Aquatic insects or water insects live some portion of their life cycle in the water. They feed in the same ways as other insects. Some diving insects, such as predatory diving beetles, can hunt for food underwater where land-living insects cannot compete.
 W
WAlderflies are megalopteran insects of the family Sialidae. They are closely related to the dobsonflies and fishflies as well as to the prehistoric Euchauliodidae. All living alderflies – about 66 species all together – are part of the subfamily Sialinae, which contains between one and seven extant genera according to different scientists' views.
 W
WAmphizoa insolens is a species of aquatic beetles. It is found in North America from Alaska to southern California.
 W
WArchichauliodes is a genus of fishflies in the family Corydalidae. There are more than 20 described species in Archichauliodes.
 W
WArchichauliodes diversus is an insect in the subfamily Chauliodinae - the fishflies, though it is often referred to as "The New Zealand Dobsonfly", despite not being a true dobsonfly. In its larval form It is commonly known by the name toe-biter, and its Maori name is puene. The species is native to New Zealand. Although there are many other species of fishfly in other parts of the world, Archichauliodes diversus is the only species of fishfly in New Zealand.
 W
WThe caddisflies, or order Trichoptera, are a group of insects with aquatic larvae and terrestrial adults. There are approximately 14,500 described species, most of which can be divided into the suborders Integripalpia and Annulipalpia on the basis of the adult mouthparts. Integripalpian larvae construct a portable casing to protect themselves as they move around looking for food, while Annulipalpian larvae make themselves a fixed retreat in which they remain, waiting for food to come to them. The affinities of the small third suborder Spicipalpia are unclear, and molecular analysis suggests it may not be monophyletic. Also called sedge-flies or rail-flies, the adults are small moth-like insects with two pairs of hairy membranous wings. They are closely related to the Lepidoptera which have scales on their wings; the two orders together form the superorder Amphiesmenoptera.
 W
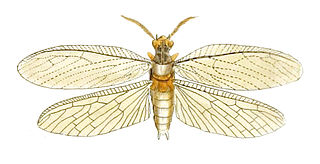
WChauliodes is a genus of fishflies in the family Corydalidae. There are about five described species in Chauliodes.
 W
WChauliodes pectinicornis known as Summer fishfly. is a species of fishfly from North America.
 W
WChauliodes rastricornis, the spring fishfly, is a species of fishfly in the family Corydalidae. It is found in North America.
 W
WDobsonflies are a subfamily of insects, Corydalinae, part of the Megalopteran family Corydalidae. The larvae are aquatic, living in streams, and the adults are often found along streams as well. The nine genera of dobsonflies are distributed in the Americas, Asia, and South Africa.
 W
WThe Dytiscidae – based on the Greek dytikos (δυτικός), "able to dive" – are the predaceous diving beetles, a family of water beetles. They occur in virtually any freshwater habitat around the world, but a few species live among leaf litter. The adults of most are between 1 and 2.5 cm (0.4–1.0 in) long, though much variation is seen between species. The European Dytiscus latissimus and Brazilian Megadytes ducalis are the largest, reaching up to 4.5 cm (1.8 in) and 4.75 cm (1.9 in) respectively. In contrast, the smallest is likely the Australian Limbodessus atypicali of subterranean waters, which only is about 0.9 mm (0.035 in) long. Most are dark brown, blackish, or dark olive in color with golden highlights in some subfamilies. The larvae are commonly known as water tigers due to their voracious appetite. They have short, but sharp mandibles and immediately upon biting, they deliver digestive enzymes into prey to suck their liquefied remains. The family includes more than 4,000 described species in numerous genera.
 W
WElophila gyralis, the waterlily borer moth, is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by George Duryea Hulst in 1886. It is found in eastern North America, where it has been recorded from Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Louisiana, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, New Brunswick, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Nova Scotia, Ohio, Oklahoma, Ontario, Pennsylvania, Quebec, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas and Wisconsin.
