 W
WThe Action of 12 October 1950 was a battle fought during the Korean War. While conducting Operation Wonsan against sea mines in Wonsan Harbor, a squadron of US Navy warships was attacked by Korean People's Army (KPA) batteries. During the operation, two US ships struck mines and sank while the remaining vessels and aircraft silenced the enemy guns.
 W
WThe APRA coup d'état was a coup d'état by Raymond Westerling's Legion of Ratu Adil (APRA) to capture Bandung and Jakarta, and to overthrow Sukarno’s unitary Republic of Indonesia. Westerling was a demobilised Dutch Captain of the KNIL, who sought to preserve the federal Republic of the United States of Indonesia, which retained the support of the Netherlands and various minority elements. Westerling's forces succeeded in capturing Bandung in the early hours of 23 January 1950.
 W
WThe Battle of Battle Mountain was an engagement between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces early in the Korean War from August 15 to September 19, 1950, on and around the Sobuk-san mountain area in South Korea. It was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously during the Battle of Pusan Perimeter. The battle ended in a victory for the UN after large numbers of United States Army (US) and Republic of Korea Army (ROK) troops were able to prevent a Korean People's Army (KPA) division from capturing the mountain area.
 W
WThe Battle of Chumonchin Chan or the Action of 2 July 1950 was the battle fought between surface combatants during the main phase of the Korean War. It began after an Allied flotilla encountered a Korean People's Navy supply fleet.
 W
WThe Battle of Ongjin was a part of the Operation Pokpoong that marked the beginning of the Korean War. The Republic of Korea Army (ROK) 17th Infantry Regiment fought against Korean People's Army (KPA) 14th Infantry Regiment and the 3rd Guards Brigade supported by a tank company at Ongjin.
 W
WThe Battle of Korea Strait was a single ship action fought on the first day of the Korean War, 25–26 June 1950, between the navies of South Korea and North Korea. A North Korean troop transport carrying hundreds of soldiers attempted to land its cargo near Busan but was encountered by a South Korean patrol ship and sunk. It was one of the first surface actions of the war and resulted in an important South Korean victory.
 W
WThe Battle of Route Coloniale 4, also called the Autumn-Winter Border Campaign by the Viet Minh, was a battle of the First Indochina War. It took place along Route Coloniale 4, a road used to supply the French military base at Cao Bằng. French military traffic along the road had previously been subject to an ongoing series of ambushes during 1947–1949.
 W
WIn the Battle of the Bowling Alley , United Nations Command (UN) forces defeated North Korean forces early in the Korean War near the city of Taegu, South Korea. The battle took place in a narrow valley, dubbed the "Bowling Alley", which was north of Taegu. It followed a week of fighting between the Korean People's Army (KPA) 13th Division and the Republic of Korea Army's (ROK) 1st Division along the latter's last defensible line in the hills north of the city. Reinforcements, including the US Army's 27th and 23rd Infantry Regiments were committed to bolster the ROK defenses. This battle and several others were smaller engagements of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter.
 W
WThe Battle of the Ch'ongch'on River, also known as the Battle of the Ch'ongch'on, was a decisive battle in the Korean War, and it took place from November 25 to December 2, 1950, along the Ch'ongch'on River Valley in the northwestern part of North Korea. In response to the successful Chinese First Phase Campaign against the United Nations (UN) forces, General Douglas MacArthur launched the Home-by-Christmas Offensive to expel the Chinese forces from Korea and to end the war. Anticipating this reaction, the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) Commander Peng Dehuai planned a counteroffensive, dubbed the "Second Phase Campaign", against the advancing UN forces.
 W
WThe Battle of Chamdo occurred from 6 through 19 October 1950. It was a military campaign by the People's Republic of China (PRC) to take the Chamdo Region from a de facto independent Tibetan state after months of failed negotiations on the status of Tibet. The campaign resulted in the capture of Chamdo and further negotiations between the PRC and Tibetan representatives that eventually resulted in the annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China.
