 W
WA 3D selfie is a 3D-printed scale replica of a person or their face. These three-dimensional selfies are also known as 3D portraits, 3D figurines, 3D-printed figurines, mini-me figurines and miniature statues. In 2014 a first 3D printed bust of a President, Barack Obama, was made. 3D-digital-imaging specialists used handheld 3D scanners to create an accurate representation of the President.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WApathy is a lack of feeling, emotion, interest, or concern about something. It is a state of indifference, or the suppression of emotions such as concern, excitement, motivation, or passion. An apathetic individual has an absence of interest in or concern about emotional, social, spiritual, philosophical, virtual, or physical life and the world. Apathy can also be defined as a person's lack of goal orientation.
 W
WShmuel "Sam" Vaknin is an Israeli writer and professor of psychology..He is the author of Malignant Self Love: Narcissism Revisited (1999), was the last editor-in-chief of the now-defunct political news website Global Politician, and runs a private website about narcissistic personality disorder (NPD). He has also postulated a theory on chronons and time asymmetry.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WIn sociology, codependency is a concept that attempts to characterize imbalanced relationships where one person enables another person's self-destructive tendencies and/or undermines the other person's relationship. Definitions of codependency vary, but typically include high self-sacrifice, a focus on others' needs, suppression of one's own emotions, and attempts to control or fix other people's problems. People who self-identify as codependents exhibit low self-esteem, but it is unclear whether this is a cause or an effect of characteristics associated with codependency. Codependency is generally defined as a subclinical, situational, and/or episodic behavioral condition similar to that of dependent personality disorder. Codependency is not limited to married, partnered or romantic relationships as co-workers, friends and family can be codependent.
 W
WConfidence is a state of being clear-headed either that a hypothesis or prediction is correct or that a chosen course of action is the best or most effective. Confidence comes from a Latin word 'fidere' which means "to trust"; therefore, having self-confidence is having trust in one's self. Arrogance or hubris, in comparison, is the state of having unmerited confidence – believing something or someone is capable or correct when they are not. Overconfidence or presumptuousness is excessive belief in someone succeeding, without any regard for failure. Confidence can be a self-fulfilling prophecy as those without it may fail or not try because they lack it and those with it may succeed because they have it rather than because of an innate ability.
 W
WIn sociology and in economics, the term conspicuous consumption describes and explains the consumer practice of buying and using goods of a higher quality, price, or in greater quantity than practical. The sociologist Thorstein Veblen coined the term conspicuous consumption to explain the spending of money on and the acquiring of luxury commodities specifically as a public display of economic power — the income and the accumulated wealth of the buyer. To the conspicuous consumer, the public display of discretionary income is an economic means of either attaining or of maintaining a given social status.
 W
WConspicuous leisure is a concept introduced by the American economist and sociologist Thorstein Veblen, in The Theory of the Leisure Class (1899). Conspicuous or visible leisure is engaged in for the sake of displaying and attaining social status.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WA dandy is a man who places particular importance upon physical appearance, refined language, and leisurely hobbies, pursued with the appearance of nonchalance, in his cult of the Self. A dandy could be a self-made man who strove to imitate an aristocratic lifestyle despite coming from a middle-class background, especially in late 18th- and early 19th-century Britain.
 W
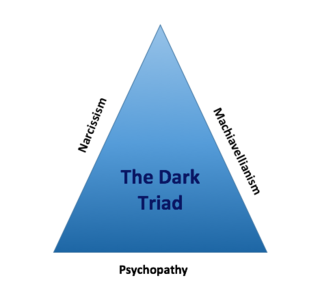
WThe Dark Triad Dirty Dozen (DTDD) is a brief 12-item personality inventory that simultaneously assesses the three socially maladaptive, dark triad traits: Machiavellianism, narcissism, and psychopathy. It was developed by Jonason and Webster in 2010 based on already existing, longer measures of each dark triad trait.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WEgocentrism is the inability to differentiate between self and other. More specifically, it is the inability to accurately assume or understand any perspective other than one's own.
