 W
WSchizophrenia is a psychiatric disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically come on gradually, begin in young adulthood, and in many cases never resolve. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders that often includes an anxiety disorder such as panic disorder, an obsessive–compulsive disorder, or a substance use disorder.
 W
WAngel Baby is a 1995 Australian drama film written and directed by Michael Rymer and starring John Lynch, Jacqueline McKenzie and Colin Friels. The film was produced in 1993–94. It is a love story of two people with schizophrenia.
 W
WResearch into the mental disorder of schizophrenia, involves multiple animal models as a tool, including in the preclinical stage of drug development.
 W
WAutumn Leaves is a 1956 American film noir drama film directed by Robert Aldrich and starring Joan Crawford in an older woman/younger man tale of mental illness. The film was distributed by Columbia Pictures. The screenplay was written by Jean Rouverol and Hugo Butler, though it was credited to Jack Jevne, since Rouverol and Butler were blacklisted at the time of the film's release.
 W
WBasic symptoms of schizophrenia are subjective symptoms, described as experienced from a person's perspective, which show evidence of underlying psychopathology. Basic symptoms have generally been applied to the assessment of people who may be at risk to develop psychosis. Though basic symptoms are often disturbing for the person, problems generally do not become evident to others until the person is no longer able to cope with their basic symptoms. Basic symptoms are more specific to identifying people who exhibit signs of prodromal psychosis (prodrome) and are more likely to develop schizophrenia over other disorders related to psychosis. Schizophrenia is a psychotic disorder, but is not synonymous with psychosis. In the prodrome to psychosis, uncharacteristic basic symptoms develop first, followed by more characteristic basic symptoms and brief and self-limited psychotic-like symptoms, and finally the onset of psychosis. People who were assessed to be high risk according to the basic symptoms criteria have a 48.5% likelihood of progressing to psychosis. In 2015, the European Psychiatric Association issued guidance recommending the use of a subscale of basic symptoms, called the Cognitive Disturbances scale (COGDIS), in the assessment of psychosis risk in help-seeking psychiatric patients; in a meta-analysis, COGDIS was shown to be as predictive of transition to psychosis as the Ultra High Risk (UHR) criteria up to 2 years after assessment, and significantly more predictive thereafter. The basic symptoms measured by COGDIS, as well as those measured by another subscale, the Cognitive-Perceptive basic symptoms scale (COPER), are predictive of transition to schizophrenia.
 W
WBenny & Joon is a 1993 psychological romantic comedy film released by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer about how two eccentric individuals, Sam and Juniper "Joon", find each other and fall in love. Aidan Quinn also stars, and it was directed by Jeremiah S. Chechik.
 W
WBradyphrenia is the slowness of thought common to many disorders of the brain. Disorders characterized by bradyphrenia include Parkinson's disease and forms of schizophrenia consequently causing a delayed response and fatigue. Patients with bradyphrenia may describe or may manifest slowed thought processes, evidenced by increased latency of response and also involve severe memory impairment and poor motor control. The word 'bradyphrenia' originates from the ancient Greek meaning 'slow mind.'
 W
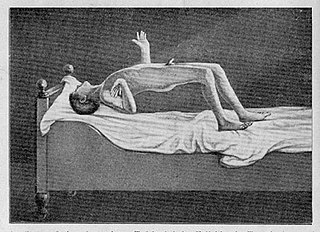
WCatalepsy is a nervous condition characterized by muscular rigidity and fixity of posture regardless of external stimuli, as well as decreased sensitivity to pain.
 W
WCatatonia is a state of psycho-motor immobility and behavioral abnormality. It was first described in 1874 by Karl Ludwig Kahlbaum as Die Katatonie oder das Spannungsirresein.
 W
WCrowding is a perceptual phenomenon where the recognition of objects presented away from the fovea is impaired by the presence of other neighbouring objects. It has been suggested that crowding occurs due to mandatory integration of the crowded objects by a texture-processing neural mechanism, but there are several competing theories about the underlying mechanisms. It is considered a kind of grouping since it is "a form of integration over space as target features are spuriously combined with flanker features."
 W
WDementia praecox is a disused psychiatric diagnosis that originally designated a chronic, deteriorating psychotic disorder characterized by rapid cognitive disintegration, usually beginning in the late teens or early adulthood. Over the years, the term "dementia praecox" was gradually replaced by "schizophrenia", which remains in current diagnostic use.
 W
WThe diathesis–stress model is a psychological theory that attempts to explain a disorder, or its trajectory, as the result of an interaction between a predispositional vulnerability, the diathesis, and a stress caused by life experiences. The term diathesis derives from the Greek term (διάθεσις) for a predisposition, or sensibility. A diathesis can take the form of genetic, psychological, biological, or situational factors. A large range of differences exists among individuals' vulnerabilities to the development of a disorder.
