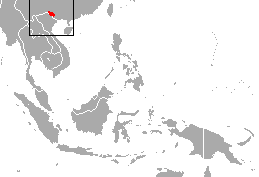
 W
WThe eastern black crested gibbon, also known as the Cao-vit black crested gibbon or the Cao-vit crested gibbon, is a species of gibbon from southeast China and northern Vietnam.
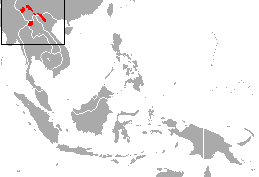 W
WThe black crested gibbon is an endangered species of gibbon found in China, Laos, and northern Vietnam, with four subspecies.
 W
WThe Hainan black-crested gibbon or Hainan gibbon, is a species of gibbon found only on Hainan Island, China. It was formerly considered a subspecies of the eastern black crested gibbon from Hòa Bình and Cao Bằng provinces of Vietnam and Jingxi County in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. Molecular data, together with morphology and call differences, suggest it is a separate species. Its habitat consists of broad-leaved forests and semi-deciduous monsoon forests. It feeds on ripe, sugar-rich fruit, such as figs and, at times, leaves, and insects.
 W
WThe eastern hoolock gibbon is a primate from the gibbon family, Hylobatidae. It is one of three species of hoolock gibbon. This species is found in extreme eastern corner of Assam and parts of Arunachal Pradesh, Myanmar east of the Chindwin River, such as the Mahamyaing Wildlife Sanctuary, and in south west Yunnan of China. The other hoolock gibbon, the western hoolock, occurs farther to the west. Indian records for the eastern species may actually represent the western hoolock.
 W
WThe northern white-cheeked gibbon is a species of gibbon native to South East Asia. It is closely related to the southern white-cheeked gibbon, with which it was previously considered conspecific. The females of the two species are virtually indistinguishable in appearance.
 W
WThe François' langur, also known as the Francois' leaf monkey, Tonkin leaf monkey, or white side-burned black langur is a species of lutung and the type species of its species group. It is one of the least studied of the species belonging to the Colobinae subfamily.
 W
WThe white-headed langur is a critically endangered langur. Two subspecies are recognized: T. p. poliocephalus in Cát Bà Island, Vietnam, and T. p. leucocephalus in Guangxi, China. The former, often known as the golden-headed or Cat Ba langur, is among the rarest primates in the world, and possibly the rarest primate in Asia, with population size estimated at less than 70 individuals.
 W
WThe Japanese macaque, also known as the snow monkey, is a terrestrial Old World monkey species that is native to Japan. They get their name "snow monkey" because some live in areas where snow covers the ground for months each year – no other non-human primate is more northern-living, nor lives in a colder climate. Individuals have brownish grey fur, pinkish-red faces, and short tails. Two subspecies are known.
 W
WThe Formosan rock macaque, Formosan rock monkey, or Taiwanese macaque, is a macaque endemic to the island of Taiwan, which has also been introduced to Japan. Besides humans, Formosan rock macaques are the only native primates living in Taiwan. The species was first described by Robert Swinhoe in 1862.
 W
WThe Tibetan macaque, also known as the Chinese stump-tailed macaque or Milne-Edwards' macaque, is a macaque species found from eastern Tibet east to Guangdong and north to Shaanxi in China. It has also been reported from northeastern India. This species lives in subtropical forests at elevations from 800 to 2,500 m above sea level.
 W
WThe black snub-nosed monkey, also known as the Yunnan snub-nosed monkey, is a large black and white primate that lives only in the southern Chinese province of Yunnan, where it is known to the locals as the Yunnan golden hair monkey (滇金丝猴) and the black-and-white snub-nosed monkey (黑白仰鼻猴). The common name, black snub-nosed monkey, is issued to Rhinopithecus strykeri, inhabiting in Northern Sino-Myanmar border. Coniferous and deciduous forests in the mountainous regions of Yunnan are the ideal terrain for these primates. It is threatened by habitat loss, and is considered an endangered species. With their unique adaptations to their environment, these monkeys thrive at extreme altitudes despite the below freezing temperatures and thin air. This primate's diet is mainly made up of the large amounts of lichens available in their region. Recent studies have provided more information on the black-and-white snub-nosed monkey, but there is still much to learn about them.
 W
WThe golden snub-nosed monkey is an Old World monkey in the subfamily Colobinae. It is endemic to a small area in temperate, mountainous forests of central and Southwest China. They inhabit these mountainous forests of Southwestern China at elevations of 1,500–3,400 m (4,900–11,200 ft) above sea level. The Chinese name is Sichuan golden hair monkey (四川金丝猴). It is also widely referred to as the Sichuan snub-nosed monkey. Of the three species of snub-nosed monkeys in China, the golden snub-nosed monkey is the most widely distributed throughout China.
 W
WThe gray snub-nosed monkey, also known as Brelich's snub-nosed monkey, Guizhou snub-nosed monkey, and Guizhou golden monkey, is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. It is endemic to China, where it is known as the Guizhou golden hair monkey (黔金丝猴) or gray golden hair monkey (灰金丝猴). It is threatened by habitat loss. Of the three species of snub-nosed monkeys in China, the gray snub-nosed monkey is the most threatened, with a total population of less than 750 in around 20 groups surviving in the wild.