 W
WThe Battle of Chochiwon was an early engagement between United States and North Korean forces during the Korean War, taking place in the villages of Chonui and Chochiwon in western South Korea on July 10–12, 1950. After three days of intense fighting, the battle ended in a North Korean victory.
 W
WThe Battle of Chonan was the third engagement between United States and North Korean forces during the Korean War. It occurred on the night of July 7/8, 1950 in the village of Chonan in western South Korea. The fight ended in a North Korean victory after intense fighting around the town, which took place throughout the night and into the morning.
 W
WThe Battle of Chongju took place during the United Nations Command (UN) offensive towards the Yalu River, which followed the North Korean invasion of South Korea at the start of the Korean War. The battle was fought between Australian forces from 3rd Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment and the 17th Tank Brigade of the Korean People's Army (KPA) for control of Chongju, North Korea and the surrounding area. After detecting a strong KPA armoured force equipped with T-34 tanks and SU-76 self-propelled guns on a thickly wooded ridgeline astride the line of advance, the Australians launched a series of company attacks with American M4 Sherman tanks and aircraft in support. Despite heavy resistance the KPA were forced to withdraw and the Australians captured their objectives after three hours of fighting.
 W
WThe Battle of Chosin Reservoir, also known as the Chosin Reservoir Campaign or the Battle of Lake Jangjin, was an important battle in the Korean War. The name "Chosin" is derived from the Japanese pronunciation "Chōshin", instead of the Korean pronunciation.
 W
WThe Faciliteitenwet, also known as the "Act on the Position of Moluccans", regulates the position of Moluccans living in the Netherlands who do not hold Dutch nationality.
 W
WThe Great Naktong Offensive was a North Korean military offensive against United Nations Command (UN) forces early in the Korean War, taking place from September 1–15, 1950. It was the North Korean Korean People's Army (KPA)'s unsuccessful final bid to break the Pusan Perimeter established by the UN forces.
 W
WThe Hadong Ambush was an engagement between United States and North Korean forces, occurring on July 27, 1950, in the village of Hadong in southern South Korea, early in the Korean War. The fight ended in a North Korean victory following a successful ambush of US forces which resulted in heavy American casualties.
 W
WThe Battle of Haman was one engagement in the larger Battle of Pusan Perimeter between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces early in the Korean War from August 31 to September 19, 1950, in the vicinity of Haman County in South Korea. The engagement ended in a victory for the UN after large numbers of United States Army troops repelled a strong Korean People's Army (KPA) attack on the town of Haman.
 W
WThe Hungnam evacuation, also known as the Miracle of Christmas, was the evacuation of United Nations (UN) forces and North Korean civilians from the port of Hungnam, North Korea, between 15 and 24 December 1950 during the Korean War. Following the defeat of UN forces during the Battle of the Chosin Reservoir, by part of the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) in the Second Phase Campaign, UN forces had retreated to Hungnam from where they were evacuated to South Korea.
 W
WThe Battle of Inchon was an amphibious invasion and battle of the Korean War that resulted in a decisive victory and strategic reversal in favor of the United Nations Command (UN). The operation involved some 75,000 troops and 261 naval vessels, and led to the recapture of the South Korean capital of Seoul two weeks later. The code name for the operation was Operation Chromite.
 W
WThe Invasion of Ambon was a combined Indonesian military operation which aimed to seize and annex the self proclaimed Republic of South Maluku.
 W
WThe Jayuya Uprising, also known as the Jayuya Revolt or El Grito de Jayuya, was a Nationalist revolt that took place on October 30, 1950, in the town of Jayuya, Puerto Rico. The revolt, led by Blanca Canales, was one of the multiple revolts that occurred throughout Puerto Rico on that day against the Puerto Rican government supported by the United States. The Nationalists were opposed to US sovereignty over Puerto Rico.
