 W
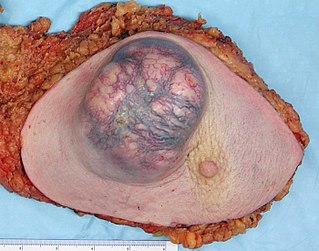
WBreast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly-inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin.
 W
WThe relationship between alcohol and breast cancer is clear: drinking alcoholic beverages, including wine, beer, or liquor, is a risk factor for breast cancer, as well as some other forms of cancer. Drinking alcohol causes more than 100,000 cases of breast cancer worldwide every year.
 W
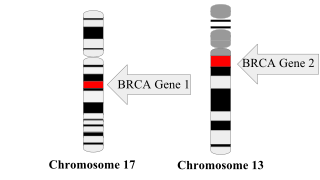
WA BRCA mutation is a mutation in either of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are tumour suppressor genes. Hundreds of different types of mutations in these genes have been identified, some of which have been determined to be harmful, while others have no proven impact. Harmful mutations in these genes may produce a hereditary breast–ovarian cancer syndrome in affected persons. Only 5-10% of breast cancer cases in women are attributed to BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, but the impact on women with the gene mutation is more profound. Women with harmful mutations in either BRCA1 or BRCA2 have a risk of breast cancer that is about five times the normal risk, and a risk of ovarian cancer that is about ten to thirty times normal. The risk of breast and ovarian cancer is higher for women with a high-risk BRCA1 mutation than with a BRCA2 mutation. Having a high-risk mutation does not guarantee that the woman will develop any type of cancer, or imply that any cancer that appears was actually caused by the mutation, rather than some other factor.
 W
WBreast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA1 gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. BRCA1 is a human tumor suppressor gene and is responsible for repairing DNA.
 W
WBRCA2 and BRCA2 are a human gene and its protein product, respectively. The official symbol and the official name are maintained by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. One alternative symbol, FANCD1, recognizes its association with the FANC protein complex. Orthologs, styled Brca2 and Brca2, are common in other vertebrate species. BRCA2 is a human tumor suppressor gene, found in all humans; its protein, also called by the synonym breast cancer type 2 susceptibility protein, is responsible for repairing DNA.
 W
WBreast Cancer Awareness Month (BCAM), also referred to in America as National Breast Cancer Awareness Month (NBCAM), is an annual international health campaign organized by major breast cancer charities every October to increase awareness of the disease and to raise funds for research into its cause, prevention, diagnosis, treatment and cure. The campaign also offers information and support to those affected by breast cancer.
 W
WBreast Cancer Care is the only specialist UK-wide charity in the UK providing care, support and information to anyone affected by breast cancer. The charity's headquarters are in London, with additional offices in Sheffield, Cardiff, and Glasgow. It is regularly quoted by media looking for the perspective of patients on breast cancer.
 W
WBreast Cancer Research and Treatment is a scientific journal focused on the treatment of and investigations in breast cancer. It is targeted towards a wide audience of clinical researchers, epidemiologists, immunologists, or cell biologists interested in breast cancer.
 W
WThe breast cancer research stamp (BCRS) is a semi-postal non-denominated postage stamp issued by the United States Postal Service, priced in 2011 as eleven cents higher than the standard first-class letter rate. The surplus above the price of the first-class stamp is collected by the United States Postal Service (USPS) and allocated to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Department of Defense (DoD) for breast cancer research. If a person used this stamp exclusively, and mailed one letter per day for a year, the resulting donation would amount to US $40.
 W
WBreast cancer survivors' dragon boating is an international movement inspired by the research of Canadian sports medicine specialist Don McKenzie. Survivors of breast cancer join together to paddle dragon boats to the benefit of their physical health and social wellbeing. It is supported internationally by the International Breast Cancer Paddlers' Commission (IBCPC), an Associate Member of the International Dragon Boat Federation.
 W
WBreast self-examination (BSE) is a screening method used in an attempt to detect early breast cancer. The method involves the woman herself looking at and feeling each breast for possible lumps, distortions or swelling.
 W
WBreast cancer chemotherapy refers to the use of cytotoxic drugs (chemotherapy) in the treatment of breast cancer.
 W
WClinical Breast Cancer is a bimonthly peer-reviewed medical journal established in 2000 and published by Elsevier. It covers all areas related to breast cancer.
