 W
WAtolla is a genus of crown jellyfish in the order Coronatae. The genus Atolla was originally proposed by Haeckel in 1880 and elevated to the monotypic family level, as Atollidae by Henry Bigelow in 1913. The six known species inhabit the mesopelagic zone. The medusae possess multiple lobes called lappets at the bell margin. Medusae also have eight tentacles, alternating with eight rhopalia, and twice as many lappets occur as tentacles.
 W
WAtorella is a genus of crown jellyfish. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Atorellidae and includes five species. Members of this family are known from the eastern coast of Africa and the western coast of Panama.
 W
WCatostylus is a genus of jellyfish in the family Catostylidae.
 W
WCephea is a genus of true jellyfish in the family Cepheidae. They are found in the Indo-Pacific and eastern Atlantic oceans. They are sometimes called the crown jellyfish, but this can cause confusion with the closely related genus Netrostoma or the distantly related species in the order Coronatae. They are also sometimes called the cauliflower jellyfish because of the cauliflower-looking form on top of its bell.
 W
WCepheidae is a family of jellyfish.
 W
WChrysaora is a genus of jellyfish, commonly called the sea nettles, in the family Pelagiidae. The origin of the genus name Chrysaora lies in Greek mythology with Chrysaor, brother of Pegasus and son of Poseidon and Medusa. Translated, Chrysaor means "he who has a golden armament."
 W
WChrysaora chinensis, or the Indonesian sea nettle, is a species of jellyfish in the family Pelagiidae. It is native to the central Indo-Pacific region and its sting is considered dangerous.
 W
WChrysaora helvola is a jellyfish in the family Pelagiidae. Although still recognized as a valid species by the World Register of Marine Species, its taxonomic history is confusing and recent reviews of the genus have not recognized it.
 W
WChrysaora melanaster, commonly known as the northern sea nettle or brown jellyfish, is a species of jellyfish native to the northern Pacific Ocean and adjacent parts of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes referred to as a Pacific sea nettle, but this name is also used for C. fuscescens; the name Japanese sea nettle was also used for this species, but that name now exclusively refers to C. pacifica. Although jellyfish kept in public aquariums sometimes are referred to as C. melanaster, this is the result of the historical naming confusion and these actually are C. pacifica.
 W
WChrysaora pacifica, commonly named the Japanese sea nettle, is a jellyfish in the family Pelagiidae. This common species is native to the northwest Pacific Ocean, including Japan and Korea, but it was formerly confused with the larger and more northerly distributed C. melanaster. As a consequence, individuals kept in public aquariums have often been mislabelled as C. melanaster. The medusae of C. pacifica typically has a bell with a diameter of 15–21 cm (5.9–8.3 in). Its sting is strong and can be dangerous to humans.
 W
WThe South American sea nettle is a species of jellyfish from the family Pelagiidae. It is found from the Pacific coast of Peru, south along Chile's coast to Tierra del Fuego, and north along the Atlantic coast of Argentina, with a few records from Uruguay. Despite its common name, it is not the only sea nettle in South America; C. lactea ranges along the Atlantic coast of the continent, but generally further north than C. plocamia. Historically, C. plocamia was often confused with C. hysoscella, a species now known to be restricted to the northeast Atlantic. C. plocamia is a large jellyfish, up to 1 m in bell diameter, although most mature individuals only are 25–40 cm (10–16 in).
 W
WCoronamedusae is a subclass of jellyfish in the class Scyphozoa. It is the sister taxon of Discomedusae and contains about 50 named species, all included in the order Coronatae. Jellyfish in this subclass are either small medusae living in shallow marine environments, or large medusae living in the deep sea.
 W
WCyanea is a genus of jellyfish, primarily found in northern waters of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans and southern Pacific waters of Australia and New Zealand, there are also several boreal, polar, tropical and sub-tropical species. Commonly found in and associated with rivers and fjords. The same genus name has been given to a genus of plants of the Hawaiian lobelioids, an example of a parahomonym.
 W
WThe Cyaneidae are a family of true jellyfish. About 20 species are in this family, including the well-known lion's-mane jellyfish.
 W
WDeepstaria is a genus of jellyfish known for their thin, sheet-like bodies. The genus is named after the Deep Star 4000, which collected the holotype of the type species, D. enigmatica.
 W
WDiplulmaris is a genus of jellyfish in the family Ulmaridae.