 W
WThe Jeju uprising was an uprising that occurred on Jeju Island in South Korea from April 1948 to May 1949. Residents of Jeju opposed to the Division of Korea had protested and had been on a general strike since 1947 against elections scheduled by the United Nations Temporary Commission on Korea (UNTCOK) to be held only in the territory controlled by the United States Army Military Government in Korea. The Workers' Party of South Korea and its supporters launched an insurgency in April 1948, attacking the police, and Northwest Youth League members stationed on Jeju mobilized to violently suppress the protests. The First Republic of Korea under President Syngman Rhee escalated the suppression of the uprising from August 1948, declaring martial law in November and beginning an "eradication campaign" against rebel forces in the rural areas of Jeju in March 1949, defeating them within two months. Many rebel veterans and suspected sympathizers were later killed upon the outbreak of the Korean War in June 1950, and the existence of the Jeju uprising was officially censored and repressed in South Korea for several decades.
 W
WThe Battle of Ka-san was an engagement between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces early in the Korean War from September 1 to September 15, 1950, in the vicinity of Ka-san in South Korea. It was a part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter, and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. The battle ended in a victory for the United Nations after large numbers of United States Army (US) and Republic of Korea Army (ROK) troops repelled a strong Korean People's Army (KPA) attack.
 W
WThe Korean War was a war between North Korea and South Korea. The war began on 25 June 1950 when North Korea invaded South Korea and ended unofficially on 27 July 1953 in an armistice.
The Battle of Kujin, also known as the Battle of the Broken Bridge, took place during the United Nations Command (UN) offensive towards the Yalu River, which followed the North Korean invasion of South Korea at the start of the Korean War. The battle was fought between Australian forces from 3rd Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment and elements of the 17th Tank Brigade of the Korean People's Army (KPA) over a key bridge across the Taeryong River near Kujin, North Korea. On 25 October the 27th British Commonwealth Brigade had resumed their advance towards Pakchon after crossing the Chongchon River, with 3 RAR as the lead battalion. Arriving at Kujin, the Australians discovered that the centre span of the 300-metre (330 yd) concrete bridge had been demolished by KPA engineers, blocking their passage across the river. A platoon-sized reconnaissance patrol crossed the river using debris from the destroyed span; however, it was soon forced to withdraw by KPA holding the high ground. Airstrikes and artillery fire were subsequently called-in at 17:15 by the Australians as they prepared to conduct an assault.
 W
WThe Kuomintang Islamic insurgency refers to a continuation of the Chinese Civil War by Chinese Muslim nationalist Kuomintang Republic of China Army forces in Northwest China, in the provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang, and another insurgency in Yunnan.
 W
WThe Battle of Kyongju was an engagement between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces early in the Korean War from August 31 to September 15, 1950, in the vicinity of Kyongju in South Korea. It was a part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter, and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. The battle ended in a victory for the UN after large numbers of United States Army (US) and Republic of Korea Army (ROK) troops repelled a strong North Korean Korean People's Army (KPA) attack.
 W
WThe Landing Operation on Hainan Island, also known as the Battle of Hainan Island (海南岛战役) or the Hainan Campaign (海南战役) for short, was a series of battles fought between the Kuomintang (Nationalists) and the People's Liberation Army (PLA) for the island of Hainan during the resumption of the Chinese Civil War in the post-World War II period, and resulted in a Communist victory.
 W
WThe Battle of Masan was an engagement between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces, which took place early in the Korean War between August 5 and September 19, 1950, in the vicinity of Masan and the Naktong River in South Korea. It was part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter, and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. The battle ended in a victory for the UN after large numbers of United States Army (US) troops were able to repel the repeated attacks of two Korean People's Army (KPA) divisions.
 W
WThe First Battle of Naktong Bulge was an engagement between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces early in the Korean War from August 5–19, 1950 in the vicinity of Yongsan and the Naktong River in South Korea. It was a part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter, and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. The battle ended in a victory for the UN after large numbers of US reinforcements destroyed an attacking North Korean division.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Naktong Bulge was an engagement between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces early in the Korean War from September 1 to September 15, 1950, along the Naktong River in South Korea. It was a part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter, and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. The battle ended in a victory for the United Nations after large numbers of United States Army (US) troops repelled a strong Korean People's Army (KPA) attack.
