 W
WAdeopapposaurus is a genus of prosauropod dinosaur from the Early Jurassic Cañón del Colorado Formation of San Juan, Argentina. It was similar to Massospondylus. Four partial skeletons with two partial skulls are known.
 W
WAlligatorellus is a genus of atoposaurid crocodyliform found in France that was related to Atoposaurus.
 W
WAnglosuchus is an extinct genus of pholidosaurid mesoeucrocodylian. Both species of Anglosuchus were originally assigned to the genus Steneosaurus by Richard Owen in 1884, but were later placed in the new genus. It was once thought to be a teleosaurid but later reassigned to the family Pholidosauridae.
 W
WArdeosaurus is an extinct genus of basal lizards, known from fossils found in the Late Jurassic Solnhofen Plattenkalk of Bavaria, southern Germany. It was originally thought to have been a species of Homeosaurus.
 W
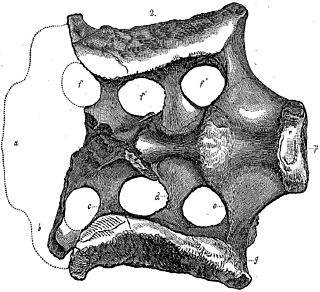
WAtlantosaurus is a dubious genus of sauropod dinosaur. It contains a single species, Atlantosaurus montanus, from the upper Morrison Formation of Colorado, United States. Atlantosaurus was the first sauropod to be described during the infamous 19th century Bone Wars, during which scientific methodology suffered in favor of pursuit of academic acclaim.
 W
WAtoposaurus is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph. It is the type genus of the family Atoposauridae. Fossils have been found that were Late Jurassic in age from two distinct species in France and Germany.
 W
WAttenborosaurus is an extinct genus of pliosaurid from the Early Jurassic of Dorset, England. The type species is A. conybeari. The genus is named after David Attenborough, the species after William Conybeare.
 W
WBavarisauridae is an extinct family of basal lizards found in the Solnhofen limestone near Bavaria, Germany. Two genera are recognized: Bavarisaurus and Schoenesmahl. Up until 2017, Bavarisaurus was the only genus in the family, and it might be the only true bavarisaurus since Schoenesmahl might have instead been part of the Eichstaettisauridae.
 W
WBellusaurus was a small short-necked sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic which measured about 4.8 metres (16 ft) long. Its fossils were found in Shishugou Formation rocks in the northeastern Junggar Basin in China.
 W
WBienosaurus is a dubious genus of thyreophoran dinosaur from the Lower Jurassic Lower Lufeng Formation in Yunnan Province in China.
 W
WCaypullisaurus is an extinct genus of large platypterygiine ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur from the Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous of Argentina. Its holotype was collected from the Vaca Muerta Formation of Cerro Lotena, Neuquen, dating to the early Tithonian stage of the Late Jurassic, about 150 million years ago. Caypullisaurus was first named by Marta Fernández in 1997 and the type species is Caypullisaurus bonapartei. It is a member of the family Ophthalmosauridae, and closely related to Platypterygius and Brachypterygius. In 2012, Caypullisaurus was found to be most closely related to Athabascasaurus and "Platypterygius" australis, and to nest within the subfamily Platypterygiinae.
 W
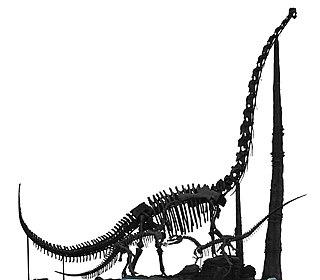
WChuanjiesaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaurs from the middle Jurassic Period. They lived in what is now China. The type species, Chuanjiesaurus anaensis, was first described by Fang, Pang, Lü, Zhang, Pan, Wang, Li and Cheng in 2000. Fossils of the species were found in the village of Chuanjie, Lufeng County, Yunnan Province, and are named after the location where the fossils were discovered. Holtz gave a length of 25 meters.
 W
WClevosaurus (CLEE-vo-SORE-us) is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian reptile from the Triassic and the Jurassic periods of Nova Scotia, Great Britain,, Yunnan and Brazil. Clevosaurus was extremely similar to the modern tuatara in almost every way; the two genera differ in only certain features of the teeth and skull anatomies, as well as size. Clevosaurus was smaller than the modern tuatara. Clevosaurus possibly ate plants as well as insects, as suggested by the form of the teeth. Fossils of Clevosaurus, as well as other sphenodontians, early mammals and dinosaurs have been found in ancient cave systems of Great Britain. Clevosaurus is now believed to have had Pangaean distribution. In regards to its Pangaean distribution, C. hadroprodon is the oldest record of a sphenodontian from Gondwana.
