 W
WAcropora aculeus is a species of acroporid corals found throughout the Indian Ocean, the central Indo-Pacific, Australia, southeast Asia, Japan and the East China Sea. It is also present in the western Pacific Ocean. It is an uncommon species and is particularly prone to coral bleaching, disease, and crown-of-thorns starfish predation; it is also harvested for use in aquaria, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed it as being a "vulnerable species". Habitat loss is a big concern.
 W
WAcropora cerealis is a species of acroporid coral found throughout the Indian and Pacific oceans, from the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the Hawaiian Islands and the Johnston Atoll. It can be found on upper reef slopes in shallow tropical reefs, from depths of 3–20 m. Crown-of-thorns starfish preferentially prey upon Acropora corals, and this species is also harvested for the aquarium trade.
 W
WAcropora echinata is a species of acroporid coral that was first described by Dana in 1846. Found in shallow, tropical, sheltered reefs in marine environments, it is found at depths of 8 to 25 m in clear water. The species is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, and has a decreasing population. It is not common but found over a large area, and is listed under CITES Appendix II.
 W
WAcropora horrida is a species of acroporid coral that was first described by James Dwight Dana in 1846. Found in tropical, shallow reefs in marine environments, it occurs near fringing reefs around turbid water, at depths of 5 to 20 m. It is listed as a vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List, and it is thought to have a decreasing population. It is not common and found over a large area, and is listed under CITES Appendix II.
 W
WAntarctic krill is a species of krill found in the Antarctic waters of the Southern Ocean. It is the dominant animal species of Earth. It is a small, swimming crustacean that lives in large schools, called swarms, sometimes reaching densities of 10,000–30,000 individual animals per cubic metre. It feeds directly on minute phytoplankton, thereby using the primary production energy that the phytoplankton originally derived from the sun in order to sustain their pelagic life cycle. It grows to a length of 6 centimetres (2.4 in), weighs up to 2 grams (0.071 oz), and can live for up to six years. It is a key species in the Antarctic ecosystem and in terms of biomass, is one of the most abundant animal species on the planet.
 W
WCalanidae is the largest taxonomic family of calanoid copepods. It includes the genus Calanus, which may be the most abundant metazoan genus on Earth.
 W
WThe Caridea, commonly known as caridean shrimp, are an infraorder of shrimp within the order Decapoda. They are found widely around the world in both fresh and salt water.
 W
WThe Caryophylliidae are a family of stony corals found from the tropics to temperate seas, and from shallow to very deep water.
 W
WThe Chaetiliidae are a family of isopod crustaceans in the suborder Valvifera, comprising these genera:Austrochaetilia Poore, 1978 Chaetilia Dana, 1849 Chiridotea Harger, 1878 Chiriscus Richardson, 1911 Glyptonotus Eights, 1852 Macrochiridothea Ohlin, 1901 Maoridotea Jones & Fenwick, 1978 Parachiridotea Daguerre de Hureaux & Elkaïm, 1972 † Proidotea Racovitza & Sevastos, 1910 Saduria Adams, 1852 Saduriella Holthuis, 1964 Stegidotea Poore, 1985 Symmius Richardson, 1904
 W
WThe Dungeness crab, Metacarcinus magister or Cancer magister, is a species of crab that inhabits eelgrass beds and water bottoms on the west coast of North America. It typically grows to 20 cm (7.9 in) across the carapace and is a popular seafood. Its common name comes from the port of Dungeness, Washington, where it is "a prized crustacean that supports the most valuable fishery on the west coast", and where ocean acidification threatens the marine environment.
 W
WThe purple shore crab, Hemigrapsus nudus, is a common crab of the family Varunidae. It can be found sheltering under rocks in inter-tidal areas along the west coast of North America, from Alaska to Baja California in Mexico. This crab primarily eats sea lettuce and other green algae, and occasionally scavenges dead animals.
 W
WDipsastraea pallida is a species of colonial stony coral in the family Merulinidae. It is found in tropical waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. This is a common species of coral with a widespread distribution, and the main threat it faces is from the destruction of its coral reef habitats. It is rated as a "least-concern species" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. This species was first described in 1846 as Favia pallida by the American zoologist James Dwight Dana; it was later transferred to the genus Dipsastraea, but some authorities continue to use the original name.
 W
WDipsastraea speciosa is a species of colonial stony coral in the family Merulinidae. It is found in tropical waters of the Indian and Pacific oceans.
 W
WEuphausia is the largest genus of krill, and is placed in the family Euphausiidae. There are 31 species known in this genus, including Antarctic krill and ice krill from the Southern Ocean, and North Pacific krill in the Pacific Ocean.
 W
WAntarctic krill is a species of krill found in the Antarctic waters of the Southern Ocean. It is the dominant animal species of Earth. It is a small, swimming crustacean that lives in large schools, called swarms, sometimes reaching densities of 10,000–30,000 individual animals per cubic metre. It feeds directly on minute phytoplankton, thereby using the primary production energy that the phytoplankton originally derived from the sun in order to sustain their pelagic life cycle. It grows to a length of 6 centimetres (2.4 in), weighs up to 2 grams (0.071 oz), and can live for up to six years. It is a key species in the Antarctic ecosystem and in terms of biomass, is one of the most abundant animal species on the planet.
 W
WKrill are small crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word krill, meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish.