 W
WDoctoring the Mind: Why psychiatric treatments fail is a 2009 book by Richard Bentall, his thesis is critical of contemporary Western psychiatry. Bentall, a professor of clinical psychology, argues that recent scientific research shows that the medical approach to mental illness is fatally flawed. According to Bentall, it seems there is no "evidence that psychiatry has made a positive impact on human welfare" and "patients are doing no better today than they did a hundred years ago".
 W
WDotter of Her Father's Eyes is a 2012 graphic novel written by Mary M. Talbot with artwork by her husband, Bryan Talbot. It is part memoir, and part biography of Lucia Joyce, daughter of modernist writer James Joyce.
 W
WEcholalia is the unsolicited repetition of vocalizations made by another person. In its profound form it is automatic and effortless. It is one of the echophenomena, closely related to echopraxia, the automatic repetition of movements made by another person; both are "subsets of imitative behavior" whereby sounds or actions are imitated "without explicit awareness". Echolalia may be an immediate reaction to a stimulus or may be delayed.
 W
WSchizophrenia affects around 0.3–0.7% of people at some point in their life, or 21 million people worldwide as of 2011. By using precise methods in its diagnosis and a large, representative population, schizophrenia seems to occur with relative consistency over time during the last half-century.
 W
WGrandiose delusions (GD), also known as delusions of grandeur or expansive delusions, are a subtype of delusion that occur in patients suffering from a wide range of psychiatric diseases, including two-thirds of patients in manic state of bipolar disorder, half of those with schizophrenia, patients with the grandiose subtype of delusional disorder, and a substantial portion of those with substance abuse disorders. GDs are characterized by fantastical beliefs that one is famous, omnipotent, wealthy, or otherwise very powerful. The delusions are generally fantastic and typically have a religious, science fictional, or supernatural theme. There is a relative lack of research into GD, in contrast to persecutory delusions and auditory hallucinations. About 10% of healthy people experience grandiose thoughts but do not meet full criteria for a diagnosis of GD.
 W
WHidden Valley Road: Inside the Mind of an American Family is a 2020 non-fiction book by Robert Kolker. It is an account of the Galvin family of Colorado Springs, Colorado, a midcentury American family with twelve children, six of them diagnosed with schizophrenia. The family became subjects of researchers investigating a genetic origin for schizophrenia.
 W
WHypofrontality is a state of decreased cerebral blood flow (CBF) in the prefrontal cortex of the brain. Hypofrontality is symptomatic of several neurological medical conditions, such as schizophrenia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. This condition was initially described by Ingvar and Franzén in 1974, through the use of xenon blood flow technique with 32 detectors to image the brains of patients with schizophrenia. This finding was confirmed in subsequent studies using the improved spatial resolution of positron emission tomography with the fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) tracer. Subsequent neuroimaging work has shown that the decreases in prefrontal CBF are localized to the medial, lateral, and orbital portions of the prefrontal cortex. Hypofrontality is thought to contribute to the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Hypofrontality was initially thought to be a side effect of antipsychotic drugs used to treat these conditions. However, reduced activity in the right frontal lobe, left temporal lobe and left cerebellum during the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test is seen in people with schizophrenia who have never received antipsychotic drugs, which suggests that this is not the case.
 W
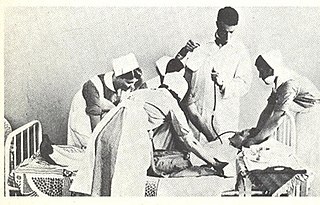
WInsulin shock therapy or insulin coma therapy was a form of psychiatric treatment in which patients were repeatedly injected with large doses of insulin in order to produce daily comas over several weeks. It was introduced in 1927 by Austrian-American psychiatrist Manfred Sakel and used extensively in the 1940s and 1950s, mainly for schizophrenia, before falling out of favour and being replaced by neuroleptic drugs in the 1960s.
 W
WLY-404,039, also known as pomaglumetad, is an amino acid analog drug that acts as a highly selective agonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor group II subtypes mGluR2 and mGluR3. Pharmacological research has focused on its potential antipsychotic and anxiolytic effects. LY-404,039 is intended as a treatment for schizophrenia and other psychotic and anxiety disorders by modulating glutamatergic activity and reducing presynaptic release of glutamate at synapses in limbic and forebrain areas relevant to these disorders. Human studies investigating therapeutic use of LY-404,039 have focused on the prodrug LY-2140023, a methionine amide of LY-404,039 (also called pomaglumetad methionil or LY-2140023 monohydrate) since LY-404,039 exhibits low oral absorption and bioavailability in humans.
 W
WThe term neurodiversity refers to variation in the human brain regarding sociability, learning, attention, mood and other mental functions. It was coined in 1998 by Australian sociologist Judy Singer, who helped popularize the concept along with American journalist Harvey Blume. It emerged as a challenge to prevailing views that certain neurodevelopmental disorders are inherently pathological and instead adopts the social model of disability, in which societal barriers are the main contributing factor that disables people.
