 W
WThe agile gracile opossum, is an opossum species from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Peru, Paraguay, and Uruguay.
Akodon azarae, also known as Azara's akodont or Azara's grass mouse, is a rodent species from South America. It is found from southernmost Brazil through Paraguay and Uruguay into eastern Argentina. It is named after Spanish naturalist Félix de Azara.
 W
WThe Chacoan naked-tailed armadillo is a species of South American armadillo.
 W
WThe greater naked-tailed armadillo is an armadillo species from South America.
 W
WThe nine-banded armadillo, or the nine-banded, long-nosed armadillo, is a medium-sized mammal found in North, Central, and South America, making it the most widespread of the armadillos. Its ancestors originated in South America, and remained there until the formation of the Isthmus of Panama allowed them to enter North America as part of the Great American Interchange. The nine-banded armadillo is a solitary, mainly nocturnal animal, found in many kinds of habitats, from mature and secondary rainforests to grassland and dry scrub. It is an insectivore, feeding chiefly on ants, termites, and other small invertebrates. The armadillo can jump 3–4 ft (91–122 cm) straight in the air if sufficiently frightened, making it a particular danger on roads. It is the state small mammal of Texas.
 W
WThe six-banded armadillo, also known as the yellow armadillo, is an armadillo found in South America. The sole extant member of its genus, it was first described by Swedish zoologist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The six-banded armadillo is typically between 40 and 50 centimeters in head-and-body length, and weighs 3.2 to 6.5 kilograms. The carapace is pale yellow to reddish brown, marked by scales of equal length, and scantily covered by buff to white bristle-like hairs. The forefeet have five distinct toes, each with moderately developed claws.
 W
WThe southern long-nosed armadillo is a species of armadillo native to South America.
 W
WThe desert red bat, also known as the western red bat or southern red bat is a species of microbat found across the Americas. Lasiurus blossevillii is most often found in tree foliage, as is most in the genus Lasiurus, and is a solitary species.
 W
WThe southern yellow bat is a species of vesper bat that belongs to suborder microchiroptera (microbat) in the family Vespertilionidae. It is native to South, North and Central America, from the Rio Grande Valley of Texas in the United States to Argentina.
 W
WThe white-lined broad-nosed bat is a bat species from South America. It is found in southern and eastern Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, northern Argentina, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, French Guiana and Suriname.
 W
WThe Brazilian guinea pig is a guinea pig species found in Argentina, Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Uruguay and Venezuela.
 W
WThe gray brocket, also known as the brown brocket, is a species of brocket deer from northern Argentina, Bolivia, southern Peru, eastern and southern Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. It formerly included the Amazonian brown brocket and sometimes also the Yucatan brown brocket as subspecies. Unlike other species of brocket deer in its range, the gray brocket has a gray-brown fur without reddish tones.
 W
WThe bunny rat, or hairy-soled conyrat is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae, native to southern South America.
 W
WThe capybara is a giant cavy rodent native to South America. It is the largest living rodent in the world. Also called capivara, chigüire, chigüiro, or fercho, carpincho and ronsoco, it is a member of the genus Hydrochoerus, of which the only other extant member is the lesser capybara. Its close relatives include guinea pigs and rock cavies, and it is more distantly related to the agouti, the chinchilla, and the coypu. The capybara inhabits savannas and dense forests and lives near bodies of water. It is a highly social species and can be found in groups as large as 100 individuals, but usually lives in groups of 10–20 individuals. The capybara is not a threatened species, but it is hunted for its meat and hide and also for grease from its thick fatty skin.
 W
WThe South American coati (can-coon), also known as the ring-tailed coati, is a coati species and a member of the raccoon family (Procyonidae), found in the tropical and subtropical parts of South America. In Brazilian Portuguese, it is known as quati. An adult generally weighs from 2–7.2 kg (4.4–15.9 lb) and is 85–113 cm (33–44 in) long, with half of that being its tail. Its colour is highly variable and the rings on the tail may be only somewhat visible, but its most distinguishing characteristic is that it lacks the largely white snout of its northern relative, the white-nosed coati.
 W
WThe collared tuco-tuco is a tuco-tuco species from South America. It is found in southern Brazil, Uruguay and northern Argentina where it lives underground in a burrow it digs in savannah habitats. It is a relatively common species and the IUCN has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".
 W
WThe coypu, also known as the nutria, is a large, herbivorous, semiaquatic rodent. Classified for a long time as the only member of the family Myocastoridae, Myocastor is now included within Echimyidae, the family of the spiny rats. The coypu lives in burrows alongside stretches of water, and feeds on river plant stems. Originally native to subtropical and temperate South America, it has since been introduced to North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa, primarily by fur farmers. Although it is still hunted and trapped for its fur in some regions, its destructive burrowing and feeding habits often bring it into conflict with humans, and it is considered an invasive species.