 W
WElitism is the belief or notion that individuals who form an elite—a select group of people perceived as having an intrinsic quality, high intellect, wealth, power, notablity, special skills, or experience—are more likely to be constructive to society as a whole, and therefore deserve influence or authority greater than that of others. The term elitism may be used to describe a situation in which power is concentrated in the hands of a limited number of people. Oppositions of elitism include egalitarianism, populism, and the political theory of pluralism.
 W
WOn 9 January 2008, 22-year-old Sophie Kate Elliott was stabbed to death by ex-boyfriend Clayton Robert Weatherston, in Dunedin, New Zealand. The crime and trial were covered extensively in the news media, and contributed to the government abolishing the partial defence of provocation in cases of murder.
 W
WIn psychology, fantasy is a broad range of mental experiences, mediated by the faculty of imagination in the human brain, and marked by an expression of certain desires through vivid mental imagery. Fantasies are typically associated with scenarios that are statistically implausible or impossible in reality.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WHubris, or, less frequently, hybris, describes a personality quality of extreme or excessive pride or dangerous overconfidence, often in combination with arrogance. The term "arrogance" comes from the Latin adrogare, meaning to feel that one has a right to demand certain attitudes and behaviors from other people. To "arrogate" means "to claim or seize without justification... To make undue claims to having", or "to claim or seize without right... to ascribe or attribute without reason". The term "pretension" is also associated with the term hubris, but is not synonymous with hubris. According to studies, hubris, arrogance and pretension are related to the need for victory instead of reconciliation, such as "friendly" groups might promote. Hubris is usually perceived as a characteristic of an individual rather than a group, although the group the offender belongs to may suffer collateral consequences from wrongful acts. Hubris often indicates a loss of contact with reality and an overestimation of one's own competence, accomplishments or capabilities. The adjectival form of the noun hubris is "hubristic" or "hybristic".
 W
WIn sociology, codependency is a concept that attempts to characterize imbalanced relationships where one person enables another person's self-destructive tendencies and/or undermines the other person's relationship. Definitions of codependency vary, but typically include high self-sacrifice, a focus on others' needs, suppression of one's own emotions, and attempts to control or fix other people's problems. People who self-identify as codependents exhibit low self-esteem, but it is unclear whether this is a cause or an effect of characteristics associated with codependency. Codependency is generally defined as a subclinical, situational, and/or episodic behavioral condition similar to that of dependent personality disorder. Codependency is not limited to married, partnered or romantic relationships as co-workers, friends and family can be codependent.
 W
WManaroopa is a 2019 Indian psychological crime thriller film based on the philosophy of Existentialism in Kannada language. The film also addresses the subject of Nihilism and Narcissism. The film is written and directed by Kiran Hegde. Produced by Kiran Hegde as well under the banner of CMCR movies, the music of movie is given by Sarvanaa and cinematography is done by Govinda Raj. Dialogues of this movie are given by Mahabala Seethalabhavi and Kiran Hegde. 90% of the movie has been shot in and around the hinterland of Sirsi and Siddapur forests of Western Ghats of Karnataka.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WMetrosexual is a portmanteau of metropolitan and sexual coined in 1994, describing a man of ambiguous sexuality, who is especially meticulous about his grooming and appearance, typically spending a significant amount of time and money on shopping as part of this.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WThe narcissism of small differences is the thesis that communities with adjoining territories and close relationships are especially likely to engage in feuds and mutual ridicule because of hypersensitivity to details of differentiation. The term was coined by Sigmund Freud in 1917, based on the earlier work of British anthropologist Ernest Crawley. In language differing only slightly from current psychoanalytic terminology, Crawley declared that each individual is separated from others by a taboo of personal isolation, a narcissism of minor differences.
 W
WIn Greek mythology, Narcissus was a hunter from Thespiae in Boeotia who was known for his beauty. According to Tzetzes, he rejected all romantic advances, eventually falling in love with his own reflection in a pool of water, staring at it for the remainder of his life. After he died, in his place sprouted a flower bearing his name.
