 W
WThe Arctic fox, also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Arctic tundra biome. It is well adapted to living in cold environments, and is best known for its thick, warm fur that is also used as camouflage. In the wild, most individuals do not live past their first year but some exceptional ones survive up to 11 years. Its body length ranges from 46 to 68 cm, with a generally rounded body shape to minimize the escape of body heat.
 W
WThe Arctic hare is a species of hare, which is highly adapted to living in the Arctic tundra and other icy biomes. The Arctic hare survives with shortened ears and limbs,a small nose,fat that makes up close to 20% of its body, and a thick coat of fur. It usually digs holes in the ground or under snow to keep warm and to sleep. Arctic hares look like rabbits but have shorter ears, are taller when standing and, unlike rabbits, can thrive in extreme cold. They can travel together with many other hares, sometimes huddling with dozens or more, but are usually found alone, sometimes taking more than one partner. The Arctic hare can run up to 60 kilometres per hour (40 mph).
 W
WThe Arctic ringed seal is a subspecies of ringed seals. Arctic ringed seals inhabit the Arctic Ocean, and are the most abundant and wide-ranging seal in the Northern Hemisphere. The ringed seal species is the smallest true seal, and gets its name from a distinctive patterning of light spots on dark grey colored fur. The ringed seal is commonly preyed upon by Polar bears, Arctic foxes, and Killer whales. Population estimates and survival rates are unknown, but average life expectancy is 15-28 years. Ringed seals have long been a component of the diet of indigenous people of the Arctic. Arctic ringed seals have been listed as threatened on the Endangered Species Act since 2012, and increasingly face loss of their habitat due to shrinking ice and snow cover.
 W
WThe beluga whale is an Arctic and sub-Arctic cetacean. It is one of two members of the family Monodontidae, along with the narwhal, and the only member of the genus Delphinapterus. It is also known as the white whale, as it is the only cetacean of this colour; the sea canary, due to its high-pitched calls; and the melonhead, though that more commonly refers to the melon-headed whale, which is an oceanic dolphin.
 W
WThe common minke whale or northern minke whale is a species of minke whale within the suborder of baleen whales.
 W
WThe Greenland wolf is a subspecies of gray wolf that is native to Greenland. Historically, it was heavily persecuted, but today it is fully protected and about 90% of the wolf's range falls within the boundaries of the Northeast Greenland National Park.
 W
WThe harp seal also known a saddleback seal or Greenland Seal, is a species of earless seal, or true seal, native to the northernmost Atlantic Ocean and Arctic Ocean. Originally in the genus Phoca with a number of other species, it was reclassified into the monotypic genus Pagophilus in 1844. In Latin, its scientific name translates to "ice-lover from Greenland," and its taxonomic synonym, Phoca groenlandica translates to "Greenlandic seal."
 W
WThe hooded seal is a large phocid found only in the central and western North Atlantic, ranging from Svalbard in the east to the Gulf of St. Lawrence in the west. The seals are typically silver-grey or white in color, with black spots that vary in size covering most of the body. Hooded seal pups are known as "blue-backs" because their coats are blue-grey on the back with whitish bellies, though this coat is shed after 14 months of age when the pups molt.
 W
WThe humpback whale is a species of baleen whale. It is one of the larger rorqual species, with adults ranging in length from 12–16 m (39–52 ft) and weighing around 25–30 metric tons. The humpback has a distinctive body shape, with long pectoral fins and a knobbly head. It is known for breaching and other distinctive surface behaviors, making it popular with whale watchers. Males produce a complex song lasting 10 to 20 minutes, which they repeat for hours at a time. All the males in a group will produce the same song, which is different each season. Its purpose is not clear, though it may help induce estrus in females.
 W
WA lemming is a small rodent, usually found in or near the Arctic in tundra biomes. Lemmings make up the subfamily Arvicolinae together with voles and muskrats, which form part of the superfamily Muroidea, which also includes rats, mice, hamsters, and gerbils. In popular culture, a longstanding myth holds that they commit mass suicide.
