 W
WBile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts.
 W
WApocholic acid is an unsaturated bile acid first characterized in the 1920s. It has questionable carcinogenic activity as experimentally, sarcomas were induced in mice with injection of desoxycholic acid.
 W
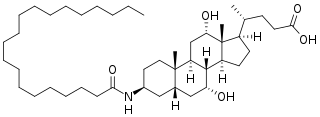
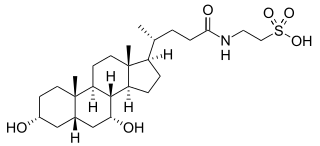
WAramchol is an investigational drug being developed by Galmed Pharmaceuticals as a first-in-class, potentially disease modifying treatment for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH, a more advanced condition of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
 W
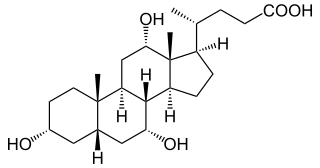
WChenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid. Salts of this carboxylic acid are called chenodeoxycholates. Chenodeoxycholic acid is one of the main bile acids. It was first isolated from the bile of the domestic goose, which gives it the "cheno" portion of its name.
 W
WCholic acid, also known as 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid is a primary bile acid that is insoluble in water, it is a white crystalline substance. Salts of cholic acid are called cholates. Cholic acid, along with chenodeoxycholic acid, is one of the two major bile acids produced by the liver, where it is synthesized from cholesterol. These two major bile acids are roughly equal in concentration in humans. Derivatives are made from cholyl-CoA, which exchanges its CoA with either glycine, or taurine, yielding glycocholic and taurocholic acid, respectively.
 W
WDehydrocholic acid is a synthetic bile acid, manufactured by the oxidation of cholic acid. It acts as a hydrocholeretic, increasing bile output to clear increased bile acid load.
 W
WDeoxycholic acid, also known as cholanoic acid, Kybella, Celluform Plus, Belkyra, and 3α,12α-dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid, is a bile acid. Deoxycholic acid is one of the secondary bile acids, which are metabolic byproducts of intestinal bacteria. The two primary bile acids secreted by the liver are cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. Bacteria metabolize chenodeoxycholic acid into the secondary bile acid lithocholic acid, and they metabolize cholic acid into deoxycholic acid. There are additional secondary bile acids, such as ursodeoxycholic acid. Deoxycholic acid is soluble in alcohol and acetic acid. When pure, it comes in a white to off-white crystalline powder form.
 W
WGlycochenodeoxycholic acid is a bile salt formed in the liver from chenodeoxycholic acid and glycine, usually found as the sodium salt. It acts as a detergent to solubilize fats for absorption.
 W
WGlycocholic acid, or cholylglycine, is a crystalline bile acid involved in the emulsification of fats. It occurs as a sodium salt in the bile of mammals. It is a conjugate of cholic acid with glycine. Its anion is called glycocholate.
 W
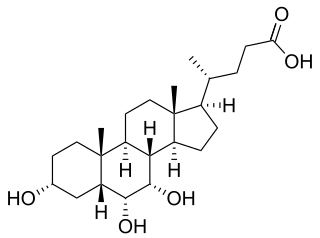
WGlycodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid derived from deoxycholic acid and glycine. Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state.
 W
WHyocholic acid or 3α,6α,7α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid is a bile acid found as one of the main forms in pig, and at low concentrations in other species including humans. Hyocholic acid differs from the primary bile acids found in humans by having a third hydroxyl group in the α-conformation at the 6-position, unlike cholic acid, which has a 12-hydroxyl, and chenodeoxycholic acid which has neither a 6- or 12-hydroxyl. It also differs from the muricholic acids found in rodents, as they are 6β-hydroxylated, and can have the 7-hydroxyl in either the α- or β positions, forming α- or β-muricholic acids.
 W
WHyodeoxycholic acid, also known as 3α,6α-Dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid or HDCA, is a secondary bile acid, one of the metabolic byproducts of intestinal bacteria. It differs from deoxycholic acid in that the 6α-hydroxyl is in the 12 position in the former. The 6α-hydroxyl group makes HDCA a hydrophilic acid, a property it shares with hyocholic acid. HDCA is present in mammalian species in different proportions. It is the main acid constituent of hog bile, and for this reason it was used industrially as precursor for steroid synthesis before total synthesis became practical.
 W
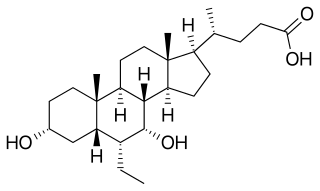
WLithocholic acid, also known as 3α-hydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid or LCA, is a bile acid that acts as a detergent to solubilize fats for absorption. Bacterial action in the colon produces LCA from chenodeoxycholic acid by reduction of the hydroxyl functional group at carbon-7 in the "B" ring of the steroid framework.
 W
WObeticholic acid, is a semi-synthetic bile acid analogue which has the chemical structure 6α-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid. It is used as a drug to treat primary biliary cholangitis, and is undergoing development for several other liver diseases and related disorders. Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. hold the worldwide rights to develop OCA outside Japan and China, where it is licensed to Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma.
 W
WSeHCAT is a drug used in a clinical test to diagnose bile acid malabsorption.
 W
WTaurochenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid formed in the liver of most species, including humans, by conjugation of chenodeoxycholic acid with taurine. It is secreted into bile and then into intestine. It is usually ionized at physiologic pH, although it can be crystallized as the sodium salt. It acts as detergent to solubilize fats in the small intestine and is itself absorbed by active transport in the terminal ileum. It is used as a cholagogue and choleretic.
 W
WTaurocholic acid, known also as cholaic acid, cholyltaurine, or acidum cholatauricum, is a deliquescent yellowish crystalline bile acid involved in the emulsification of fats. It occurs as a sodium salt in the bile of mammals. It is a conjugate of cholic acid with taurine. In medical use, it is administered as a cholagogue and choleretic.
 W
WTaurodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid.
 W
WTaurolithocholic acid is a bile acid.
 W
WTauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) is an ambiphilic bile acid. It is the taurine conjugate form of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). Humans are found to have trace amounts of TUDCA. However, bears contain large amounts of TUDCA in their bile; UDCA and conjugates comprise about 47% of the bile in American black bears and up to 76% in Asiatic bears. TUDCA has been used in ancient Asian pharmacopoeias for its supposed beneficial effects. UDCA is produced in several countries for the treatment of gallstones and liver cirrhosis. It is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration, in the U.S. while UDCA is approved in the United States for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis Ongoing research is finding TUDCA has diminishing apoptotic effects, with potential application in heart disease, Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, and stroke. Recently, TUDCA has been found to have protective effects in the eye, especially concerning retinal degenerative disorders.
 W
WUrsodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), also known as ursodiol, is a secondary bile acid, produced in humans and most other species from metabolism by intestinal bacteria. It is synthesized in the liver in some species, and was first identified in bear bile, which is the derivation of its name Ursus. In purified form, it has been used to treat or prevent several diseases of the liver or bile ducts.