 W
WThe cloacal membrane is the membrane that covers the embryonic cloaca during the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
 W
WA genital tubercle or phallic tubercle is a body of tissue present in the development of the reproductive system. It forms in the ventral, caudal region of mammalian embryos of both sexes, and eventually develops into a primordial phallus. In the human fetus, the genital tubercle develops around week 4 of gestation, and by week 9 becomes recognizably either a clitoris or penis. This should not be confused with the sinus tubercle which is a proliferation of endoderm induced by paramesonephric ducts. Even after the phallus is developed, the term genital tubercle remains, but only as the terminal end of it, which develops into either the glans penis or the glans clitoridis.
 W
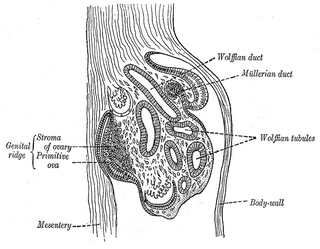
WIn embryology, the gonadal ridge is the precursor to the gonads. The gonadal ridge initially consists mainly of mesenchyme and cells of underlying mesonephric origin. Once oogonia enter this area they attempt to associate with these somatic cells. Development proceeds and the oogonia become fully surrounded by a layer of cells.
 W
WThe paired gubernacula are embryonic structures which begin as undifferentiated mesenchyme attaching to the caudal end of the gonads.
 W
WIntermediate mesoderm or intermediate mesenchyme is a narrow section of the mesoderm located between the paraxial mesoderm and the lateral plate of the developing embryo. The intermediate mesoderm develops into vital parts of the urogenital system, as well as the reproductive system.
 W
WThe labioscrotal swellings are paired structures in the human embryo that represent the final stage of development of the caudal end of the external genitals before sexual differentiation. In both males and females, the two swellings merge:In the female, they become the posterior labial commissure. The sides of the genital tubercle grow backward as the genital swellings, which ultimately form the labia majora; the tubercle itself becomes the mons pubis. In contrast, the labia minora are formed by the urogenital folds. In the male, they become the scrotum.
 W
WLateral plate mesoderm is a type of mesoderm that is found at the periphery of the embryo.
 W
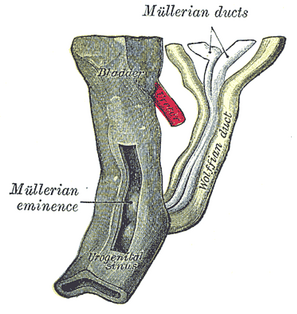
WThe mesonephric duct is a paired organ found in mammals including humans during embryogenesis. Male urogenital structures that arise from the mesonephric duct include the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles.
 W
WThe mesonephros is one of three excretory organs that develop in vertebrates. It serves as the main excretory organ of aquatic vertebrates and as a temporary kidney in reptiles, birds, and mammals. The mesonephros is included in the Wolffian body after Caspar Friedrich Wolff who described it in 1759.
 W
WParamesonephric ducts are paired ducts of the embryo that run down the lateral sides of the urogenital ridge and terminate at the sinus tubercle in the primitive urogenital sinus. In the female, they will develop to form the fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and the upper one-third of the vagina.
 W
WIn embryology, the primordial phallus refers to the clitoris of a female or the penis in the male, particularly during fetal development of the urinary and reproductive organs, before sexual differentiation is evident. This is also the case for the immature male analog, the immature glans penis.
 W
WThe urachus is a fibrous remnant of the allantois, a canal that drains the urinary bladder of the fetus that joins and runs within the umbilical cord. The fibrous remnant lies in the space of Retzius, between the transverse fascia anteriorly and the peritoneum posteriorly.
 W
WThe urogenital sinus is a part of the human body only present in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs. It is the ventral part of the cloaca, formed after the cloaca separates from the anal canal during the fourth to seventh weeks of development.
 W
WVaginal anomalies are abnormal structures that are formed during the prenatal development of the female reproductive system and are rare congenital defects that result in an abnormal or absent vagina. When present, they are often found with uterine, skeletal and urinary abnormalities. This is because these structures, like the vagina, are most susceptible to disruption during crucial times of organ-genesis. Many of these defects are classified under the broader term Müllerian duct anomalies. Müllerian duct anomalies are caused by a disturbance during the embryonic time of genitourinary development. The other isolated incidents of vaginal anomalies can occur with no apparent cause. Oftentimes vaginal anomalies are part of a cluster of defects or syndromes. In addition, inheritance can play a part as can prenatal exposure to some teratogens. Many vaginal anomalies are not detected at birth because the external genitalia appear to be normal. Other organs of the reproductive system may not be affected by an abnormality of the vagina. The uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries can be functional despite the presence of a defect of the vagina and external genitalia. A vaginal anomaly may not affect fertility. Though it depends on the extent of the vaginal defect, it is possible for conception to occur. In instances where a functional ovary exists, IVF may be successful. Functioning ovaries in a woman with a vaginal defect allows the implantation of a fertilized ovum into the uterus of an unaffected gestational carrier. A successful conception and can occur. Vaginal length varies from 6.5 to 12.5 cm. Since this is slightly shorter than older descriptions, it may impact the diagnosis of women with vaginal agenesis or hypoplasia who may unnecessarily be encouraged to undergo treatment to increase the size of the vagina. Vaginal anomalies may cause difficulties in urination, conception, pregnancy, impair sex. Psychosocial effects can also exist.
 W
WThe vaginal process is an embryonic developmental outpouching of the parietal peritoneum. It is present from around the 12th week of gestation, and commences as a peritoneal outpouching.