a high enough concentration of CO2 in order to utilize C4 metabolism, and this positive feedback loop is indicative of how it is responsible for producing 40% of organic carbon for the ocean floor (Clement et al. 2015). An engineered form of the diatom has been considered as a potential drug delivery vehicle for cancer treatment with chemotherapy drugs that are poorly soluble in water.
 W
WThalassiosiraceae is a family of diatoms in the order Thalassiosirales. The family of Thalassiosiraceae have the unique quality of having a flat valve face. These diatoms are common in brackish, nearshore, and open-ocean habitats, with approximately the same number of freshwater and marine species. Thalassiosiraceae are a centric diatom full of fultoportula. These can often be mistaken for Areola. These belong to many diatom families and can be found in different forms such as the different Areolae that can be found on Navicula or Gomphoneis known as lineolate and punctate. Unlike naviculaceae who are symmetrical in shape some Thalassiosiraceae take on being tangentially undulate.
 W
WThalassiosirales is an order of centric diatoms. The order currently contains 471 species. Species in the order Thalassiosirales are common in brackish, nearshore,and open-ocean habitats, with approximately the same number of freshwater and marine species.
 W
WTrinacria is an extinct genus of diatoms present during the early Eocene, named for its triskelion shape.