 W
WThe alpine pika is a species of small mammal in the pika family, Ochotonidae. The summer pelage of different subspecies varies drastically but, in general, it is dark or cinnamon brown, turning to grey with a yellowish tinge during the winter. The alpine pika is found in western Mongolia, eastern Kazakhstan, and Russia, as well as in China, in very cold, mountainous regions. It is a generalist herbivore, and mainly forages on mosses, tree branches, pine nuts, and plant stems. It can emit three series of different vocalizations: a long call, a short call, and an alarm call. It is rated as a species of least concern on the IUCN Red List of Endangered Species.
 W
WThe Chinese striped hamster, also known as the striped dwarf hamster, is a species of hamster. It is distributed across Northern Asia, from southern Siberia through Mongolia and northeastern China to northern North Korea. An adult Chinese striped hamster weighs 20 to 35 g, and has a body length of 72 to 116 mm with a tail of 15 to 26 mm. It is smaller and has a much shorter tail than the greater long-tailed hamster, Tscherskia triton, which inhabits much of the same range.
 W
WThe grey dwarf hamster, grey hamster or migratory hamster is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. Its range extends from Eastern Europe through the Middle East, Russia and Central Asia to Mongolia and western China. The grey dwarf hamster has grey fur and a head-body length ranging from 85 to 120 mm. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".
 W
WThe midday jird, or midday gerbil, is a species of rodent in the family Muridae and native to sandy deserts in Afghanistan, China, Iran, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. How this rodent received its common name is unclear as it is mainly nocturnal.
 W
WThe northern three-toed jerboa is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is monotypic within the genus Dipus. It ranges across Iran, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Russia, China and Mongolia. A common species, the International Union for Conservation of Nature rates it as being of "least concern".
 W
WThe Siberian weasel or kolonok is a medium-sized weasel native to Asia, where it is widely distributed and inhabits various forest habitats and open areas. It is therefore listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
 W
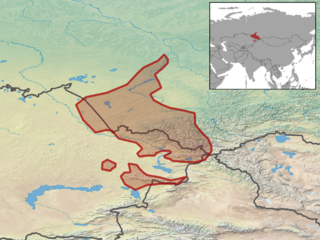
WThe Siberian zokor is a species of rodents in the family Spalacidae. It is found in Kazakhstan and Russia.
 W
WThe social vole is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in China, Iran, Kazakhstan, Syria, Turkey, and Ukraine.
 W
WThe southern birch mouse is a species of birch mouse in the family Dipodidae. It is found on the Balkan Peninsula, Ukraine, Romania, southern Russia and one isolated location in Hungary in the Borsodi Mezőség Protected Landscape Area. The Hungarian subspecies (S. subtilis trizona) is critically endangered and strictly protected. The first living specimen was captured after a 70-year-long hiatus in 2006.
 W
WThe steppe lemming or steppe vole is a small, plump, light-grey rodent, similar in appearance to the Norway lemming, but not in the same genus. The steppe lemming eats shoots and leaves and is more active at night, though it is not strictly nocturnal. In the wild, it is found in Russia and Ukraine in steppes and semiarid environments. Fossil remains of this species have been found in areas as far west as Great Britain.
 W
WThe tamarisk jird is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found in China, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. It prefers habitats with grass or shrub cover.
 W
WThe winter white dwarf hamster, also known as the Russian dwarf hamster, Djungarian hamster, striped dwarf hamster, Siberian hamster or Siberian dwarf hamster, is one of three species of hamster in the genus Phodopus. It is ball-shaped and typically half the size of the Syrian hamster, so is called a dwarf hamster along with all Phodopus species. Features of the Winter white hamster include a typically thick, dark grey dorsal stripe and furry feet. As winter approaches and the days shorten, the Winter white dwarf hamster's dark fur is almost entirely replaced with white fur. In captivity, this does not usually happen as animals maintained as pets are generally housed indoors and exposed to artificial light that prevents the recognition of short winter daylengths. In the wild, they originate from the wheat fields of Kazakhstan, the meadows of Mongolia, Siberia, and the birch stands of Manchuria.