 W
WElophila icciusalis, the pondside pyralid moth, is a moth of the family Crambidae. It is found in most of North America.
 W
WElophila nigralbalis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Aristide Caradja in 1925. It is found in Japan, Vietnam, Indonesia and Taiwan.
 W
WElophila nymphaeata, the brown china mark, is a species of moth of the family Crambidae. It was described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. It is found in Europe. The moth is notable as its larva, like most members of the crambid subfamily Acentropinae, is aquatic and has tracheal gills.
 W
WElophila obliteralis, the waterlily leafcutter moth, is a moth of the family Crambidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1859. It is native to eastern North America. It is an introduced species in Hawaii and South Africa.
Elophila rivulalis is a species of moth in the family Crambidae. It is found in the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Germany, Poland, Austria, Hungary, Croatia, Italy and Greece.
 W
WElophila tinealis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Munroe in 1972. It is found in North America, where it has been recorded from Michigan, Ontario and New York, south to Florida and west to Texas. The habitat consists of swamps and wet woods.
 W
WElophila turbata is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1881. It is found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, India, Taiwan, China, Korea, Japan and the Russian Far East.
 W
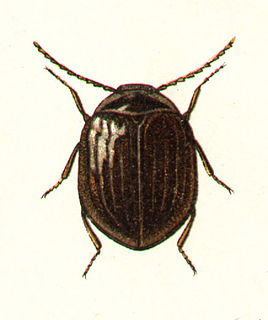
WEubriinae is an aquatic beetle subfamily in the family Psephenidae.
 W
WEusthenia is a genus of insect in the family Eustheniidae containing a number of species of stonefly most native to Tasmania. It contains the following species: E. brachyptera is considered a subspecies of E. venosa and Eusthenia extensa or Eusthenia purpurescens are considered E. costalis.Eusthenia costalis TAS Eusthenia lacustris TAS Eusthenia nothofagi VIC Eusthenia reticulata TAS Eusthenia spectabilis TAS Eusthenia venosa ACT NSW VIC
 W
WEusthenia nothofagi is a species of stonefly in the family Eustheniidae. It is endemic to Australia, where its range is restricted to Victoria. It is known only from the Otway Ranges and its common name is the Otway stonefly.
 W
WEustheniidae is a family of insects in the order Plecoptera, the stoneflies. They are native to Australia, New Zealand, and Chile.
 W
WFishflies are members of the subfamily Chauliodinae, belonging to the megalopteran family Corydalidae. They are most easily distinguished from their closest relatives, dobsonflies, by the jaws (mandibles) and antennae. In contrast to the large jaws of dobsonflies, fishfly mandibles are not particularly noticeable or distinctive, and the males have feathery antennae similar to many large moths. Chauliodes pectinicornis, the "summer fishfly", is a well-known species in North America.
 W
WGripopterygidae is a family of stoneflies in the order Plecoptera. There are more than 50 genera and 320 described species in Gripopterygidae.
 W
WHalobates or sea skaters are a genus with over 40 species of water striders. Most Halobates species are coastal and typically found in sheltered marine habitats, but five live on the surface of the open ocean and only occur near the coast when storms blow them ashore. These are the only known truly oceanic, offshore insects. They are found in tropical and subtropical marine habitats around the world, with a single species recorded in rivers a few kilometers upstream from the ocean. Halobates are generally very common.
 W
WHelotrephidae is a family of aquatic bugs found mainly in the tropical regions with many species in the Oriental Realm and a few from Africa, Madagascar and South America. These bugs are found swimming or walking amid submerged vegetation in stagnant or slow moving, shaded freshwater in forest habitats. They are a sister group of the Pleidae.
 W
WThe highland midge is a species of small flying insect, found across the Palearctic in upland and lowland areas. In the north west of Scotland and northern Wales the highland midge is usually very prevalent from late spring to late summer. Female highland midges are well known for gathering in clouds and biting humans, though the majority of the blood they obtain comes from cattle, sheep and deer. The bite of Culicoides is felt as a sharp prick. It is often followed by irritating lumps that may disappear in a few hours or last for days, depending on the individual.
