 W
WThe Atlantic Forest climbing mouse is an arboreal rodent species in the family Cricetidae from South America. It is found in the Atlantic Forest of southeastern Brazil at elevations from sea level to 1500 m. Its karyotype is 2n = 44, FN = 74–80.
 W
WThe Brazilian big-eyed bat is a species of phyllostomid bat from South America. The scientific name honours Italian naturalist Giacomo Doria.
 W
WThe Ipanema bat, is a bat species of order Chiroptera and family Phyllostomidae. It is found in South America, specifically in northern Argentina, Bolivia, southeastern Brazil and Paraguay. It is monotypic within its genus.
 W
WThe Recife broad-nosed bat, Platyrrhinus recifinus, is a species of bat from South America. It is named for the city of Recife in Brazil, where it was first recorded by Oldfield Thomas in 1901.
 W
WThe narrowmouthed catshark is a catshark of the family Scyliorhinidae, found from central Chile around the Straits of Magellan, to Argentina between latitudes 23° S and 56° S, at depths down to about 180 m (600 ft) in the Atlantic Ocean and about 360 m (1,200 ft) in the Pacific. It can grow to a length of up to 70 cm (28 in). The reproduction of this catshark is oviparous.
 W
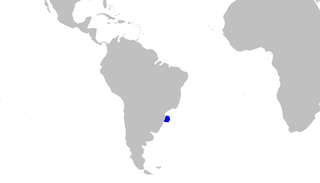
WThe southern sawtail catshark is a species of catshark, part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to southern Brazil. It inhabits deepwater reefs on the upper continental slope at a depth of 236–600 m (774–1,969 ft). Reaching at least 43 cm (17 in) in length, this slim-bodied species closely resembles the Antilles catshark. It has a prominent crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the dorsal edge of the caudal fin, as well as a distinctive color pattern of dark oval blotches, outlined in white, along its back. The southern sawtail catshark is oviparous, with females producing reddish egg capsules. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has assessed it as Vulnerable; it is often taken as bycatch and may be threatened by intensifying squid fishing.
 W
WThe red-legged cormorant also known as the red-legged shag, red-footed cormorant, red-footed shag, Gaimard's cormorant and grey cormorant, is a resident of the coastline of South America. It is non-colonial unlike most seabirds. The red-legged cormorant has not been observed wing-spreading, which is unusual among cormorant species.
 W
WCommerson's dolphin, also referred to by the common names jacobita, skunk dolphin, piebald dolphin or panda dolphin, is a small oceanic dolphin of the genus Cephalorhynchus. Commerson's dolphin has two geographically-isolated but locally-common subspecies. The principal subspecies, C.c.commersonii, has sharply-delineated black-and-white patterning and is found around the tip of South America. The secondary subspecies, C.c.kerguelenensis, is larger than C.c.commersonii, has a less-sharply delineated dark and light grey patterning with a white ventral band, and is found around the Kerguelen Islands in the Indian Ocean.
 W
WThe La Plata dolphin, franciscana or toninha is a species of dolphin found in coastal Atlantic waters of southeastern South America. It is a member of the river dolphin group and the only one that lives in the ocean and saltwater estuaries, rather than inhabiting exclusively freshwater systems. Commercialized areas that create agricultural runoffs and/or industrialized zones can affect the health of the La Plata dolphin, especially in regards to their contributions of waste and pollution, which can lead to habitat degradation and poisoned food among other concerns.
 W
WThe Brazilian guitarfish is a species of fish in the family Rhinobatidae. It is endemic to Brazil, where its natural habitat is coastal waters on the continental shelf. This fish is viviparous and has a long gestation period, concluding with the birth of live pups in February. At this time the fish are subject to intense fishing activity but catches have been dwindling in recent years as a result of overfishing. Because so few breeding-size fish remain, the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed the fish's conservation status as being "critically endangered".
 W
WThe dolphin gull, sometimes erroneously called the red-billed gull, is a gull native to southern Chile and Argentina, and the Falkland Islands. It is a coastal bird inhabiting rocky, muddy and sandy shores and is often found around seabird colonies. They have greyish feathers, and the feathers on their wings are a darker shade. Dolphin gulls have a varied diet, eating many things ranging from mussels to carrion.