 W
WThe crab-eating raccoon or South American raccoon is a species of raccoon native to marshy and jungle areas of Central and South America. It is found from Costa Rica south through most areas of South America east of the Andes down to northern Argentina and Uruguay. Despite its name, this species is not restricted to eating only crabs, and the common raccoon also seeks and eats crabs where they are available.
 W
WThe marsh deer, sometimes known as the swamp deer, is the largest deer species from South America reaching a length of 2 m (6.6 ft) and a shoulder height of 1.2 m (3.9 ft). It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay and Paraguay. Formerly found in much of tropical and subtropical South America, it ranged east of the Andes, south from the Amazon rainforest, west of the Brazilian Atlantic rainforest and north of the Argentinian Pampa. Today it is largely reduced to isolated populations at marsh and lagoon zones in the Paraná, Paraguay, Araguaia and Guapore river basins. Small populations also occur in the southern Amazon, including Peru where protected in Bahuaja-Sonene National Park. It is listed as a vulnerable species by the IUCN and on CITES Appendix I.
 W
WThe diminutive serotine, is a bat species from South America. It is found in Argentina, Colombia, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, and Venezuela.
 W
WThe dwarf dog-faced bat is a species of free-tailed bat from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Paraguay and Uruguay, typically at lower elevations. It is one of two species in the genus Molossops, the other being the rufous dog-faced bat. Three subspecies are often recognized, though mammalogist Judith Eger considers it monotypic with no subspecies. It is a small free-tailed bat, with a forearm length of 28.9–32.5 mm (1.14–1.28 in) and a weight of 5–8 g (0.18–0.28 oz); males are larger than females. It is brown, with paler belly fur and darker back fur. Its wings are unusual for a free-tailed bat, with exceptionally broad wingtips. Additionally, it has low wing loading, meaning that it has a large wing surface area relative to its body weight. Therefore, it flies more similarly to a vesper bat than to other species in its own family. As it forages at night for its insect prey, including moths, beetles, and others, it uses two kinds of frequency-modulated echolocation calls: one type is to navigate in open areas and to search for prey, while the other type is used for navigating in cluttered areas or while approaching a prey item.
 W
WThe crab-eating fox, also known as the forest fox, wood fox, bushdog or maikong, is an extant species of medium-sized canid endemic to the central part of South America, and which appeared during the Pliocene epoch. Like South American foxes, which are in the genus Lycalopex, it is not closely related to true foxes. Cerdocyon comes from the Greek words kerdo and kyon (dog) referring to the dog- and fox-like characteristics of this animal.
 W
WThe pampas fox, also known as grey pampean fox, pampas zorro, Azara's fox, or Azara's zorro, is a medium-sized zorro, or "false" fox, native to the South American pampas. Azara in some of its alternative common names is a reference to Spanish naturalist Félix de Azara.
 W
WGeoffroy's cat is a small wild cat native to the southern and central regions of South America. It is about the size of a domestic cat. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List because it is widespread and abundant over most of its range.
 W
WThe greater guinea pig is a species of rodent found in the coastal strip of Brazil and Uruguay, where it lives in moist grassland and marshes.
 W
WHolochilus brasiliensis, also known as the Brazilian marsh rat or web-footed marsh rat, is a species of semiaquatic rodent from South America. It is found in northeastern Argentina, southern and eastern Brazil and in eastern Uruguay.
 W
WThe La Plata dolphin, franciscana or toninha is a species of dolphin found in coastal Atlantic waters of southeastern South America. It is a member of the river dolphin group and the only one that lives in the ocean and saltwater estuaries, rather than inhabiting exclusively freshwater systems. Commercialized areas that create agricultural runoffs and/or industrialized zones can affect the health of the La Plata dolphin, especially in regards to their contributions of waste and pollution, which can lead to habitat degradation and poisoned food among other concerns.
 W
WThe lowland paca, also known as the spotted paca, is a large rodent found in tropical and sub-tropical America, from east-central Mexico to northern Argentina, and has been introduced to Cuba and Algeria.
 W
WLundomys molitor, also known as Lund's amphibious rat or the greater marsh rat, is a semiaquatic rat species from southeastern South America.
 W
WThe lutrine opossum, also known as the little water opossum, thick-tailed opossum, or coligrueso is an opossum species from South America in the genus Lutreolina.
 W
WMolina's hog-nosed skunk is similar to the common skunk with scent glands used to spray an odorous liquid to offend potential predators. They have a resistance to pit viper venom, distinct thin white markings and a pink, hog-like, fleshy nose.
 W
WThe ocelot is a wild cat native to the southwestern United States, Mexico, and Central and South America, as well as the Caribbean islands of Trinidad and Margarita. This medium-sized cat is characterized by solid black spots and streaks on its coat, round ears, and white neck and undersides. It weighs between 8 and 15.5 kg and reaches 40–50 cm at the shoulders. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758. Two subspecies are recognized: L. p. pardalis and L. p. mitis.
