 W
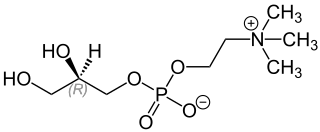
WL-Alpha glycerylphosphorylcholine is a natural choline compound found in the brain. It is also a parasympathomimetic acetylcholine precursor which has been investigated for its potential for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias.
 W
WAnabaseine (3,4,5,6-Tetrahydro-2,3’-bipyridine) is an alkaloid toxin produced by Nemertines and Aphaenogaster ants. It is structurally similar to nicotine and anabasine. Similarly, it has been shown to act as an agonist on most nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system.
 W
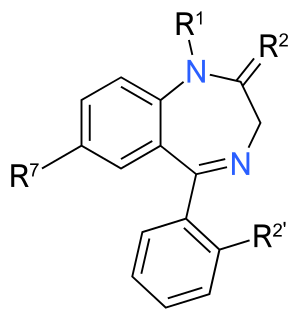
WThe effects of long-term benzodiazepine use include drug dependence and neurotoxicity as well as the possibility of adverse effects on cognitive function, physical health, and mental health. Long term use is sometimes described as use not shorter than three months. Benzodiazepines are generally effective when used therapeutically in the short term, but even then the risk of dependency can be significantly high. There are significant physical, mental and social risks associated with the long-term use of benzodiazepines. Although anxiety can temporarily increase as a withdrawal symptom, there is evidence that a reduction or withdrawal from benzodiazepines can lead in the long run to a reduction of anxiety symptoms. Due to these increasing physical and mental symptoms from long-term use of benzodiazepines, slow withdrawal is recommended for long-term users. Not everyone, however, experiences problems with long-term use.
 W
WOSU-6162 (PNU-96391) is a compound which acts as a partial agonist at both dopamine D2 receptors and 5-HT2A receptors. It acts as a dopamine stabilizer in a similar manner to the closely related drug pridopidine, and has antipsychotic, anti-addictive and anti-Parkinsonian effects in animal studies. Both enantiomers show similar activity but with different ratios of effects, with the (S) enantiomer (–)-OSU-6162 that is more commonly used in research, having higher binding affinity to D2 but is a weaker partial agonist at 5-HT2A, while the (R) enantiomer (+)-OSU-6162 has higher efficacy at 5-HT2A but lower D2 affinity.
 W
WA psychiatric or psychotropic medication is a psychoactive drug taken to exert an effect on the chemical makeup of the brain and nervous system. Thus, these medications are used to treat mental illnesses. Usually prescribed in psychiatric settings, these medications are typically made of synthetic chemical compounds. Since the mid-20th century, such medications have been leading treatments for a broad range of mental disorders and have decreased the need for long-term hospitalization, therefore lowering the cost of mental health care. The recidivism or rehospitalization of the mentally ill is at a high rate in many countries and the reasons for the relapses are under research.
 W
WPsychopharmacology is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mood, sensation, thinking, and behavior. It is distinguished from neuropsychopharmacology, which emphasizes the correlation between drug-induced changes in the functioning of cells in the nervous system and changes in consciousness and behavior.
 W
WMiodrag (Misha) Radulovacki, was a Serbian American scientist and inventor. He was Professor of Pharmacology in the College of Medicine at the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC), Radulovacki's research accomplishments include: (1) the Adenosine Sleep Theory, and (2) pioneering pharmacological studies for the treatment of sleep apnea, together with research collaborator, David W. Carley,. Radulovacki and Carley invented several drug therapies for the treatment of sleep apnea which have been patented by the UIC. The UIC recognized them as the 2010 "Inventors of the Year." Radulovacki published more than 170 scientific papers. Radulovacki was also a Foreign Member of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts.
 W
WA reuptake inhibitor (RI) is a type of drug known as a reuptake modulator that inhibits the plasmalemmal transporter-mediated reuptake of a neurotransmitter from the synapse into the pre-synaptic neuron. This leads to an increase in extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter and an increase in neurotransmission. Various drugs exert their psychological and physiological effects through reuptake inhibition, including many antidepressants and psychostimulants.
 W
WReward dependence is characterized as a tendency to respond markedly to signals of reward, particularly to verbal signals of social approval, social support, and sentiment. When reward dependence levels deviate from normal we see the rise of several personality and addictive disorders.
 W
WSerotonin syndrome (SS) is a group of symptoms that may occur with the use of certain serotonergic medications or drugs. The degree of symptoms can range from mild to severe. Symptoms in mild cases include high blood pressure and a fast heart rate; usually without a fever. Symptoms in moderate cases include high body temperature, agitation, increased reflexes, tremor, sweating, dilated pupils, and diarrhea. In severe cases body temperature can increase to greater than 41.1 °C (106.0 °F). Complications may include seizures and extensive muscle breakdown.