 W
WEuphyllia is a genus of large-polyped stony coral. Several species are commonly found in marine aquariums. The genus includes the following species:Euphyllia ancora Veron & Pichon, 1980 – hammer coral Euphyllia baliensis Turak, Devantier & Erdman, 2012 – bubble coral Euphyllia cristata Chevalier, 1971 – grape coral Euphyllia divisa Veron & Pichon, 1980 – frogspawn coral Euphyllia glabrescens (Chamisso & Eysenhardt, 1821) – torch coral Euphyllia paraancora Veron, 1990 – branching hammer coral Euphyllia paradivisa Veron, 1990 – branching frogspawn coral Euphyllia paraglabrescens Veron, 1990 Euphyllia yaeyamaensis (Shirai, 1980)
 W
WThe Fungiidae are a family of Cnidaria, often known as plate corals. The family contains thirteen extant genera. They range from solitary corals to colonial species. Some genera such as Cycloseris and Fungia are solitary organisms, Polyphyllia consists of a single organism with multiple mouths, and Ctenactis and Herpolitha might be considered as solitary organisms with multiple mouths or a colony of individuals, each with its separate mouth.
 W
WHemigrapsus is a genus of varunid crabs comprising thirteen species native almost exclusively in the Pacific Ocean, but two have been introduced to the North Atlantic region.
 W
WHemigrapsus oregonensis is a small shore crab of the family Varunidae; it was formerly classified under the family Grapsidae. It is known under several common names, including yellow shore crab, hairy shore crab, green shore crab, mud-flat crab, and Oregon shore crab.
 W
WKrill are small crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word krill, meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish.
 W
WLithophyllon repanda is a species of mushroom or disc coral in the family Fungiidae.This species is able to move to another location on occasion. The International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) rated it as a least-concern species and it was originally described by Dana in 1846. It occurs at depths of 1 to 30 metres.
 W
WLobsters are a family of large marine crustaceans.
 W
WThe graceful rock crab or slender crab, Metacarcinus gracilis or Cancer gracilis, is one of only two members of the genus Metacarcinus, recognized by WoRMS, whose chelae (claws) are white tipped, the other crab being M. magister. Both of these eastern Pacific crab species are recognized by ITIS as belonging to the much larger genus Cancer. M. gracilis has been caught from Alaska to Bahía Magdelena, Baja California. Although M. gracilis is only found in the Pacific Ocean, it has cousins in the Atlantic Ocean. The genus Cancer apparently evolved in the Pacific Ocean and later migrated to the Atlantic Ocean. Larvae and small juveniles of this species are often seen riding jellyfish, especially Phacellophora camtschatica. The juvenile crabs steal food from the jellyfish and also clean off parasitic amphipods.
 W
WThe Dungeness crab, Metacarcinus magister or Cancer magister, is a species of crab that inhabits eelgrass beds and water bottoms on the west coast of North America. It typically grows to 20 cm (7.9 in) across the carapace and is a popular seafood. Its common name comes from the port of Dungeness, Washington, where it is "a prized crustacean that supports the most valuable fishery on the west coast", and where ocean acidification threatens the marine environment.
 W
WLobsters are a family of large marine crustaceans.
 W
WNephropoidea is a superfamily of decapod crustaceans. It contains the true lobsters in the Nephropidae, and three fossil families: Chilenophoberidae, Protastacidae and Stenochiridae. Their closest relatives are the reef lobsters.
 W
WOregonia gracilis, commonly known as the graceful decorator crab, is a species of crab belonging to the family Oregoniidae. Like other decorator crabs it habitually attaches other organisms to its back. The sessile organisms are attached to hooked setae that act as a sort of velcro attachment. This decoration provides visual and chemical camouflage thus reducing predation risk. Pacific halibut are a major predator of O. gracilis. Other predators include octopus and sea otters. The main food source of O. gracilis is floating kelp and algae that they capture utilizing a waiting strategy in order to maintain cryptosis.
 W
WPocillopora grandis, is a colonial species of stony coral in the family Pocilloporidae. It is known commonly as antler coral, and is found in the Indo-West Pacific to the Eastern Tropical Pacific.
 W
WPocillopora meandrina, commonly known as cauliflower coral, is a species of coral occurring in the Indo-Pacific and Pacific oceans. This coral lives in shallow reef environments.
 W
WPorites compressa, also known as finger coral or hump coral, is a species of marine stony coral in the family Poritidae. It is found growing on coral reefs and in shallow lagoons in tropical parts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
 W
WPorites lobata, known by the common name lobe coral, is a species of stony coral in the family Poritidae. It is found growing on coral reefs in tropical parts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
 W
WPugettia gracilis, commonly known as the graceful kelp crab, is a species of small crab in the family Epialtidae. It lives among forests of kelp on the Pacific coast of North America.
 W
WThe signal crayfish is a North American species of crayfish. It was introduced to Europe in the 1960s to supplement the North European Astacus astacus fisheries, which were being damaged by crayfish plague, but the imports turned out to be a carrier of that disease. The signal crayfish is now considered an invasive species across Europe, Japan, and California ousting native species there.
 W
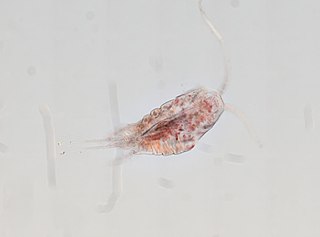
WTemora stylifera is a copepod primarily found in the Atlantic and surrounding waters.
 W
WTemora turbinata is a copepod in the Temoridae family. It is an epipelagic species, having been recorded in coastal waters around the world. It was first described in 1849 by American scientist James Dwight Dana.