 W
WThe 2014 Ukrainian revolution took place in Ukraine in February 2014, when a series of violent events involving protesters, riot police, and unknown shooters in the capital, Kyiv, culminated in the ousting of the elected Ukrainian President, Viktor Yanukovych, and the overthrow of the Ukrainian Government.
 W
WThe Allied Democratic Forces insurgency is an ongoing conflict waged by the Allied Democratic Forces in Uganda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, against the governments of those two countries. The insurgency began in 1995, intensifying in 2013, resulting in hundreds of deaths. The ADF is known to currently control a number of hidden camps which are home to about 2,000 people; in these camps, the ADF operates as proto-state with "an internal security service, a prison, health clinics, and an orphanage" as well as schools for boys and girls.
 W
WThe Iraq War was a protracted armed conflict that began in 2003 with the invasion of Iraq by a United States-led coalition that overthrew the government of Saddam Hussein. The conflict continued for much of the next decade as an insurgency emerged to oppose the occupying forces and the post-invasion Iraqi government. An estimated 151,000 to 1,033,000 Iraqis were killed in the first three to four years of conflict. US troops were officially withdrawn in 2011. However, following the spread of the Syrian Civil War and the territorial gains of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Obama administration decided to redeploy US forces to Iraq in 2014. Many former soldiers are employed by defense contractors and private military companies. The U.S. became re-involved in 2014 at the head of a new coalition; the insurgency and many dimensions of the civil armed conflict continue. The invasion occurred as part of the George W. Bush administration's War on Terror, following the September 11 attacks.
 W
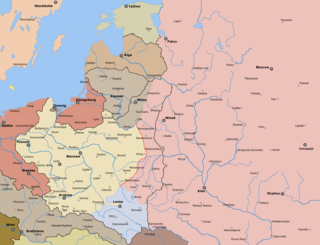
WThe Polish–Ukrainian War of November 1918 and 1919 was a conflict between the Second Polish Republic and Ukrainian forces. The conflict had its roots in ethnic, cultural and political differences between the Polish and Ukrainian populations living in the region. The war started in Eastern Galicia after the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and spilled over into Chełm Land and Volhynia (Wołyń) regions formerly belonging to the Russian Empire, which were both claimed by the Ukrainian State and the Ukrainian People's Republic.
 W
WThe Russian Civil War was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire immediately after the two Russian revolutions of 1917, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. The two largest combatant groups were the Red Army, fighting for the Bolshevik form of socialism led by Vladimir Lenin, and the loosely allied forces known as the White Army, which included diverse interests favouring political monarchism, capitalism and social democracy, each with democratic and anti-democratic variants. In addition, rival militant socialists, notably Makhnovia anarchists and Left SRs, as well as non-ideological Green armies, fought against both the Reds and the Whites. Thirteen foreign nations intervened against the Red Army, notably the former Allied military forces from the World War with the goal of re-establishing the Eastern Front. Three foreign nations of the Central Powers also intervened, rivaling the Allied intervention with the main goal of retaining the territory they had received in the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk.
 W
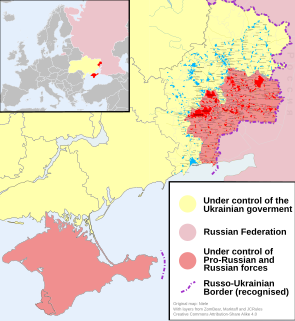
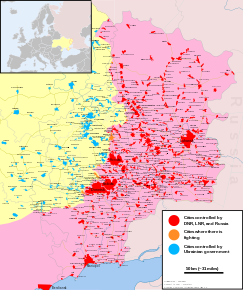
WThe Russo-Ukrainian War is a protracted conflict between Russia and Ukraine that began in February 2014. The war has centered around the status of the Ukrainian regions of Crimea and Donbass.
 W
WThe Ukrainian War of Independence, a period of sustained warlike conflict, lasted from 1917 to 1921 and resulted in the establishment and development of a Ukrainian republic, most of which was later absorbed into the Soviet Union as the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic of 1922–1991.
 W
WThe Ukrainian–Soviet War is the term commonly used in post-Soviet Ukraine for the events taking place between 1917–21, nowadays regarded essentially as a war between the Ukrainian People's Republic and the RSFSR. The war ensued soon after the October Revolution when Lenin dispatched the Antonov's expeditionary group to Ukraine and Southern Russia.
 W
WThe War in Donbass is an armed conflict in the Donbass region of Ukraine, part of the Ukrainian crisis and the broader Russo-Ukrainian War. From the beginning of March 2014, in the aftermath of the 2014 Ukrainian revolution and the Euromaidan movement, protests by Russia-backed anti-government separatist groups took place in the Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts of Ukraine, collectively called the "Donbass". These demonstrations, which followed the February–March 2014 annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, and which were part of a wider group of concurrent protests across southern and eastern Ukraine, escalated into an armed conflict between the separatist forces of the self-declared Donetsk and Luhansk People's Republics, and the Ukrainian government. While the initial protests were largely native expressions of discontent with the new Ukrainian government, Russia took advantage of them to launch a co-ordinated political and military campaign against Ukraine. Russians citizens led the separatist movement in Donetsk from April until August 2014, and were supported by volunteers and materiel from Russia. As the conflict escalated in May 2014, Russia employed a "hybrid approach", deploying a combination of disinformation tactics, irregular fighters, regular Russian troops, and conventional military support to destabilise the Donbass region. According to the Ukrainian government, at the height of the conflict in the summer of 2014, Russian paramilitaries were reported to make up between 15% to 80% of the combatants.