 W
WDressed to Kill is a 1995 book by Sydney Ross Singer and Soma Grismaijer that proposes a link between bras and breast cancer. According to the authors, the restrictive nature of a brassiere inhibits the lymphatic system, leading to an increased risk of breast cancer. The book's claims are considered unfounded by the scientific community, and researchers have criticized the authors' methodology as faulty. Major medical organizations including the National Institutes of Health and the American Cancer Society have found no evidence that bra-wearing increases breast-cancer risk.
 W
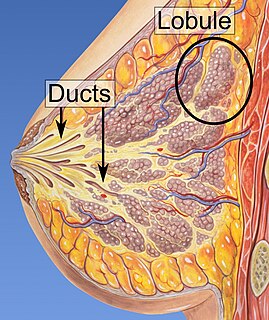
WDuctal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, is a pre-cancerous or non-invasive cancerous lesion of the breast. DCIS is classified as Stage 0. It rarely produces symptoms or a breast lump one can feel, typically being detected through screening mammography.
 W
WWorldwide, breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women. Breast cancer comprises 22.9% of invasive cancers in women and 16% of all female cancers.
 W
WGlobal Pink Hijab Day was an initiative that began as an experiment by founder, Hend El-Buri and a group of high school students in Columbia, Missouri. It was intended to remove stereotypes of Muslim women by having Muslims engage in dialogue about breast cancer awareness, joining walks in groups while wearing pink headscarves, and holding other events promoting awareness and support for the cause. Global Pink Hijab Day was last celebrated in 2011
 W
WGene HEPACAM*, named based on its original site of identification - hepatocytes and the nature of its protein product - a cell adhesion molecule (CAM), was first discovered and characterised in human liver and reported by Shali Shen in 2005. The gene encodes a protein of 416 amino acids, designated as hepaCAM**, which is a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of cell adhesion molecules. The main biological functions of hepaCAM include a) modulating cell-matrix adhesion and migration, and b) inhibiting cancer cell growth.
 W
WHereditary breast–ovarian cancer syndromes (HBOC) are cancer syndromes that produce higher than normal levels of breast cancer, ovarian cancer and additional cancers in genetically related families. It accounts for 90% of the hereditary cancers. The hereditary factors may be proven or suspected to cause the pattern of breast and ovarian cancer occurrences in the family. The name HBOC may be misleading because it implies that this genetic susceptibility to cancer is mainly in women. In reality, all sexes have the same rates of gene mutations and HBOC can predispose to other cancers including prostate cancer and pancreatic cancer. For this reason, the term "King syndrome" has recently come into use. The new name references Mary-Claire King who identified the genes BRCA1 and BRCA2.
 W
WIn the Family is a 2008 documentary film, produced by Kartemquin Films, about predicting breast and ovarian cancer and the choices women make when they are faced with the dangers of a possible life-threatening disease. The film's director, Joanna Rudnick, tests positive for the familial BRCA mutation that increases her chances of developing breast cancer by 60%. Faced with these odds, Rudnick must examine her choices of possibly taking her chances or possibly having her breasts and ovaries removed.
 W
WInvasive carcinoma of no special type (NST) also known as invasive ductal carcinoma or ductal NOS and previously known as invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified (NOS) is a group of breast cancers that do not have the "specific differentiating features". Those that have these features belong to other types.
 W
WInvasive lobular carcinoma is breast cancer arising from the lobules of the mammary glands. It accounts for 5-10% of invasive breast cancer.
 W
WConstance Johnson was an Australian philanthropist. She suffered from bone cancer at age 11, uterine cancer at age 22 and finally breast cancer at age 33. Johnson founded the Love Your Sister charity in 2012 with her brother Samuel Johnson, aiming to raise $10 million for cancer research. At the time of her death the charity had raised almost $6 million. She was awarded the Medal of the Order of Australia on 7 September 2017 and died the following day, aged 40.
 W
WLiving Proof is a 2008 Lifetime Television film, directed by Dan Ireland. The film stars Harry Connick, Jr. as Dr. Dennis Slamon, a doctor who is trying to find a cure for breast cancer. The film also stars Paula Cale, Angie Harmon and Amanda Bynes in supporting roles.
 W
WLobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) is an incidental microscopic finding with characteristic cellular morphology and multifocal tissue patterns. The condition is a laboratory diagnosis and refers to unusual cells in the lobules of the breast. The lobules and acini of the terminal duct-lobular unit (TDLU), the basic functional unit of the breast, may become distorted and undergo expansion due to the abnormal proliferation of cells comprising the structure. These changes represent a spectrum of atypical epithelial lesions that are broadly referred to as lobular neoplasia (LN).
 W
WMale breast cancer is a rare cancer in males that originates from the breast. Many males with breast cancer have inherited a BRCA mutation, but there are other causes, including alcohol abuse and exposure to certain hormones and ionizing radiation.
