 W
WAscidiacea, commonly known as the ascidians, tunicates, and sea squirts, is a paraphyletic class in the subphylum Tunicata of sac-like marine invertebrate filter feeders. Ascidians are characterized by a tough outer "tunic" made of the polysaccharide cellulose.
 W
WCathaymyrus is a genus of Early Cambrian cephalochordate known from the Chengjiang locality in Yunnan Province, China. Both species have a long segmented body with no distinctive head. The segments resemble the v-shaped muscle blocks found in similar cephalochordates such as Amphioxus. A long linear impression runs along the "back" of the body looking something like a chordate notochord. Cathaymyrus is related to Pikaia, another cephalochordate from the Burgess Shale.
 W
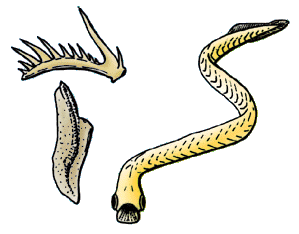
WConodonts are extinct agnathan chordates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from tooth-like microfossils found in isolation and now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. The animals are also called Conodontophora to avoid ambiguity.
 W
WHaikouella is an agnathan chordate from the Lower Cambrian Maotianshan shales of Chengjiang County in Yunnan Province, China.
 W
WHaikouichthys is an extinct genus of craniate believed to have lived 525 million years ago, during the Cambrian explosion of multicellular life. Haikouichthys had a defined skull and other characteristics that have led paleontologists to label it a true craniate, and even to be popularly characterized as one of the earliest fishes. Cladistic analysis indicates that the animal is probably a basal chordate or a basal craniate; but it does not possess sufficient features to be included uncontroversially even in either stem group. It was formally described in 1999.
 W
WMetaspriggina is a genus of chordate initially known from two specimens in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale and 44 specimens found in 2012 at the Marble Canyon bed in Kootenay National Park.
 W
WMyllokunmingiidae is a group of very early, jawless prehistoric fish (Agnathans) which lived during the Cambrian period. The Myllokunmingiids are the earliest known group of craniates. The group contains three genera, Haikouichthys, Myllokunmingia, and Zhongjianichthys. Their fossils have been found only in the Maotianshan Shales lagerstätte.
 W
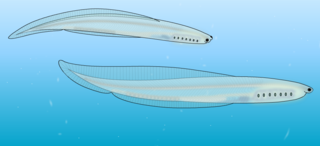
WPikaia gracilens is an extinct, primitive chordate animal known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia. Sixteen specimens are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprised 0.03% of the community. It resembled the lancelet and perhaps swam much like an eel.
 W
WZhongjianichthys rostratus is an extinct basal chordate that lived in the Cambrian period, approximately 530 million years ago. It is sometimes regarded as an early fish, and therefore as one of the first vertebrates. Zhongjianichthys is named after Zhongjian in China.
 W
WZhongxiniscus is a genus of primitive chordate from eastern Yunnan that lived during the Early Cambrian. Known from a single specimen, it had a small, broad and short, fish-like body that was roughly ten millimeters in length. It possessed S-shaped myomeres, numbering roughly seven per one millimeter of length. Two triangular fins are evident on the dorsal margin.