 W
WCimolodonta is a taxon of extinct mammals that lived from the Cretaceous to the Eocene. They were some of the more derived members of the extinct order Multituberculata. They probably lived something of a rodent-like existence until their ecological niche was assumed by true rodents. The more basal multituberculates are found in a different suborder, "Plagiaulacida".
 W
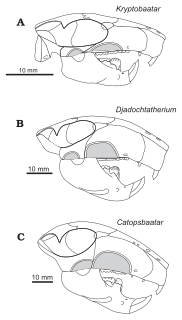
WCatopsbaatar is a genus of multituberculate, an extinct order of rodent-like mammals. It lived in what is now Mongolia during the late Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 72 million years ago. The first fossils were collected in the early 1970s, and the animal was named as a new species of the genus Djadochtatherium in 1974, D. catopsaloides. The specific name refers to the animal's similarity to the genus Catopsalis. The species was moved to the genus Catopsalis in 1979, and received its own genus in 1994. Five skulls, one molar, and one skeleton with a skull are known; the last is the genus' most complete specimen. Catopsbaatar was a member of the family Djadochtatheriidae.
 W
WChulsanbaatar is a genus of mammal from the Cretaceous of Mongolia. It lived during the Mesozoic, also known as the "age of the dinosaurs." This small creature was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata and is within the suborder Cimolodonta. The genus Chulsanbaatar was named by Kielan-Jaworowska Z. in 1974.
 W
WCimexomys is an extinct North American mammal that lived from the Upper Cretaceous to the Paleocene. For a while, it shared the world with dinosaurs, but outlived them. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata and lies within the suborder Cimolodonta. It is perhaps a member of the Paracimexomys group, though it is not certain.
 W
WCimolomys is a mammal genus from the Upper Cretaceous of North America. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Cimolomyidae.
 W
WCorriebaatar is the type and only genus of Corriebaataridae, a family of multituberculate mammals. It contains the single species Corriebaatar marywaltersae and represents the first evidence of Australian multituberculates Fossils found in the Wonthaggi Formation date back to the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous.
 W
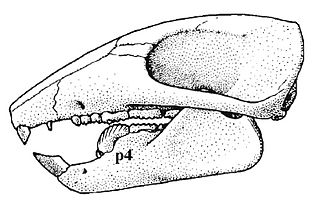
WDjadochtatheriidae is a family of fossil mammals within the extinct order Multituberculata. Remains are known from the Upper Cretaceous of Central Asia. These animals lived during the Mesozoic, also known as the "age of the dinosaurs". This family is part of the suborder of Cimolodonta. The taxon Djadochtatheriidae was named by Z. Kielan-Jaworowska and J. H. Hurum in 1997.
 W
WDjadochtatherioidea is a group of extinct mammals known from the upper Cretaceous of Central Asia. They were members of an also extinct order called Multituberculata. These were generally somewhat rodent-like creatures, who scurried around during the "age of the dinosaurs", though nonetheless very ecologically diverse; several were jerboa-like hoppers, while others like Mangasbaatar were large sized and fossorial. Unusually for multituberculates, some of this group are represented by very good remains. All upper Cretaceous Mongolian multituberculates are included with one exception, the genus Buginbaatar.
 W
WDjadochtatherium is a mammal genus that lived in Mongolia during the Upper Cretaceous. It coexisted with some of the late dinosaurs. This animal was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. It is within the suborder of Cimolodonta, and a member of the family Djadochtatheriidae. It was named by G. G. Simpson in 1925, the name meaning "Djadokhta beast".
 W
WKamptobaatar is a Mongolian mammal genus from the Upper Cretaceous. It lived at the same time as the later dinosaurs. This animal was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Sloanbaataridae.
 W
WKogaionon is a mammal genus from the Upper Cretaceous of Romania. It lived in Transylvania the same time as some of the last non-avian dinosaurs and was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. It was named after Kogaionon, the holy mountain of the ancient Dacians. It lies within the suborder Cimolodonta and the family Kogaionidae. The genus Kogaionon was named by Rădulescu R. and Samson P. in 1996.
 W
WKryptobaatar and also known as Gobiaatar, Gobibaatar or Tugrigbaatar is an extinct mammalian genus dating from the Upper Cretaceous Period and identified in Central Asia. This animal was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta, and was a member of the family Djadochtatheriidae. It lived contemporaneously with some of the dinosaurs. Its skull had a length of perhaps 3 cm.
 W
WLambdopsalis bulla is an extinct multituberculate mammal from the Late Paleocene of China and Mongolia. It is placed within the suborder Cimolodonta and is a member of the superfamily Taeniolabidoidea. Fossil remains have been found in the Late Paleocene Nomogen and Khashat Formations in Nao-mugen and Bayn Ulan of China and Mongolia.
 W
WMeniscoessus is a genus of extinct mammal from the Upper Cretaceous Period of what is now North America. It lived toward the end of the "age of the dinosaurs" and was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata. It lies within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Cimolomyidae.
 W
WNemegtbaatar is a genus of mammal from the Upper Cretaceous Period of what is now Mongolia. It existed in the company of much larger dinosaurs, found together in the Nemegt Basin. This creature was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata. It is within the suborder Cimolodonta and is a member of the superfamily Djadochtatherioidea. It was a hopping, gerboa-like species.
 W
WTaeniolabis is a genus of extinct multituberculate mammal from the Paleocene of North America.
 W
WTombaatar is a mammal genus that existed during the Mongolian Upper Cretaceous period. It co-existed with some of the late dinosaurs. This animal was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata, within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Djadochtatheriidae. The genus Tombaatar was named by Rougier G.W., Novacek M. and Dashzeveg D. in 1997.
 W
WYubaatar is a genus of multituberculate, an extinct order of rodent-like mammals, which lived in what is now China during the Late Cretaceous. The first specimen was discovered in the Qiupa Formation of Luanchuan County, in the Henan Province. The specimen consists of a partial skeleton with a nearly complete skull, and was made the holotype of the new genus and species Yubaartar zhongyuanensis by the Chinese palaeontologist Li Xu and colleagues in 2015. The generic name consists of the word Yu, which is the pinyin spelling of the Chinese character for the Henan Province, and the Mongolian word baatar, which means "hero", a word commonly used as suffix in the names of Asian multituberculates. The specific name comes from Zhongyuan, an ancient name for the geographic area of the province.