 W
WOperation Abstention was a code name given to a British invasion of the Italian island of Kastelorizo (Castellorizo) off the Turkish Aegean coast, during the Second World War, in late February 1941. The goal was to establish a torpedo-boat base to challenge Italian naval and air supremacy on the Greek Dodecanese islands. The British landings were challenged by Italian land, air and naval forces, which forced the British troops to re-embark amidst some confusion and led to recriminations between the British commanders for underestimating the Italians.
 W
WThe Battle of Abukir of 8 March 1801 was the second pitched battle of the French campaign in Egypt and Syria to be fought at Abu Qir on the Mediterranean coast, near the Nile Delta.
 W
WOperation Agreement was a ground and amphibious operation carried out by British, Rhodesian and New Zealand forces on Axis-held Tobruk from 13 to 14 September 1942, during the Second World War. A Special Interrogation Group party, fluent in German, took part in missions behind enemy lines. Diversionary actions extended to Benghazi, Jalo oasis and Barce. The Tobruk raid was an Allied disaster; the British lost several hundred men killed and captured, one cruiser, two destroyers, six motor torpedo boats and dozens of small amphibious craft.
 W
WThe Allied invasion of Italy was the Allied amphibious landing on mainland Italy that took place on 3 September 1943 during the early stages of the Italian Campaign of World War II. The operation was undertaken by General Sir Harold Alexander's 15th Army Group and followed the successful invasion of Sicily. The main invasion force landed around Salerno on 9 September on the western coast in Operation Avalanche, while two supporting operations took place in Calabria and Taranto.
 W
WThe Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland was a military campaign from 27 August to 19 November 1799 during the War of the Second Coalition, in which an expeditionary force of British and Russian troops invaded the North Holland peninsula in the Batavian Republic. The campaign had two strategic objectives: to neutralize the Batavian fleet and to promote an uprising by followers of the former stadtholder William V against the Batavian government. The invasion was opposed by a slightly smaller joint Franco-Batavian army. Tactically, the Anglo-Russian forces were successful initially, defeating the defenders in the battles of Callantsoog and the Krabbendam, but subsequent battles went against the Anglo-Russian forces. Following a defeat at Castricum, the Duke of York, the British supreme commander, decided upon a strategic retreat to the original bridgehead in the extreme north of the peninsula. Subsequently, an agreement was negotiated with the supreme commander of the Franco-Batavian forces, General Guillaume Marie Anne Brune, that allowed the Anglo-Russian forces to evacuate this bridgehead unmolested. However, the expedition partly succeeded in its first objective, capturing a significant proportion of the Batavian fleet.
 W
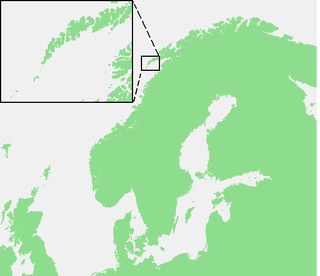
WOperation Anklet was the codename given to a British Commando raid during the Second World War. The raid on the Lofoten Islands was carried out in December 1941, by 300 men from No. 12 Commando and the Norwegian Independent Company 1. The landing party was supported by 22 ships from three navies.
 W
WThe Battle of Anzio was a battle of the Italian Campaign of World War II that took place from January 22, 1944 to June 5, 1944. The operation was opposed by German forces in the area of Anzio and Nettuno. Nettuno was the German name for the Battle of Anzio.
 W
WOperation Archery, also known as the Måløy Raid, was a British Combined Operations raid during World War II against German positions on the island of Vågsøy, Norway, on 27 December 1941.
 W
WThe Raid on Bardia was an amphibious landing at the coastal town of Bardia in North Africa by British Commandos over the night of 19/20 April 1941 during the Second World War. The raid was carried out by No. 7 Commando also known as A Battalion Layforce together with a small detachment from the Royal Tank Regiment supported by five navy ships and a submarine. The raid—which destroyed an Italian artillery battery and a supply dump—was deemed a success despite the loss of 71 men. The more lasting strategic effect of the raid was the diversion of a German armoured brigade from the front line to provide rear area security.
 W
WThe Battle of Amoy was fought between British and Qing forces at Amoy on Xiamen Island, Fujian, in the Qing Empire on 26 August 1841 during the First Opium War. The British captured the forts at Xiamen and on nearby Gulangyu Island.
 W
WThe Battle of Cartagena de Indias took place during the 1739 to 1748 War of Jenkins' Ear between Spain and Britain. The result of long-standing commercial tensions, the war was primarily fought in the Caribbean; the British tried to capture key Spanish ports in the region, including Porto Bello and Chagres in Panama, Havana, and Cartagena de Indias in present-day Colombia.
 W
WThe Battle of First Bar was fought between British and Chinese forces at First Bar Island and its surrounding area in the Pearl River, Guangdong province, China, on 27 February 1841 during the First Opium War.
