 W
WDuring butchering, beef is first divided into primal cuts, pieces of meat initially separated from the carcass. These are basic sections from which steaks and other subdivisions are cut. The term "primal cut" is quite different from "prime cut", used to characterize cuts considered to be of higher quality. Since the animal's legs and neck muscles do the most work, they are the toughest; the meat becomes tenderer as distance from hoof and horn increases. Different countries and cuisines have different cuts and names, and sometimes use the same name for a different cut; e.g., the cut described as "brisket" in the US is from a significantly different part of the carcass than British "brisket". "Cut" often refers narrowly to skeletal muscle, but can also include other edible flesh, such as offal or bones without significant muscles attached.
 W
WThe 7-bone roast or 7-bone steak is from the chuck section of the steer or heifer and it includes a cross cut of the shoulder blade. The bone is shaped like the numeral "7", which gives these cuts their name. The steak differs from the 7-bone roast only in thickness: 7-bone steaks are cut 1⁄2- to 3⁄4-inch thick.
 W
WBaseball steak is a center cut of beef taken from the top sirloin cap steak. Baseball steaks differ from sirloin steaks in that the bone and the tenderloin and bottom round muscles have been removed; and the cut is taken from biceps femoris. A baseball steak is essentially a center cut top sirloin cap steak. This cut of beef is very lean, and is considered very flavorful.
 W
WThe beef clod or shoulder clod is one of the least expensive cuts of beef and is taken from the shoulder (chuck) region of the animal. Beef clod is a large muscle system, with some fat that covers the muscles. The clod's composition is mainly three muscles: the shoulder tender, the top blade and the clod heart and is one of two chuck subprimal cuts. It is often divided into its three separate muscle cuts for retail sale.
 W
WThe beef shank is the leg portion of a steer or heifer. In Britain, the corresponding cuts of beef are the shin, and the leg.
 W
WA beefsteak, often called just steak, is a flat cut of beef with parallel faces, usually cut perpendicular to the muscle fibers. In common restaurant service a single serving will have a raw mass ranging from 120 to 600 grams. Beef steaks are usually grilled, pan fried, or broiled. The more tender cuts from the loin and rib are cooked quickly, using dry heat, and served whole. Less tender cuts from the chuck or round are cooked with moist heat or are mechanically tenderized.
 W
WThe beef top blade steak comes from the chuck section of a steer or heifer. The steaks are cross-cut from the top blade subprimal, also known as Infraspinatus. It is becoming more popular and profitable to abstain from cross cutting the top blade and instead produce flat iron steaks which is cut with the grain and eliminates the connective tissue that runs down the middle of this steak.
 W
WThe bottom sirloin steak is a steak cut from the back of the animal below top sirloin and above the flank. The meat is often used to cook the tri-tip and flap steak.
 W
WBrisket is a cut of meat from the breast or lower chest of beef or veal. The beef brisket is one of the nine beef primal cuts, though the definition of the cut differs internationally. The brisket muscles include the superficial and deep pectorals. As cattle do not have collar bones, these muscles support about 60% of the body weight of standing or moving cattle. This requires a significant amount of connective tissue, so the resulting meat must be cooked correctly to tenderise it.
 W
WChateaubriand is a dish that traditionally consists of a large center cut fillet of tenderloin grilled between two lesser pieces of meat that are discarded after cooking. While the term originally referred to the preparation of the dish, Auguste Escoffier named the specific center cut of the tenderloin the Chateaubriand.
 W
WChuck steak is a cut of beef and is part of the sub-prime cut known as the chuck.
 W
WCow's trotters, are the feet of cattle. The cuts are used in various dishes around the world, especially in Asian, African, French, and the Caribbean cuisine. Latin American cuisine also uses cow's trotters for several traditional dishes.
 W
WCube steak or cubed steak is a cut of beef, usually top round or top sirloin, tenderized and flattened by pounding with a meat tenderizer. The name refers to the shape of the indentations left by that process. This is the most common cut of meat used for the American dish chicken fried steak.
 W
WDelmonico steak or steak Delmonico is one of several cuts of beef, with a thick-cut preparation popularized by Delmonico's restaurant in New York City during the mid-19th century.
 W
WIn French, entrecôte is a premium cut of beef used for steaks.
 W
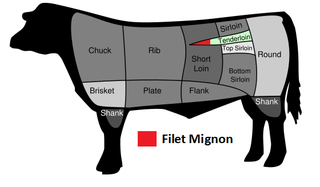
WFilet mignon is a steak cut of beef taken from the smaller end of the tenderloin, or psoas major of the cow carcass, usually a steer or heifer. In French, this cut is always called filet de bœuf, as filet mignon refers to pork tenderloin.