 W
WCrocodilaemus is an extinct genus of pholidosaurid mesoeucrocodylian. Fossils have been found from the Cerin Lagerstätte of eastern France and are of late Kimmeridgian age. The depositional environment in Cerin at the time is thought to have been the bottom of a lagoon that was enclosed by an emergent reef complex, evidence of the shallow tropical sea that covered much of western Europe during the Jurassic period.
 W
WCryopterygius is an extinct genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur known from the uppermost Jurassic of Central Spitsbergen, Norway. The type species, Cryopterygius kristiansenae , is known from a single, but largely complete specimen from the Slottsmøya Member of the Agardhfjellet Formation. With a total length of 5.0–5.5 metres (16.4–18.0 ft), it is a large ichthyosaur. A second species, C. kielanae, was found in the Kcynia Formation from the Late Jurassic of Poland. It is smaller than the type species, with a length of 3.5–4 metres (11–13 ft).
 W
WCryptoclididae is a family of medium-sized plesiosaurs that existed from the middle Jurassic to the early Cretaceous period. They had long necks, broad and short skulls and densely packed teeth. They fed on small soft-bodied preys such as small fish and crustaceans.
 W
WCryptosaurus is a dubious genus of dinosaur known from a partial femur from the Late Jurassic of England. The sole species is Cryptosaurus eumerus.
 W
WDaanosaurus was a genus of dinosaur. It was a brachiosaurid sauropod which lived during the Late Jurassic. It lived in what is now China, and was similar to Bellusaurus. When it was described, Daanosaurus was placed in the Bellusaurinae, a sub-family of Brachiosauridae that Dong Zhiming had raised in 1990 to house Bellusaurus, or the Klamelisauridae, used to house Klamelisaurus, possibly Dannosaurus and Abrosaurus. More recently, other authors have placed Daanosaurus in the Eusauropoda.
 W
WDinochelys is an extinct genus of paracryptodiran turtle from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation.
 W
WDysalotosaurus is a genus of herbivorous iguanodontian dinosaur. It was a dryosaurid iguanodontian, and its fossils have been found in late Kimmeridgian-age rocks of the Tendaguru Formation, Tanzania. The type and only species of the genus is D. lettowvorbecki. This species was named by Josef Felix Pompeckj in 1920 in honor of the Imperial German Army Officer, Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck. For much of the 20th century the species was referred to the related and approximately contemporary genus Dryosaurus, but newer studies reject this synonymy.
 W
WHallopodidae is a family of Late Jurassic crocodylomorphs. They have been recovered as the closest relatives of the Crocodyliformes.
 W
WHomoeosaurus is an extinct genus of sphenodont reptile. It was found in limestone in Bavaria, Germany, as well as in France and the United Kingdom. It was related to the modern tuatara, though it was a considerably more gracile. There were several species varying greatly in size and morphology.
 W
WOenosaurus is an extinct genus of sphenodontian reptile from the Late Jurassic of Germany.
 W
WPalaeopleurosaurus is an extinct genus of diapsid reptiles belonging to the group Sphenodontia.
 W
W"Rhamphocephalus" is an extinct genus of fossil reptile from the Middle Jurassic Great Oolite Group of Gloucestershire, England. The name was erected as a genus of pterosaur and became a 'wastebasket taxon' for British Jurassic pterosaur remains until a recent revision. Rhamphocephalus comprises several named species, two of which are pterosaurian, but the type species - "R. prestwichi" - is based on remains now identified as a thalattosuchian. Because it is poorly preserved and lacks features that distinguish it from other thalattosuchians, "R. prestwichi" is considered an invalid species and the genus Rhamphocephalus is a nomen dubium. Reassessments of other "Rhamphocephalus" species suggest they are also undiagnostic to species level, although they have properties allowing referral to some Jurassic pterosaur groups.
 W
WSericodon is an extinct genus of teleosaurid crocodyliform from the Late Jurassic (Tithonian) of Germany and Switzerland. The genus contains a single species, S. jugleri.
 W
WSinaspideretes is an extinct genus of turtle from the Late Jurassic of China. It is considered the earliest and most basal representative of the Trionychia.
 W
WStegopodus was a new ichnogenus erected in 1998 for the second set of stegosaur tracks from the Morrison Formation. The tracks were found near Arches National Park, also in Utah. Unlike the first, this trackway preserved traces of the forefeet. Fossil remains indicate that stegosaurs have five digits on the forefeet and three weight-bearing digits on the hind feet. From this, paleontologists were able to successfully predict the appearance of stegosaur tracks in 1990, six years in advance of the first actual discovery of Morrison stegosaur tracks. Since the erection of Stegopodus, more trackways have been found, however none have preserved traces of the front feet, and stegosaur traces remain rare.