 W
WA Mammotome device is a vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (VAC) device that uses image guidance such as x-ray, ultrasound and/or MRI to perform breast biopsies. A biopsy using a Mammotome device can be done on an outpatient basis with a local anesthetic. Mammotome is a registered trademark of Devicor Medical Products, Inc., part of Leica Biosystems.
 W
WAlexa Ann McDonough is a Canadian politician who became the first woman to lead a major, recognized political party in Canada, when she was elected the Nova Scotia New Democratic Party's (NSNDP) leader in 1980. She served as a member of the Nova Scotia Legislature from 1981 to 1994, representing the Halifax Chebucto and Halifax Fairview electoral districts. She stepped down as the NSNDP's leader and as a member of the legislature in 1994. She subsequently ran for, and was elected, leader of the federal New Democratic Party (NDP) in 1995. McDonough was elected the Member of Parliament (MP) for the federal electoral district of Halifax in 1997. She stepped down as party leader in 2003, but continued to serve as an MP for two more terms, until 2008, when she retired from politics altogether. In 2009, she became the interim president of Mount Saint Vincent University and was appointed an Officer of the Order of Canada in December of that year.
 W
WMCF-7 is a breast cancer cell line isolated in 1970 from a 69-year-old Caucasian woman. MCF-7 is the acronym of Michigan Cancer Foundation-7, referring to the institute in Detroit where the cell line was established in 1973 by Herbert Soule and co-workers. The Michigan Cancer Foundation is now known as the Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Institute.
 W
WMedullary breast carcinoma is a rare type of breast cancer that often can be treated successfully. It is relatively circumscribed.
 W
WMetastatic breast cancer, also referred to as metastases, advanced breast cancer, secondary tumors, secondaries or stage IV breast cancer, is a stage of breast cancer where the breast cancer cells have spread to distant sites beyond the axillary lymph nodes. There is no cure for metastatic breast cancer; it often can be effectively treated. There is no stage after IV.
 W
WMiR-206 is a microRNA that in humans is a member of the myomiR family which also includes miR-1, miR-133, miR-208a/b among few others.
 W
WPaget's disease of the breast is a type of cancer that outwardly may have the appearance of eczema, with skin changes involving the nipple of the breast. The condition is an uncommon disease accounting for 1 to 4.3% of all breast cancers and was first described by Sir James Paget in 1874.
 W
WPink Ribbons, Inc. is a 2011 National Film Board of Canada (NFB) documentary about the pink ribbon campaign, directed by Léa Pool and produced by Ravida Din. The film is based on the 2006 book Pink Ribbons, Inc: Breast Cancer and the Politics of Philanthropy by Samantha King, associate professor of kinesiology and health studies at Queen's University.
 W
WPinkwashing is a form of cause marketing that uses a range of pink ribbon logos, displayed on various products. The Pink ribbon logo symbolizes support for breast cancer-related charities or foundations.
 W
WBreast cancer screening is the medical screening of asymptomatic, apparently healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to achieve an earlier diagnosis. The assumption is that early detection will improve outcomes. A number of screening tests have been employed, including clinical and self breast exams, mammography, genetic screening, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.
 W
WThe sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node or group of nodes draining a cancer. In case of established cancerous dissemination it is postulated that the sentinel lymph node/s is/are the target organs primarily reached by metastasizing cancer cells from the tumor.
 W
WSandra M. Swain is an American oncologist, breast cancer specialist and clinical translational researcher. She is currently a professor of Medicine at the Georgetown University School of Medicine and the Associate Dean for Research Development at Georgetown University Medical Center (GUMC) and MedStar Health as well as an adjunct professor of Medicine at the F. Edward Hébert School of Medicine of the Uniformed Services University of Health Sciences. She is also a past President of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), serving from 2012 through 2013.
 W
WTomosynthesis, also digital tomosynthesis (DTS), is a method for performing high-resolution limited-angle tomography at radiation dose levels comparable with projectional radiography. It has been studied for a variety of clinical applications, including vascular imaging, dental imaging, orthopedic imaging, mammographic imaging, musculoskeletal imaging, and chest imaging.
 W
WYoung Survival Coalition (YSC) is an international organization focusing on women ages 40 and under who are diagnosed with breast cancer. Founded in 1998 by three young women with breast cancer, YSC is a 501(c)(3) non-profit based in New York City with an additional office in Atlanta, Georgia. It is currently led by board president Karen Lawson and CEO Jennifer Merschdorf.