 W
WFlank steak is a cut of beef taken from the abdominal muscles or lower chest of the steer. French butchers refer to it as bavette, which means "bib". Similarly, it is known in Brazil as fraldinha. The cut is common in Colombia, where it is known as sobrebarriga.
 W
WFlap steak, or flap meat is a low-end beef steak cut. It comes from a bottom sirloin butt cut of beef, and is generally a very thin steak. Flap steak is sometimes called sirloin tips in New England, but is typically ground for hamburger or sausage meat, elsewhere.
 W
WFlat iron steak (US), butlers' steak (UK), or oyster blade steak is a cut of steak cut with the grain from the chuck, or shoulder of the animal. This produces a flavorful cut that is a bit tough because it contains a gristly fascia membrane unless removed. Some restaurants offer it on their menu, often at lower price than the more popular rib-eye and strip steaks of the same grade. This is used, in some places, as a means of selling a less expensive cut from the same animal, for example Kobe beef.
 W
WA hanger steak, also known as butcher's steak or hanging tenderloin, is a cut of beef steak prized for its flavor. This cut is taken from the plate, which is the upper belly of the animal. In the past it was sometimes known as "butcher's steak", because butchers would often keep it for themselves rather than offer it for sale. This is because the general populace believed this to be a crude cut of meat, although it's actually one of the most tender.
 W
WOxtail is the culinary name for the tail of cattle. Formerly, it referred only to the tail of an ox. An oxtail typically weighs 7–8 lb (3.2–3.6 kg) and is skinned and cut into short lengths for sale.
 W
WPicanha is a cut of beef that is popular in Brazil, and later also adopted in Portugal. In the United States, it is little known, but referred to as the top sirloin cap, rump cover, rump cap, or culotte. North American butchers generally divide it into other cuts like the rump, the round, and the loin. It consists of the biceps femoris muscle and its fat cap.
 W
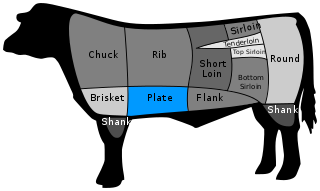
WIn U.S. butchery, the plate of beef is a forequarter cut from the belly of the cow, just below the rib cut. It is typically a cheap, tough, and fatty meat. In U.K. butchery, this cut is considered part of the brisket.
 W
WPopeseye steak is thinly sliced rump steak, originating in Scotland.
 W
WThe Ranch steak comes from the chuck cut of a cow, namely the shoulder. Technically it is called a "boneless chuck shoulder center cut steak", but supermarkets usually use the shorter and more memorable term: "Ranch steak". A ranch steak is usually cut no thicker than one inch, weighs 10 ounces or less, and is usually trimmed of all excess fat.
 W
WThe rib eye or ribeye is a beef steak from the rib section. The rib section of beef spans from ribs six through twelve. Ribeye steaks are mostly composed of the longissimus dorsi muscle but also contain the complexus and spinalis muscles.
 W
WA rib steak is a beef steak sliced from the rib primal of a beef animal, with rib bone attached. In the United States, the term rib eye steak is used for a rib steak with the bone removed; however, in some areas, and outside the U.S., the terms are often used interchangeably. The "rib eye" or "ribeye" was originally, the central portion of the rib steak, without the bone, resembling an eye.
 W
WA round steak is a beef steak from the "round", the rear leg of the cow. The round is divided into cuts including the eye (of) round, bottom round, and top round, with or without the "round" bone (femur), and may include the knuckle, depending on how the round is separated from the loin. This is a lean cut and it is moderately tough. Lack of fat and marbling makes round dry out when cooked with dry-heat cooking methods like roasting or grilling. Round steak is commonly prepared with slow moist-heat methods including braising, to tenderize the meat and maintain moisture. The cut is often sliced thin, then dried or smoked at low temperature to make jerky.
 W
WRump steak is a cut of beef. It may refer to:A steak from the top half of an American-cut round steak primal A British- or Australian-cut from the rump primal, largely equivalent to the American sirloin
 W
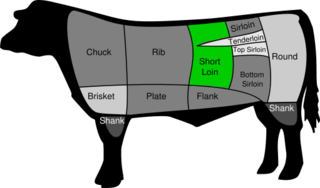
WShort loin is the American name for a cut of beef that comes from the back of the cattle. It contains part of the spine and includes the top loin and the tenderloin. This cut yields types of steak including porterhouse, strip steak, and T-bone. The T-bone is a cut that contains less of the tenderloin than does the porterhouse. Webster's Dictionary defines it as "a portion of the hindquarter of beef immediately behind the ribs that is usually cut into steaks." The short loin is considered a tender beef.