 W
WThe muskox, also spelled musk ox and musk-ox, is an Arctic hoofed mammal of the family Bovidae, noted for its thick coat and for the strong odor emitted by males during the seasonal rut, from which its name derives. This musky odor is used to attract females during mating season. Its Inuktitut name "umingmak" translates to "the bearded one". Its Woods Cree names "mâthi-môs" and "mâthi-mostos" translate to "ugly moose" and "ugly bison", respectively. Muskoxen primarily live in Greenland and the Canadian Arctic of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, with introduced populations in the American state of Alaska, the Canadian territory of Yukon, the Scandinavian Peninsula, and Siberia.
 W
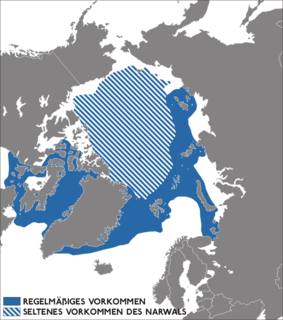
WThe narwhal or narwhale is a medium-sized toothed whale that possesses a large "tusk" from a protruding canine tooth. It lives year-round in the Arctic waters around Greenland, Canada, and Russia. It is one of two living species of whale in the family Monodontidae, along with the beluga whale. The narwhal males are distinguished by a long, straight, helical tusk, which is an elongated upper left canine. The narwhal was one of many species described by Carl Linnaeus in his publication Systema Naturae in 1758.
 W
WThe northern collared lemming or Nearctic collared lemming, sometimes called the Peary Land collared lemming in Canada, is a small North American lemming. At one time, it was considered to be a subspecies of the Arctic lemming. Some sources believe several other species of collared lemmings found in North America are actually subspecies of D. groenlandicus.
 W
WThe polar bear is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear species, as well as the largest extant predatory carnivore. A boar weighs around 350–700 kg (770–1,540 lb), while a sow is about half that size. Although it is the sister species of the brown bear, it has evolved to occupy a narrower ecological niche, with many body characteristics adapted for cold temperatures, for moving across snow, ice and open water, and for hunting seals, which make up most of its diet. Although most polar bears are born on land, they spend most of their time on the sea ice. Their scientific name means "maritime bear" and derives from this fact. Polar bears hunt their preferred food of seals from the edge of sea ice, often living off fat reserves when no sea ice is present. Because of their dependence on the sea ice, polar bears are classified as marine mammals.
 W
WThe reindeer, also known as the caribou in North America, is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, sub-Arctic, tundra, boreal, and mountainous regions of northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. This includes both sedentary and migratory populations. Rangifer herd size varies greatly in different geographic regions. The Taimyr herd of migrating Siberian tundra reindeer in Russia is the largest wild reindeer herd in the world, varying between 400,000 and 1,000,000. What was once the second largest herd is the migratory boreal woodland caribou George River herd in Canada, with former variations between 28,000 and 385,000. As of January 2018, there are fewer than 9,000 animals estimated to be left in the George River herd, as reported by the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. The New York Times reported in April 2018 of the disappearance of the only herd of southern mountain caribou in the contiguous United States with an expert calling it "functionally extinct" after the herd's size dwindled to a mere three animals.
 W
WThe ringed seal, is an earless seal inhabiting the Arctic and sub-Arctic regions. The ringed seal is a relatively small seal, rarely greater than 1.5 m in length, with a distinctive patterning of dark spots surrounded by light grey rings, hence its common name. It is the most abundant and wide-ranging ice seal in the Northern Hemisphere: ranging throughout the Arctic Ocean, into the Bering Sea and Okhotsk Sea as far south as the northern coast of Japan in the Pacific, and throughout the North Atlantic coasts of Greenland and Scandinavia as far south as Newfoundland, and include two freshwater subspecies in northern Europe. Ringed seals are one of the primary prey of polar bears and killer whales, and have long been a component of the diet of indigenous people of the Arctic.
 W
WThe walrus is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the family Odobenidae and genus Odobenus. This species is subdivided into two subspecies: the Atlantic walrus, which lives in the Atlantic Ocean, and the Pacific walrus, which lives in the Pacific Ocean.