 W
WThe Oedipus complex is a concept of psychoanalytic theory. Sigmund Freud introduced the concept in his book Interpretation of Dreams (1899) and coined the expression in his paper A Special Type of Choice of Object made by Men (1910). In Freud's original formulation, the Oedipus complex is a purportedly universal phase in the life of a young boy in which he hates his father and wishes to have sex with his mother. These wishes may be unconscious.
 W
WOmnipotence is the quality of having unlimited power. Monotheistic religions generally attribute omnipotence only to the deity of their faith. In the monotheistic religious philosophy of Abrahamic religions, omnipotence is often listed as one of a deity's characteristics, along with omniscience, omnipresence, and omnibenevolence. The presence of all these properties in a single entity has given rise to considerable theological debate, prominently including the problem of evil, the question of why such a deity would permit the existence of evil. It is accepted in philosophy and science that omnipotence can never be effectively understood.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WIn opera or commedia dell'arte, a prima donna is the leading female singer in the company, the person to whom the prime roles would be given.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WPsychological projection is the process of misinterpreting what is "inside" as coming from "outside". It forms the basis of empathy by the projection of personal experiences to understand someone else's subjective world. In its malignant forms, it is a defense mechanism in which the ego defends itself against disowned and highly negative parts of the self by denying their existence in themselves and attributing them to others, breeding misunderstanding and causing untold interpersonal damage. A bully may project their own feelings of vulnerability onto the target, or a person who is confused may project feelings of confusion and inadequacy onto other people. Projection incorporates blame shifting and can manifest as shame dumping. Projection has been described as an early phase of introjection.
 W
WA selfie is a self-portrait photograph, typically taken with a digital camera or smartphone, which may be held in the hand or supported by a selfie stick. Selfies are often shared on social media, via social networking services such as Facebook, Twitter, Snapchat, and Instagram.
 W
WNarcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance and an excessive pre-occupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
 W
WShame is an unpleasant self-conscious emotion typically associated with a negative evaluation of the self; withdrawal motivations; and feelings of distress, exposure, mistrust, powerlessness, and worthlessness.
 W
WSnob is a pejorative term for a person who believes there is a correlation between social status and human worth. Snob also refers to a person who feels superiority over those from lower social classes, education levels, or other social areas. The word snobbery came into use for the first time in England during the 1820s.
 W
WShmuel "Sam" Vaknin is an Israeli writer and professor of psychology..He is the author of Malignant Self Love: Narcissism Revisited (1999), was the last editor-in-chief of the now-defunct political news website Global Politician, and runs a private website about narcissistic personality disorder (NPD). He has also postulated a theory on chronons and time asymmetry.
 W
WA status symbol is a visible, external symbol of one's social position, an indicator of economic or social status. Many luxury goods are often considered status symbols. Status symbol is also a sociological term – as part of social and sociological symbolic interactionism – relating to how individuals and groups interact and interpret various cultural symbols.
 W
WA tantrum, temper tantrum, meltdown, fit or hissy fit is an emotional outburst, usually associated with those in emotional distress, that is typically characterized by stubbornness, crying, screaming, violence, defiance, angry ranting, a resistance to attempts at pacification, and, in some cases, hitting and other physically violent behavior. Physical control may be lost; the person may be unable to remain still; and even if the "goal" of the person is met, they may not be calmed. Throwing a temper tantrum can lead to a child being placed in timeout, being grounded, or even getting detention or being suspended from school for older school age children. A tantrum may be expressed in a tirade: a protracted, angry speech.
 W
WA thirst trap is a type of social media post intended to entice viewers sexually. It refers to a user's "thirst", a colloquialism likening sexual frustration to dehydration, implying desperation. Originating around the early 2010s, the meaning has changed over time.
 W
WVanity is the excessive belief in one's own abilities or attractiveness to others. Prior to the 14th century it did not have such narcissistic undertones, and merely meant futility. The related term vainglory is now often seen as an archaic synonym for vanity, but originally meant considering one's own capabilities and that God's help was not needed, i.e. unjustified boasting; although glory is now seen as having a predominantly positive meaning, the Latin term from which it derives, gloria, roughly means boasting, and was often used as a negative criticism.