 W
WThe Battle of Nam River was an engagement between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces early in the Korean War from August 31 to September 19, 1950, in the vicinity of the Nam River and the Naktong River in South Korea. It was a part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter, and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. The battle ended in a victory for the United Nations after large numbers of United States Army (US) troops were able to repel a Korean People's Army (KPA) attack across the river.
 W
WThe San Juan Nationalist revolt was one of many uprisings against United States Government rule which occurred in Puerto Rico on October 30, 1950 during the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party revolts. Amongst the uprising's main objectives were an attack on La Fortaleza, and the U.S. Federal Court House Building in Old San Juan.
 W
WThe Battle of Onjong, also known as the Battle of Wenjing, was one of the first engagements between Chinese and United Nations (UN) forces during the Korean War. It took place around Onjong in present-day North Korea from 25 to 29 October 1950. As the main focus of the Chinese First Phase Offensive, the People's Volunteer Army (PVA) 40th Corps conducted a series of ambushes against the Republic of Korea Army (ROK) II Corps, effectively destroying the right flank of the United States Eighth Army while stopping the UN advance north toward the Yalu River.
 W
WThe Battle of Osan was the first engagement between United States and North Korean forces during the Korean War, on July 5, 1950. Task Force Smith, a U.S. task force of 400 infantry supported by an artillery battery, was moved to Osan, south of the South Korean capital of Seoul, and ordered to fight as a rearguard to delay advancing North Korean forces while additional U.S. troops arrived in the country to form a stronger defensive line to the south. The task force lacked both anti-tank guns and effective infantry anti-tank weapons, having been equipped with obsolescent 2.36 in. rocket launchers and a few 75 mm recoilless rifles. Aside from a limited number of HEAT shells for the unit's 105 mm howitzers, crew-served weapons capable of defeating the T-34-85 Soviet tank had not been distributed to U.S. Army forces in Korea.
 W
WThe Battle of Pakchon, also known as the Battle of Bochuan, took place ten days after the start of the Chinese First Phase Offensive, following the entry of the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) into the Korean War. The offensive reversed the United Nations Command (UN) advance towards the Yalu River which had occurred after their intervention in the wake of the North Korean invasion of South Korea at the start of the war. The battle was fought between British and Australian forces from the 27th British Commonwealth Brigade with American armour and artillery in support, and the PVA 117th Division of the 39th Army, around the village of Pakchon on the Taeryong River. After capturing Chongju on 30 October the British and Australians had been ordered to pull back to Pakchon in an attempt to consolidate the western flank of the US Eighth Army. Meanwhile, immediately following their success at Unsan against the Americans, the PVA 117th Division had attacked southward, intending to cut off the UN forces as they withdrew in the face of the unexpected PVA assault. To halt the PVA advance, the 27th British Commonwealth Brigade was ordered to defend the lower crossings of the Taeryong and Chongchon rivers as part of a rearguard, in conjunction with the US 24th Infantry Division further upstream on the right.
 W
WThe Battle of the Pusan Perimeter was a large-scale battle between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces lasting from August 4 to September 18, 1950. It was one of the first major engagements of the Korean War. An army of 140,000 UN troops, having been pushed to the brink of defeat, were rallied to make a final stand against the invading Korean People's Army (KPA), 98,000 men strong.
 W
WLogistics in the Battle of Pusan Perimeter during the Korean War played a decisive role in the battle. Efficient logistics, the management of personnel and materiel, supported United Nations (UN) supply lines while the North Koreans' routes of supply were steadily reduced and cut off. UN logistics improved throughout the Battle of Inchon and the defeat of the North Korean army at Pusan.
 W
WThe Pusan Perimeter Offensive was a large-scale offensive by United Nations Command (UN) forces against North Korean forces commencing on 16 September 1950.
