 W
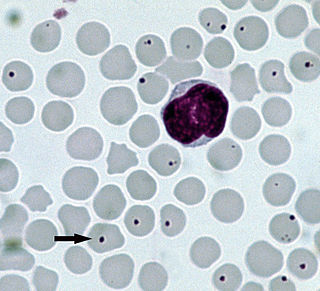
WAnaplasmosis is a disease caused by a rickettsial parasite of ruminants, Anaplasma spp and is therefore related to rickettsial disease. The microorganisms are Gram-negative, and infect red blood cells. They are transmitted by natural means through a number of haematophagous species of ticks. The Ixodes tick that commonly transmits Lyme disease also spreads anaplasmosis.
 W
WChronic wasting disease (CWD), sometimes commonly referred to as zombie deer disease is a transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) affecting deer. TSEs are a family of diseases thought to be caused by misfolded proteins called prions and includes similar diseases such as BSE in cattle, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) in humans and scrapie in sheep. In the US, CWD affects mule deer, white-tailed deer, red deer, sika deer, elk, caribou, and moose. Natural infection causing CWD affects members of the deer family. Experimental transmission of CWD to other species such as squirrel monkeys, and genetically modified mice has been shown.
 W
WCoenurosis, also known as caenurosis, coenuriasis, gid or sturdy, is a parasitic infection that develops in the intermediate hosts of some tapeworm species. It is caused by the coenurus, the larval stage of these tapeworms. The disease occurs mainly in sheep and other ungulates, but it can also occur in humans by accidental ingestion of tapeworm eggs.
 W
WCutaneous fibromas are common neoplasms occurring in wild and domestic deer of many species and are caused by host-specific viral infections. The fibromas occur most frequently in animals under 2 years of age, with cases in older deer reported occasionally/rarely.
 W
WDictyocaulus is a genus of nematode parasites of the bronchial tree of horses, sheep, goats, deer, and cattle. Dictyocaulus arnfieldi is the lungworm of horses, and Dictyocaulus viviparus is the lungworm affecting ruminants.
 W
WFascioloides magna, also known as giant liver fluke, large American liver fluke or deer fluke, is trematode parasite that occurs in wild and domestic ruminants in North America and Europe. Adult flukes occur in the liver of the definitive host and feed on blood. Mature flukes measure 4 to 10 cm in length × 2 to 3.5 cm in width, and have an oval dorso-ventrally flattened body with oral and ventral sucker. The flukes are reddish-brown in colour and are covered by tegument. As with other digenean trematodes, the life cycle includes intramolluscan phase in snails. The parasite is currently distributed in wild ruminants in North America and Europe, including Austria, Canada, the Czech Republic, Croatia, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Poland, Serbia, Slovakia, and the United States.
 W
WHardware disease is a common term for bovine traumatic reticulopericarditis. It is usually caused by the ingestion of a sharp, metallic object. These pieces of metal settle in the reticulum and can irritate or penetrate the lining. It is most common in dairy cattle, but is occasionally seen in beef cattle. It is very rarely reported in any other ruminants. It can be difficult to conclusively diagnose, but can be prevented by the oral administration of a magnet around the time that the animal reaches the age of one year.
 W
WMurrain is an antiquated term for various infectious diseases affecting cattle and sheep. It literally means "death" and was used in medieval times to represent just that. Murrain did not refer to a specific disease, but was an umbrella term for what are now recognized as a number of different diseases, including rinderpest, erysipelas, foot-and-mouth disease, anthrax, and streptococcus infections. Some of these could also affect humans. The term murrain also referred to an epidemic of such a disease. There were major sheep and cattle murrains in Europe during the 14th century, which, combined with the Little Ice Age, resulted in the Great Famine of 1315-1317, weakening the population of Europe before the onset of the Black Death in 1348.
 W
WRed deerpox virus (RDPV) is a species of virus in the genus Parapoxvirus. It has been reported in deer in New Zealand, and in wild ruminants in Italy.
 W
WSchistosoma spindale is a species of digenetic trematode in the family Schistosomatidae. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis in the ruminants.