 W
WAcral necrosis is a symptom common in bubonic plague. The striking black discoloration of skin and tissue, primarily on the extremities ("acral"), is commonly thought to have given rise to the name "Black Death," associated both with the disease and the pandemic which occurred in the 14th century. The term in fact came from the figural sense of "black", that is ghastly, lugubrious or dreadful.
 W
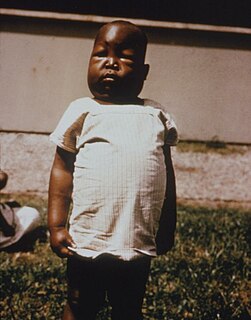
WAnasarca is a severe and generalized form of edema, with subcutaneous tissue swelling throughout the body. Unlike edema, which almost everyone will experience at some time and can be relatively benign, Anasarca is a pathological process reflecting a severe disease state and can involve the cavities of the body in addition to the tissues.
 W
WA bubo is adenitis or inflammation of the lymph nodes and is an example of reactive lymphadenopathy.
 W
WCyanosis is the bluish or purplish discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes due to the tissues near the skin surface having low oxygen saturation. Based on Lundsgaard and Van Slyke's work, it is classically described as occurring if 5.0 g/dL of deoxyhemoglobin or greater is present. This was based on an estimate of capillary saturation based on a mean of arterial versus peripheral venous blood gas measurements. Since estimation of hypoxia is usually now based either on arterial blood gas measurement or pulse oximetry, this is probably an overestimate, with evidence that levels of 2.0 g/dL of deoxyhemoglobin may reliably produce cyanosis. Since, however, the presence of cyanosis is dependent upon there being an absolute quantity of deoxyhemoglobin, the bluish color is more readily apparent in those with high hemoglobin counts than it is with those with anemia. Also, the bluer the color, the more difficult it is to detect on deeply pigmented skin. When signs of cyanosis first appear, such as on the lips or fingers, intervention should be made within 3–5 minutes because a severe hypoxia or severe circulatory failure may have induced the cyanosis.
 W
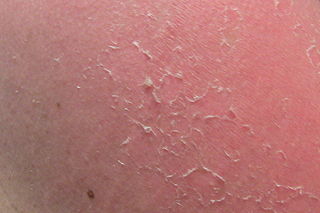
WDesquamation, commonly called skin peeling, is the shedding of the outermost membrane or layer of a tissue, such as the skin. The term is from Latin desquamare 'to scrape the scales off a fish'.
 W
WElephantiasis is the enlargement and hardening of limbs or body parts due to tissue swelling. It is characterised by edema, hypertrophy, and fibrosis of skin and subcutaneous tissues, due to obstruction of lymphatic vessels. It may affect the genitalia. The term elephantiasis is often used in reference to parasitic worm infections, but may refer to a variety of diseases where parts of a person's body swell to massive proportions.
 W
WEnanthem or enanthema is a rash on the mucous membranes. It is characteristic of patients with viral infections causing hand foot and mouth disease, measles, and sometimes chicken pox, or COVID-19. In addition, bacterial infections such as Scarlet fever may also be a cause of enanthema. The aforementioned diseases usually present with exanthema and enanthema.
 W
WErythema is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology include nervous blushes.
 W
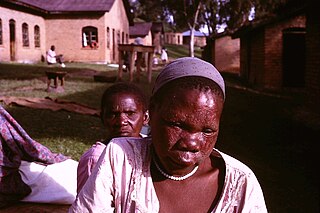
WFlushing is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation between them, from blushing, which is milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or ears, and generally assumed to reflect emotional stress, such as embarrassment, anger, or romantic stimulation. Flushing is also a cardinal symptom of carcinoid syndrome—the syndrome that results from hormones being secreted into systemic circulation.
 W
WLeonine facies is a facies that resembles that of a lion. It is seen in multiple conditions and has been classically described for Lepromatous leprosy as well as Paget's disease of bone. It is a dermatological symptom, with characteristic facial features that are visible on presentation, and is useful for focusing on differential diagnosis.
 W
WPallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eyes on physical examination.
 W
WPeripheral edema is edema in tissues perfused by the peripheral vascular system, usually in the lower limbs. In the most dependent parts of the body, it may be called dependent edema.
 W
WA petechia is a small (1–2 mm) red or purple spot on the skin or conjunctiva, caused by a minor bleed from broken capillary blood vessels. The word is derived from Latin 'petigo', meaning ‘scab' or 'eruption’.
 W
WA rash is a change of the human skin which affects its color, appearance, or texture.
 W
WSplinter hemorrhages are tiny blood clots that tend to run vertically under the nails. Splinter hemorrhages are not specific to any particular condition, and can be associated with subacute infective endocarditis, scleroderma, trichinosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic nails, antiphospholipid syndrome, haematological malignancy, and trauma. At first they are usually plum-colored, but then darken to brown or black in a couple of days. In certain conditions, clots can migrate from the affected heart valve and find their way into various parts of the body. If this happens in the finger, it can cause damage to the capillaries resulting in a splinter hemorrhage.