 W
WThe Battle of Pyongtaek was the second engagement between United States and North Korean forces during the Korean War, occurring on July 6, 1950 in the village of Pyongtaek in western South Korea. The fight ended in a North Korean victory following unsuccessful attempts by American forces to inflict significant damage or delays on advancing North Korean units, despite several opportunities to do so.
 W
WThe Battle of Pyongyang was one of the major battles of the United Nations' offensive during the Korean War. Following the Battle of Inchon, the UN forces re-captured Seoul, the capital of South Korea, and proceeded to advance into North Korea. Shortly after advancing, the American and South Korean forces faced the North Korean defenses near Pyongyang, the capital of North Korea, on 17 October.
 W
WThe Battle of Sangju was an engagement between the United Nations and North Korean forces, occurring on July 20–31, 1950, in the village of Sangju in southern South Korea, early in the Korean War. It ended in a victory for the North Korean forces after they were able to push troops of the United States and South Korea out of the area.
 W
WThe Battle of Sariwon took place on 17 October 1950 during the United Nations (UN) counter-offensive against the North Korean forces which had invaded South Korea. With many Korean People's Army (KPA) units falling back under pressure from UN forces the 27th British Commonwealth Brigade under Brigadier Basil Coad—–comprising the 1st Battalion, the Argyll and Sutherland Highland Regiment, the 1st Battalion, the Middlesex Regiment and 3rd Battalion, the Royal Australian Regiment (3RAR) captured the town of Sariwon during a confused and largely one-sided action. Elements of the 7th US Cavalry Regiment were also involved. KPA casualties included 215 killed and more than 3,700 captured, whilst British-Commonwealth losses were 1 killed and 3 wounded.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Seoul was a battle that resulted in United Nations forces recapturing Seoul from the North Koreans in late September 1950.
 W
WThe Sinchon Massacre was an alleged massacre of civilians between 17 October and 7 December 1950, in or near the town of Sinchon. North Korean sources claim the massacre was committed by South Korean military forces under the authorization of the U.S. military and that 30–35,000 people were killed. Other sources dispute the death toll and accuse Korean right-wing security police and communists of the killings. The event allegedly took place during the second phase of the Korean War and the retreat of the DPRK government from Hwanghae Province.
 W
WThe Battle of Tabu-dong was an engagement between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces early in the Korean War from September 1 to September 18, 1950, in the vicinity of Tabu-dong, north of Taegu in South Korea. It was a part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter, and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. The battle ended in a victory for the UN after large numbers of United States Army (US) and Republic of Korea Army (ROK) troops repelled a strong Korean People's Army (KPA) attack.
 W
WThe Battle of Taegu was an engagement between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces early in the Korean War, with fighting continuing from August 5–20, 1950 around the city of Taegu, South Korea. It was a part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter, and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. The battle ended in a victory for the UN after their forces were able to drive off an offensive by Korean People's Army (KPA) divisions attempting to cross the Naktong River and assault the city.
 W
WThe Battle of Taejon was an early battle of the Korean War, between U.S. and North Korean forces. Forces of the United States Army attempted to defend the headquarters of the 24th Infantry Division. The 24th Infantry Division was overwhelmed by numerically superior forces of the Korean People's Army (KPA) at the major city and transportation hub of Taejon. The 24th Infantry Division's regiments were already exhausted from the previous two weeks of delaying actions to stem the advance of the KPA.
 W
WThe Regimental Combat Team 31 (RCT-31), commonly referred to as Task Force Faith of the "Chosin Few", is a United States Army unit known for its role in the Battle of Chosin Reservoir during the Korean War where 90-95% of its force was killed, wounded, and/or captured on the eastern side of the reservoir.
 W
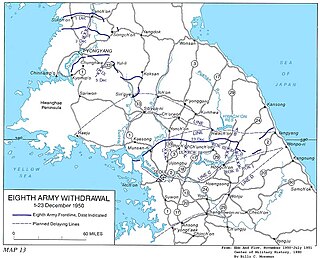
WThe UN retreat from North Korea was the withdrawal of United Nations (UN) forces from North Korea that took place from 2–25 December 1950.