 W
WOlrog's gull is a species of gull found along the Atlantic coast of southern Brazil, Uruguay, and northern Argentina. It was formerly considered a subspecies of the very similar L. belcheri. It is a large gull with a black back and wings, white head and underparts, a black band in the otherwise white tail, and a yellow bill with a red and black tip. Nonbreeding adults have a blackish head and a white eye ring. The species is named after Swedish-Argentine biologist Claes C. Olrog. It has a rather restricted breeding range and is threatened by habitat loss, and the IUCN has rated it as being "near threatened".
 W
WThe southern hagfish is a hagfish of the genus Myxine.
 W
WThe hāpuku, hapuka or whapuku, also known as groper, is a wreckfish of the family Polyprionidae, found around southern Australia, southern South America, South Africa, Tristan da Cunha and New Zealand at depths between 30 and 800 m. Its length is between 60 and 180 cm, and it can weigh up to 100 kg. It is sometimes described locally as cod, although that properly refers to other fish.
 W
WOlrog's gull is a species of gull found along the Atlantic coast of southern Brazil, Uruguay, and northern Argentina. It was formerly considered a subspecies of the very similar L. belcheri. It is a large gull with a black back and wings, white head and underparts, a black band in the otherwise white tail, and a yellow bill with a red and black tip. Nonbreeding adults have a blackish head and a white eye ring. The species is named after Swedish-Argentine biologist Claes C. Olrog. It has a rather restricted breeding range and is threatened by habitat loss, and the IUCN has rated it as being "near threatened".
 W
WThe buffy-tufted marmoset, also known as the buffy tufted-ear marmoset or white-eared marmoset, is a New World monkey that lives in the forests on the Atlantic coast of southeast Brazil. Of all the marmosets, it has the southernmost range.
 W
WThe northern three-striped opossum is an opossum species from South America.
 W
WThe southeastern four-eyed opossum is an opossum species native to South America. It is found in Atlantic Forest ecoregions, in Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina.
 W
WThe soft-spined Atlantic spiny-rat, Trinomys dimidiatus, is a spiny rat species from South America. It is endemic to Brazil.
 W
WThe apron ray is a small electric ray in the numbfish family, Narcinidae, known for being able to generate electric shocks for defense. It is one of two species in the genus Discopyge.
 W
WThe Remo flounder, Oncopterus darwinii, is an edible flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on bottoms at depths of between 20 and 80 metres. Its native habitat is the southwestern Atlantic along the southeast coast of South America, from Santa Catarina, Brazil in the north to the San Matías Gulf, Argentina in the south. It can reach 30 centimetres (12 in) in length.
 W
WSanta Catarina's guinea pig or Moleques do Sul cavy is a rare guinea pig species of southeastern South America.
 W
WThe imperial shag or imperial cormorant is a black and white cormorant native to southern South America, primarily in rocky coastal regions, but locally also at large inland lakes. Some taxonomic authorities, including the International Ornithologists' Union, place it in the genus Leucocarbo, others in the genus Phalacrocorax. It is also known as the blue-eyed shag, blue-eyed cormorant and by many other names, and is one of a larger group of cormorants called blue-eyed shags. The taxonomy is very complex, and several former subspecies are often considered separate species.
 W
WThe rock shag, also known as the Magellanic cormorant, is a marine cormorant found around the southernmost coasts of South America. Its breeding range is from around Valdivia, Chile, south to Cape Horn and Tierra del Fuego, and north to Punta Tombo in Argentina. In winter it is seen further north, with individuals reaching as far as Santiago, Chile on the west coast and Uruguay on the east. The birds also breed around the coasts of the Falkland Islands.