 W
WMayflies are aquatic insects belonging to the order Ephemeroptera. This order is part of an ancient group of insects termed the Palaeoptera, which also contains dragonflies and damselflies. Over 3,000 species of mayfly are known worldwide, grouped into over 400 genera in 42 families.
 W
WA mosquito is any member of a group of about 3,500 species of small insects belonging to the order Diptera (flies). Within Diptera, mosquitoes constitute the family Culicidae. The word "mosquito" is Spanish and Portuguese for "little fly". Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, one pair of halteres, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and elongated mouthparts.
 W
WNymphula nitidulata, the beautiful china-mark, is a species of moth of the family Crambidae described by Johann Siegfried Hufnagel in 1767. It is found in Europe, Japan (Hokkaido), Turkey, Armenia, Russia and China.
 W
WThe Odonata are an order of flying insects that includes the dragonflies and damselflies. Like most other flying insects, they evolved in the early Mesozoic era. Their prototypes, the giant dragonflies of the Carboniferous, 325 mya, are no longer placed in the Odonata but included in the Protodonata or Meganisoptera.
 W
WThe Plecoptera are an order of insects, commonly known as stoneflies. Some 3,500 species are described worldwide, with new species still being discovered. Stoneflies are found worldwide, except Antarctica. Stoneflies are believed to be one of the most primitive groups of Neoptera, with close relatives identified from the Carboniferous and Lower Permian geological periods, while true stoneflies are known from fossils only a bit younger. Their modern diversity, however, apparently is of Mesozoic origin.
 W
WRat-tailed maggots are the larvae of certain species of hoverflies belonging to the tribes Eristalini and Sericomyiini. A characteristic feature of rat-tailed maggots is a tube-like, telescoping breathing siphon located at its posterior end. This acts like a snorkel, allowing the larva to breathe air while submerged. The siphon is usually about as long as the maggot's body, but can be extended as long as 150 mm (5.9 in). This organ gives the larva its common name.
 W
WSialis lutaria, common name alderfly, is a species of alderfly belonging to the order Megaloptera family Sialidae.
 W
WStenoperla is a genus of insect in the family Eustheniidae containing a number of species of stonefly all endemic to New Zealand.
 W
WA water beetle is a generalized name for any beetle that is adapted to living in water at any point in its life cycle. Most water beetles can only live in fresh water, with a few marine species that live in the intertidal zone or littoral zone. There are approximately 2000 species of true water beetles native to lands throughout the world.
 W
WWater-penny beetles are a family of 272 species of aquatic beetles found on all continents except Antarctica, in both tropical and temperate areas. The young, which live in water, resemble tiny pennies. The larvae feed – usually nocturnally – on algae on rock surfaces. The presence of water-penny larvae in a stream can be used as a test for the quality of the water, as they are pollution-sensitive. They cannot live in habitats where rocks acquire a thick layer of algae, fungi, or inorganic sediment. Therefore, their presence along with other diverse phyla signifies good-quality water. They are around 6 to 10 millimeters in length.
 W
WThe whirligig beetles are a family (Gyrinidae) of water beetles that usually swim on the surface of the water if undisturbed, though they swim underwater when threatened. They get their common name from their habit of swimming rapidly in circles when alarmed, and are also notable for their divided eyes which are believed to enable them to see both above and below water. The family includes some 700 extant species worldwide, in 15 genera, plus a few fossil species. Most species are very similar in general appearance, though they vary in size from perhaps 3 mm to 18 mm in length. They tend to be flattened and rounded in cross section, in plain view as seen from above, and in longitudinal section. In fact their shape is a good first approximation to an ellipsoid, with legs and other appendages fitting closely into a streamlined surface.