 W
WThe root-mouthed jellyfish is a species of cnidarian, a jellyfish in the small family Rhizostomatidae. It is the only member of the genus Eupilema.
 W
WFloresca is a genus of jellyfish in the family Ulmaridae It is monotypic with the type species Floresca parthenia.
 W
WLinuchidae is a family of crown jellyfish.
 W
WMastigias is a genus of true jellyfish in the family Mastigiidae. It contains seven described species. Members of this genus are found widely in coastal regions of the Indo-Pacific, including saline lakes of Palau, but there are also records from the West Atlantic at Florida and Puerto Rico. The West Atlantic records are most likely the result of accidental introductions by humans.
 W
WMastigiidae is a family of true jellyfish. The family is native to the Indo-Pacific, but a species of Mastigias has been introduced to the West Atlantic, and Phyllorhiza punctata has been introduced to the West Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea.
 W
WNausithoe aurea is a species of crown jellyfish found off the southeastern coast of Brazil. The central disc has been measured to be 10.5 mm. N. aurea is transparent with yellow and brown spots located around the gonads. N. aurea can reproduce either asexually by strobilation or sexually. Either ephyrae or planuloids may be produced by strobilation; only ephyrae can produce the medusal form. Strobilation can be induced to occur when food is abundant. In polyps, a large availability of food leads to strobilation if it is not regulated.
 W
WNausithoidae is a family of jellyfish.
 W
WNetrostoma is a genus of true jellyfish in the family Cepheidae. They are found in the Indo-Pacific. They are sometimes called crown jellyfish, but this can cause confusion with the closely related genus Cephea or the distantly related species in the order Coronatae.
 W
WAn oral arm is an anatomical structure of "true" sea jellies, which belong to the class Scyphozoa. Oral arms characterize Semaeostomeae, an order of large jellyfish.
 W
WParaphyllina is a genus of crown jellyfish. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Paraphyllinidae, and includes three species.
 W
WPelagia is a genus of jellyfish in the family Pelagiidae. It is currently considered monotypic, consisting of only one species: P. noctiluca (Forsskål, 1775).
 W
WThe Pelagiidae are a family of jellyfish. Members of the family Pelagiidae have no ring canal, and the marginal tentacles arise from umbrella margin.
 W
WPeriphyllidae is a family of jellyfish containing four genera and six species. The most well-known member of the family, Periphylla periphylla, is usually considered a deep-sea species, but it forms large blooms in surface waters of Norwegian fjords.
 W
WPhyllorhiza is a genus of jellyfish in the family Mastigiidae.
 W
WRhizostoma is a genus of medium to large rhizostomatid jellyfish found in the East Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea.
 W
WRhizostoma pulmo, commonly known as the barrel jellyfish, the dustbin-lid jellyfish or the frilly-mouthed jellyfish, is a scyphomedusa in the family Rhizostomatidae. It is found in the northeast Atlantic, and in the Adriatic, Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea and Sea of Azov. It is also known from the southern Atlantic off the western South African coast and into False Bay.
 W
WRhizostomatidae is a family of cnidarians in the class Scyphozoa.
 W
WRhopilema is a genus of jellyfish.
 W
WSanderia is a genus of jellyfish in the family Pelagiidae. There are two species recognized.
 W
WSemaeostomeae is an order of large jellyfish characterized by four long, frilly oral arms flanking their quadrate mouths. The umbrella is domed with scalloped margins, and the gastrovascular system consists of four unbranched pouches radiating outwards from the central stomach; no ring canal is present. They usually possess eight tentacles; four are per-radical and four are inter-radical.
 W
WStellamedusa is a genus of jellyfish. The genus is monotypic with a single species recognized, Stellamedusa ventana.
 W
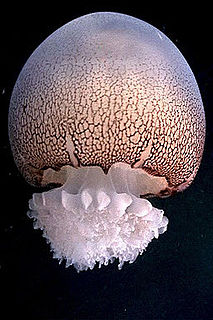
WSthenonia is a genus of jellyfish in the family Ulmaridae.
 W
WStomolophus is a genus of true jellyfish from the West Atlantic and Pacific. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Stomolophidae. Formerly, Nomura's jellyfish was also included in this genus, but has now been reclassified to the family Rhizostomatidae.
 W
WThysanostomatidae is a family of true jellyfish from the Indo-Pacific.
 W
WThe Ulmaridae are a family of jellyfish.
 W
WUlmaris is a genus of jellyfish in the family Ulmaridae.