 W
WThe copper shark, bronze whaler, or narrowtooth shark, is a species of requiem shark, family Carcharhinidae, and the only member of its genus found mostly at temperate latitudes. It is distributed in a number of separate populations in the northeastern and southwestern Atlantic, off southern Africa, in the northwestern and eastern Pacific, and around Australia and New Zealand, with scattered reports from equatorial regions. This species can be found from brackish rivers and estuaries, to shallow bays and harbors, to offshore waters 100 m (330 ft) deep or more. Females are found apart from males for most of the year, and conduct seasonal migrations. A large species reaching 3.3 m (11 ft) long, the copper shark is difficult to distinguish from other large requiem sharks. It is characterized by its narrow, hook-shaped upper teeth, lack of a prominent ridge between the dorsal fins, and plain bronze coloration.
 W
WThe school shark is a houndshark of the family Triakidae, and the only member of the genus Galeorhinus. Common names also include tope shark, snapper shark, and soupfin shark. It is found worldwide in temperate seas at depths down to about 800 m (2,600 ft). It can grow to nearly 2 m long. It feeds both in midwater and near the seabed, and its reproduction is ovoviviparous. This shark is caught in fisheries for its flesh, its fins, and its liver, which has a very high vitamin A content. The IUCN has classified this species as critically endangered in its Red List of Threatened Species.
 W
WThe dusky smooth-hound, also called the smooth dogfish or the dog shark, is a species of houndshark in the family Triakidae. This shark is an olive grey or brown in color, and may have shades of yellow or grayish white. Females live to 16 years and males have a lifespan of 10 years. M. canis was the first shark recognised to have viral infections.
 W
WThe narrownose smooth-hound is a houndshark of the family Triakidae. It is found on the continental shelves of the subtropical southwest Atlantic, from southern Brazil to northern Argentina, between latitudes 30° S and 44° S, at depths between 60 m to 195 m. It can reach a length of 74 centimeters.
 W
WThe speckled smooth-hound is a houndshark of the family Triakidae. It is found on the continental shelf of the eastern Pacific, between latitudes 0° and 54° S, at depths between 16 and 50 m. It can reach a length of 130 cm (51 in). Collectively with certain other species of shark, it is known as "tollo".
 W
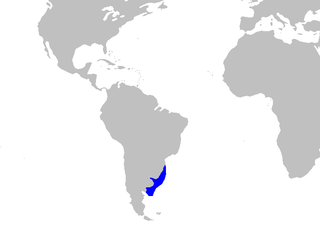
WThe striped smooth-hound is a houndshark of the family Triakidae, found on the continental shelves of the subtropical southwest Atlantic from southern Brazil to northern Argentina between latitudes 30° S and 47° S, from the surface to 250 m. It can grow up to a length of 1.77 m. The reproduction of this shark is Ovoviviparous, with the length at birth up to 39 cm.
 W
WThe South American sea lion, also called the Southern Sea Lion and the Patagonian sea lion, is a sea lion found on the Ecuadorian, Peruvian, Chilean, Falkland Islands, Argentinean, Uruguayan, and Southern Brazilian coasts. It is the only member of the genus Otaria. Its scientific name was subject to controversy, with some taxonomists referring to it as Otaria flavescens and others referring to it as Otaria byronia. The former eventually won out, although that may still be overturned. Locally, it is known by several names, most commonly lobo marino (es)/lobo marinho (pt) and león marino (es)/leão marinho (pt) and the hair seal.
 W
WThe southern blue whiting is a codfish of the genus Micromesistius, found in the southern oceans with temperatures between 3 and 7 °C, at depths of 50 to 900 m. Its length is commonly between 30 and 60 cm, with a maximum length of 90 cm. Maximum weight is at least 1350 g.
 W
WThe South American tern is a species of tern found in coastal regions of southern South America, including the Falkland Islands, ranging north to Peru and Brazil. It is generally the most common tern in its range. The smaller, highly migratory common tern closely resembles it. The specific epithet refers to the "swallow-like" forked tail feathering.
 W
WThe Atlantic titi or masked titi is a species of titi, a type of New World monkey, endemic to Brazil.
 W
WThe saffron toucanet is a species of bird in the family Ramphastidae found in the Atlantic Forest in far north-eastern Argentina, south-eastern Brazil, and eastern Paraguay.