 W
WThe British Conquest of Egypt (1882), also known as Anglo-Egyptian War, occurred in 1882 between Egyptian and Sudanese forces under Ahmed ‘Urabi and Great Britain. It ended a nationalist uprising against the Khedive Tewfik Pasha. It established firm British influence over Egypt at the expense of the Egyptians, the French and the Ottoman Empire, which retained only nominal authority.
 W
WThe Crusader invasions of Egypt (1154–1169) were a series of campaigns undertaken by the Kingdom of Jerusalem to strengthen its position in the Levant by taking advantage of the weakness of Fatimid Egypt.
 W
WThe Fatimid conquest of Egypt took place in 969, as the troops of the Fatimid Caliphate under the general Jawhar captured Egypt, then ruled by the autonomous Ikhshidid dynasty in the name of the Abbasid Caliphate.
 W
WThe Hyksos were people of probable Levantine origin, who established the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt based at the city of Avaris in the Nile delta, from where they ruled the northern part of the country. While the Hellenistic Egyptian historian Manetho portrayed the Hyksos as invaders and oppressors, modern Egyptology no longer believes that the Hyksos conquered Egypt in an invasion. Instead, Hyksos rule had been preceded by groups of Canaanite peoples settled in the eastern delta who probably seceded from central Egyptian control near the end of the Thirteenth Dynasty.
 W
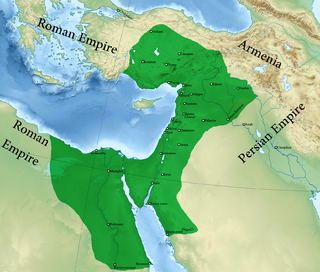
WThe Italian invasion of Egypt was an offensive in the Second World War, against British, Commonwealth and Free French forces in the Kingdom of Egypt. The invasion by the Italian 10th Army ended border skirmishing on the frontier and began the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) proper. The Italian strategy was to advance from Libya along the Egyptian coast to seize the Suez Canal. After numerous delays, the scope of the offensive was reduced to an advance as far as Sidi Barrani and the engagement of any British forces in the area.
 W
WThe Palmyrene invasion of Egypt occurred in the summer, or possibly in October, of 270 AD when the forces of Queen Zenobia of Palmyra, led by her general Zabdas and aided by an Egyptian general named Timagenes, invaded and subsequently annexed Egypt, which was under control of the Roman Empire at the time.
 W
WThe Sea Peoples are a purported seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions of the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse. Following the creation of the concept in the nineteenth century, it became one of the most famous chapters of Egyptian history, given its connection with, in the words of Wilhelm Max Müller: "the most important questions of ethnography and the primitive history of classic nations". Their origins undocumented, the various Sea Peoples have been proposed to have originated from places that include western Asia Minor, the Aegean, the Mediterranean islands and Southern Europe. Although the archaeological inscriptions do not include reference to a migration, the Sea Peoples are conjectured to have sailed around the eastern Mediterranean and invaded Anatolia, Syria, Phoenicia, Canaan, Cyprus and Egypt toward the end of the Bronze Age.
 W
WThe Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War, or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between 5 and 10 June 1967 by Israel and the neighboring states of Jordan, Syria, and Egypt.
 W
WThe Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the tripartite aggression in the Arab world and Sinai War in Israel, was an invasion of Egypt in late 1956 by Israel, followed by the United Kingdom and France. The aims were to regain Western control of the Suez Canal and to remove Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser, who had just nationalised the canal. After the fighting had started, political pressure from the United States, the Soviet Union and the United Nations led to a withdrawal by the three invaders. The episode humiliated the United Kingdom and France and strengthened Nasser.