Primary polydipsia, or psychogenic polydipsia, is a form of polydipsia characterised by excessive fluid intake in the absence of physiological stimuli to drink. Psychogenic polydipsia which is caused by psychiatric disorders, often schizophrenia, is often accompanied by the sensation of dry mouth. Some forms of polydipsia are explicitly non-psychogenic. Primary polydipsia is a diagnosis of exclusion.
 W
WThe prognosis of schizophrenia is varied at the individual level. In general it has great human and economics costs. It results in a decreased life expectancy of 12–15 years primarily due to its association with obesity, little exercise, and smoking, while an increased rate of suicide plays a lesser role. These differences in life expectancy have increased between the 1970s and 1990s, and between the 1990s and 2000s has not substantially changed in a health system with open access to care (Finland).
 W
WProof is a 2005 American drama film directed by John Madden and starring Gwyneth Paltrow, Anthony Hopkins, Jake Gyllenhaal, and Hope Davis. The screenplay was written by Rebecca Miller and David Auburn, based on Auburn's Pulitzer Prize-winning play Proof.
 W
WSchizoid personality disorder is a personality disorder characterized by a lack of interest in social relationships, a tendency toward a solitary or sheltered lifestyle, secretiveness, emotional coldness, detachment and apathy. Affected individuals may be unable to form intimate attachments to others and simultaneously possess a rich and elaborate but exclusively internal fantasy world. Other associated features include stilted speech, a lack of deriving enjoyment from most activities, feeling as though one is an "observer" rather than a participant in life, an inability to tolerate emotional expectations of others, apparent indifference when praised or criticized, a degree of asexuality, and idiosyncratic moral or political beliefs. Symptoms typically start in late childhood or adolescence.
 W
WSchizophrenia Research Foundation (SCARF), was founded in 1984 with the primary objective of providing quality care and rehabilitation to those suffering from severe mental disorders. SCARF has a Mental Health Center located in Anna Nagar, Chennai, along with two residential rehabilitation centres at Thiruverkadu and Mahabalipuram.
 W
WOn 4 September 2014, 82-year-old Palmira Silva was beheaded in her back garden in Edmonton, London, by 25-year-old Nicholas Salvador, who was on a rampage. Friends of Salvador had recently noticed odd behaviour by him, including drug and alcohol abuse and an obsession with videos of beheadings.
 W
WThe Snake Pit is a 1948 American drama film directed by Anatole Litvak and starring Olivia de Havilland, Mark Stevens, Leo Genn, Celeste Holm, Beulah Bondi, and Lee Patrick. Based on Mary Jane Ward's 1946 semi-autobiographical novel of the same name, the film recounts the tale of a woman who finds herself in an insane asylum and cannot remember how she got there.
 W
WSoteria is a community service that provides a space for people experiencing mental distress or crisis. Based on a recovery model, common elements of the Soteria approach include primarily non-medical staffing; preserving resident's personal power, social networks, and communal responsibilities; finding meaning in the subjective experience of psychosis by "being with" clients; and no or minimal use of antipsychotic medication.
 W
WExecutive functions are a cognitive apparatus that controls and manages cognitive processes. Norman and Shallice (1980) proposed a model on executive functioning of attentional control that specifies how thought and action schemata become activated or suppressed for routine and non-routine circumstances. Schemas, or scripts, specify an individual's series of actions or thoughts under the influence of environmental conditions. Every stimulus condition turns on the activation of a response or schema. The initiation of appropriate schema under routine, well-learned situations is monitored by contention scheduling which laterally inhibits competing schemas for the control of cognitive apparatus. Under unique, non-routine procedures the supervisory attentional system (SAS) controls schema activation. The SAS is an executive monitoring system that oversees and controls contention scheduling by influencing schema activation probabilities and allowing for general strategies to be applied to novel problems or situations during automatic attentional processes.
 W
WThe Manic Monologues is a play developed and premiered by Zachary Burton and Elisa Hofmeister at Stanford University. The play consists of autobiographical accounts of mental illness from people diagnosed with mental health disorders, the family and friends of mental health patients, and health professionals. The play explores diagnoses including bipolar, schizophrenia, depression, OCD, and PTSD in stories that are by turns tragic, humorous, and uplifting.
 W
WVisual processing abnormalities in schizophrenia are commonly found, and contribute to poor social function.
 W
WWaxy flexibility is a psychomotor symptom of catatonia as associated with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or other mental disorders which leads to a decreased response to stimuli and a tendency to remain in an immobile posture. Attempts to reposition the patient are met by "slight, even resistance", and after being repositioned, the patient will typically remain in the new position. Waxy flexibility rarely occurs in cases of delirium. The presence of waxy flexibility along with at least two other catatonic symptoms such as stupor or negativism are enough to warrant a diagnosis of catatonia.