 W
WShort ribs are a cut of beef taken from the brisket, chuck, plate, or rib areas of beef cattle. They consist of a short portion of the rib bone, which is overlain by meat which varies in thickness. There are two major types of cuts: The "flanken", which is cut across the bone and leaves the bone just 1 to 2 inches in length, and the "English", which is cut parallel to the bone and leaves the bone up to 6 inches (15 cm) in length. English cut short ribs may be served individually, or three or four may served connected to one another. Short ribs are popular in many international cuisines.
 W
WThe beef clod or shoulder clod is one of the least expensive cuts of beef and is taken from the shoulder (chuck) region of the animal. Beef clod is a large muscle system, with some fat that covers the muscles. The clod's composition is mainly three muscles: the shoulder tender, the top blade and the clod heart and is one of two chuck subprimal cuts. It is often divided into its three separate muscle cuts for retail sale.
 W
WSilverside is a term used in the UK, Ireland, South Africa, Australia and New Zealand for a cut of beef from the hindquarter of cattle, just above the leg cut. It gets its name because of the "silverwall" on the side of the cut, a long fibrous "skin" of connective tissue (epimysium) which has to be removed as it is too tough to eat. The primary muscle is the biceps femoris.
 W
WThe sirloin steak is cut from the sirloin, the subprimal posterior to the short loin where the T-bone, porterhouse, and club steaks are cut. The sirloin is actually divided into several types of steak. The top sirloin is the most prized of these and is specifically marked for sale under that name. The bottom sirloin, which is less tender and much larger, is typically marked for sale simply as "sirloin steak". The bottom sirloin, in turn, connects to the sirloin tip roast.
 W
WSkirt steak is a cut of beef steak from the plate. It is long, flat, and prized for its flavor rather than tenderness. It is not to be confused with flank steak, a generally similar adjacent cut nearer the animal's rear quarter.
 W
WSpare ribs are a variety of ribs cut from the lower portion of a pig, specifically the belly and breastbone, behind the shoulder, and include 11 to 13 long bones. There is a covering of meat on top of the bones and also between them. Spare ribs (pork) are distinguished from short ribs, which are beef.
 W
WA standing rib roast, also known as prime rib, is a cut of beef from the primal rib, one of the nine primal cuts of beef. While the entire rib section comprises ribs six through 12, a standing rib roast may contain anywhere from two to seven ribs.
 W
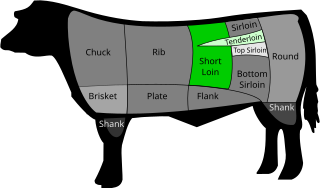
WThe strip steak is a cut of beef steaks from the short loin from a cow. It consists of a muscle that does little work, the longissimus, making the meat particularly tender, although not as tender as the nearby psoas major or tenderloin. Unlike the tenderloin, the longissimus is a sizable muscle, allowing it to be cut into larger portions.
 W
WThe T-bone and porterhouse are steaks of beef cut from the short loin. Both steaks include a "T"-shaped lumbar vertebra with sections of abdominal internal oblique muscle on each side. Porterhouse steaks are cut from the rear end of the short loin and thus include more tenderloin steak, along with a large strip steak. T-bone steaks are cut closer to the front, and contain a smaller section of tenderloin. The smaller portion of a T-bone, when sold alone, is known as a filet mignon, especially if cut from the small forward end of the tenderloin.
 W
WA beef tenderloin, known as an eye fillet in Australasia, filet in France, Filet Mignon in Brazil, and fillet in the United Kingdom and South Africa, is cut from the loin of beef.
 W
WTop sirloin is a cut of beef from the primal loin or subprimal sirloin. Top sirloin steaks differ from sirloin steaks in that the bone and the tenderloin and bottom round muscles have been removed; the remaining major muscles are the gluteus medius and biceps femoris.
 W
WThe tri-tip is a triangular cut of beef from the bottom sirloin subprimal cut, consisting of the tensor fasciae latae muscle. Untrimmed, the tri-tip weighs around 5 pounds. In the U.S., the tri-tip is taken from NAMP cut 185C.