 W
WThe UN September 1950 counteroffensive was a large-scale offensive by United Nations Command (UN) forces against North Korean forces commencing on 23 September 1950.
 W
WThe Battle of Unsan, also known as the Battle of Yunshan, was a series of engagements of the Korean War that took place from 25 October to 4 November 1950 near Unsan, North Pyongan province in present-day North Korea. As part of the People's Republic of China's First Phase Campaign, the People's Volunteer Army (PVA) made repeated attacks against the Republic of Korea Army (ROK) 1st Infantry Division near Unsan beginning on 25 October, in an attempt to take advancing United Nations forces by surprise. In an accidental first encounter with the United States military during the Korean War, the PVA 39th Corps attacked the unprepared US 8th Cavalry Regiment in Unsan on 1 November, resulting in one of the most devastating US losses of the Korean War.
 W
WThe Utuado uprising, also known as the Utuado revolt or El Grito de Utuado, refers to the revolt against the United States government in Puerto Rico which occurred on October 30, 1950 in various localities in Puerto Rico.
 W
WThe Battle of Wawon(Korean: 군우리 전투; hanja: 軍隅里戰鬪; rr: Gunuri Jeontu; Turkish: Kunuri Muharebeleri), also known as the Battle of Wayuan, was a series of delay actions of the Korean War that took place from 27-29 November 1950 near Wawon in present-day North Korea. After the collapse of the US Eighth Army's right flank during the Battle of the Ch'ongch'on River, the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) 38th Corps advanced rapidly towards the critical road junction at Kunu-ri in an effort to cut off United Nations forces' retreat route. In what was considered to be Turkey's first real combat action since the aftermath of World War I, the Turkish Brigade attempted to delay the Chinese advances at Wawon. Although during the battle the Turkish Brigade was crippled after being encircled by Chinese forces with superior numbers, they were still be able to breach the Chinese trap and rejoin the US 2nd Infantry Division. Delay of the PVA advance after meeting with heavy Turkish resistance helped the other United Nations forces to withdraw without suffering many casualties and reassemble later in December.
 W
WThe Witzieshoek revolt was a rebellion of Basotho residents in Witzieshoek in the Orange Free State of South Africa during the mid 20th century. It arose as a result of South African government interventions into the traditional farming practices of the Basotho, specifically those that limited the number of stock Basotho could keep and required the culling of excess. Passive resistance to the government’s legislation had escalated in the 1940s to active disobedience, when in November 1950 a confrontation between police and Basotho farmers turned violent. Fourteen Basotho were killed, and eight others deemed to be ringleaders were later sentenced to terms of imprisonment and banishment from Witzieshoek.
 W
WThe Battle of Yongdong was an engagement between United States and North Korean forces early in the Korean War. It occurred on July 22–25, 1950, in the village of Yongdong in southern South Korea. The newly arrived US Army 1st Cavalry Division was ordered there to cover the retreat of the US 24th Infantry Division after the Battle of Taejon. The 1st Cavalry Division soldiers, however, were untried in combat, and the North Korean Korean People's Army's (KPA) 3rd Division was able to outmaneuver them and force them back.
 W
WThe Battle of Yongyu, also known as the Battle of the Apple Orchard or the Battle of Yongju to the Australians who fought in it, took place between 21 and 22 October 1950 during the United Nations Command (UNC) offensive into North Korea against the Korean People's Army (KPA) that had invaded South Korea during the Korean War. The battle was fought between the 3rd Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment of the 27th British Commonwealth Brigade and the KPA 239th Regiment.
 W
WThe Battle of Yongsan was an engagement between United Nations Command (UN) and North Korean forces early in the Korean War from September 1–5, 1950, at Yongsan in South Korea. It was part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. The battle ended in a victory for the UN after large numbers of United States Army (US) repelled a strong Korean People's Army (KPA) attack.