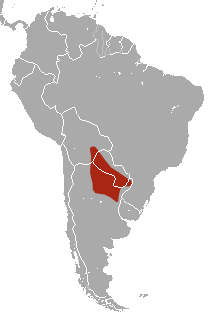 W
WThe common fat-tailed mouse opossum is a species of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It occurs in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay in chaco and Andean foothill habitats. Its head-and-body length is about 75 to 120 mm, and its tail length is about 90 to 134 mm. Its dorsal fur is brownish gray, and its ventral fur is yellowish to white. The legs and cheeks are the same color as the ventral surface. Its tail is sharply bicolored. A ring of faintly darker fur surrounds each eye. Its tail often lacks fat deposits, but does not always.
 W
WThe yellow-sided opossum is an opossum species from South America. It is found in Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay. They have grey or black fur on their dorsal side with yellowish fur on the lateral side that continues down to the feet. They are the most mysterious of all the Monodelphis that is found specifically in the Pampean region or Pampa of Argentina. It is suspected to be a once-in-a-lifetime breeder as seen in a three-year observational study of one population in the marshy grasslands of the Pampean region. Maintaining their native grasslands is important for them to keep a stable population. They show sexual dimorphism in overall size: adult males are typically 100-150 g whereas adult females are 30-70 g.
 W
WThe neotropical otter or neotropical river otter is an otter species found in Central America, South America and the island of Trinidad. It is physically similar to the northern and southern river otter, which occur directly north and south of this species' range. The length of the neotropical otter can range from 36–66 centimetres (14–26 in), plus a tail of 37–84 centimetres (15–33 in). Body weight ranges from 5–15 kilograms (11–33 lb). Otters are members of the family Mustelidae, the most species-rich family in the order Carnivora.
 W
WThe Pampas deer is a species of deer that live in the grasslands of South America at low elevations. They are known as venado or gama in Spanish and as veado-campeiro in Portuguese. Their habitat includes water and hills, often with winter drought, and grass that is high enough to cover a standing deer. Many of them live on the Pantanal wetlands, where there are ongoing conservation efforts, and other areas of annual flooding cycles. Human activity has changed much of the original landscape. They are known to live up to 12 years in the wild, longer if captive, but are threatened due to over-hunting and habitat loss. Many people are concerned over this loss, because a healthy deer population means a healthy grassland, and a healthy grassland is home to many species, some also threatened. Many North American birds migrate south to these areas, and if the Pampas deer habitat is lost, they are afraid these bird species will also decline. There are approximately 80,000 Pampas deer total, with the majority of them living in Brazil.
 W
WPearson's tuco-tuco is a species of rodent in the family Ctenomyidae. It is endemic to Uruguay, where it is found at elevations below 200 m. This tuco-tuco constructs burrows with multiple openings containing one to two nests of dried grass; it prefers areas of sandy soil but is somewhat adaptable. It is threatened by loss of habitat to development, agriculture and ranching. Multiple karyotypes have been reported, including 2n = 68-70, FN = 80-88, as well as 2n = 56, FN = 77-79, suggesting the taxon may represent several species. C. dorbignyi appears to be cytogenetically indistinguishable from the 2n = 70 form. The species is named after American zoologist Oliver Payne Pearson.
 W
WBurmeister's porpoise is a species of porpoise endemic to the coast of South America. It was first described by Hermann Burmeister, for whom the species is named, in 1865. Locally it is known as marsopa espinosa and chancho marino.
 W
WThe small vesper mouse is a rodent species from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. It is one of the hosts of hantavirus, causing hantavirus pulmonary syndrome
 W
WThe South American sea lion, also called the Southern Sea Lion and the Patagonian sea lion, is a sea lion found on the Ecuadorian, Peruvian, Chilean, Falkland Islands, Argentinean, Uruguayan, and Southern Brazilian coasts. It is the only member of the genus Otaria. Its scientific name was subject to controversy, with some taxonomists referring to it as Otaria flavescens and others referring to it as Otaria byronia. The former eventually won out, although that may still be overturned. Locally, it is known by several names, most commonly lobo marino (es)/lobo marinho (pt) and león marino (es)/leão marinho (pt) and the hair seal.
 W
WThe southern tamandua, also called the collared anteater or lesser anteater, is a species of anteater from South America. It is a solitary animal, found in many habitats from mature to highly disturbed secondary forests and arid savannas. It feeds on ants, termites, and bees. Its very strong fore claws can be used to break insect nests or to defend itself.
 W
WThe white-eared opossum is an opossum species found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. It is a terrestrial and, sometimes, arboreal animal, and a habitat generalist, living in a wide range of different habitats.