 W
WThe Siege of Havana was a successful British siege against Spanish-ruled Havana that lasted from March to August 1762, as part of the Seven Years' War. After Spain abandoned its former policy of neutrality by signing the family compact with France, resulting on a British declaration of war on Spain in January 1762, the British government decided to mount an attack on the important Spanish fortress and naval base of Havana, with the intention of weakening the Spanish presence in the Caribbean and improving the security of its own North American colonies. A strong British naval force consisting of squadrons from Britain and the West Indies, and the military force of British and American troops it convoyed, were able to approach Havana from a direction that neither the Spanish governor nor Admiral expected and were able to trap the Spanish fleet in the Havana harbour and land its troops with relatively little resistance.
 W
WThe Battle of Santa Cruz de Tenerife was an amphibious assault by the Royal Navy on the Spanish port city of Santa Cruz de Tenerife in the Canary Islands. Launched by Rear-Admiral Horatio Nelson on 22 July 1797, the assault was defeated, and on 25 July the remains of the landing party withdrew under a truce, having lost several hundred men. Nelson himself had been wounded in the arm, which was subsequently partially amputated: a stigma that he carried to his grave as a constant reminder of his failure.
 W
WThe Battle of the Bogue was fought between British and Chinese forces in the Pearl River Delta, Guangdong province, China, on 23–26 February 1841 during the First Opium War. The British launched an amphibious attack at the Humen strait (Bogue), capturing the forts on the islands of Anunghoy and North Wangtong. This allowed the fleet to proceed further up the Pearl River towards the city of Canton (Guangzhou), which they captured the following month.
 W
WThe Battle of Whampoa was fought between British and Chinese forces at Whampoa Island on the Pearl River near the city of Canton (Guangzhou), Guangdong, China, on 2 March 1841 during the First Opium War.
 W
WThe Battle of Beauport, also known as the Battle of Montmorency, fought on 31 July 1759, was an important confrontation between the British and French Armed Forces during the Seven Years' War of the French province of Canada. The attack conducted by the British against the French defense line of Beauport, some 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) east of Quebec was checked, and the British soldiers of General James Wolfe retreated with 443 casualties and losses.
 W
WThe Battle of Bomarsund, in August 1854, took place during the Åland War, which was part of the Crimean War, when an Anglo-French expeditionary force attacked a Russian fortress. It was the only major action of the war to take place at Bomarsund in the Baltic Sea.
 W
WThe British invasions of the River Plate were a series of unsuccessful British attempts to seize control of areas in the Spanish colonial Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata that were located around the Río de la Plata in South America — in present-day Argentina and Uruguay. The invasions took place between 1806 and 1807, as part of the Napoleonic Wars, when Spain was an ally of Napoleonic France.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Canton was fought between British and Chinese forces in Canton (Guangzhou), Guangdong province, China, in May 1841 during the First Opium War.
 W
WThe First Capture of Chusan by British forces in China occurred on 5–6 July 1840 during the First Opium War. The British captured Chusan (Zhoushan), the largest island of an archipelago of that name.
 W
WThe second capture of Chusan occurred on 1 October 1841 during the First Opium War when British forces captured the city of Dinghai, capital of the Chusan (Zhoushan) islands off the east Chinese coast.
 W
WThe Capture of Menorca saw the island of Menorca captured from Spain by British-Dutch forces acting on behalf of Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor the Austrian claimant to the Spanish throne in September 1708 during the War of the Spanish Succession. The British would later annex the island as their own possession at the Treaty of Utrecht (1713).
 W
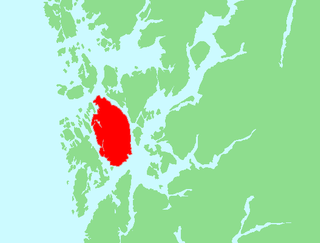
WOperation Cartoon was a British Commando raid on the island of Stord near Leirvik in Hordaland, Norway on the night of 23/24 January 1943. The operation was carried out by 53 men of No. 12 Commando supported by ten men from the Norwegian 10 (IA) Commando. RAF Coastal Command co-operated with the Commandos, with aircraft from 18 Group.
 W
WOperation Checkmate was the codename for a raid on shipping at Haugesund, Norway in April 1943 during the Second World War by British Commandos. The raiding party consisted of seven men of No. 14 (Arctic) Commando who managed to sink one ship using limpet mines. While waiting in hiding for the transport back to the United Kingdom they were captured on 14 and 15 May 1943 and eventually taken to Sachsenhausen and Belsen concentration camps where six of them were executed, victims of the Commando Order. The seventh man died of typhus.
 W
WOperation Claymore was a British commando raid on the Norwegian Lofoten Islands during the Second World War. The Lofoten Islands were an important centre for the production of fish oil and glycerine, used in the German war economy. The landings were carried out on 4 March 1941, by the men of No. 3 Commando, No. 4 Commando, a Royal Engineers section and 52 men from the Norwegian Independent Company 1. Supported by the 6th Destroyer Flotilla and two troop transports of the Royal Navy, the force made an unopposed landing and generally continued to meet no opposition. The original plan was to avoid contact with German forces and inflict the maximum of damage to German-controlled industry. They achieved their objective of destroying fish oil factories and some 3,600 t of oil and glycerine. The British experienced only one accident; an officer injuring himself with his own revolver and returned with some 228 German prisoners, 314 loyal Norwegian volunteers and a number of Quisling regime collaborators.
 W
WOperation Collar was the codeword for the first commando raid, conducted by the British forces, during the Second World War. The location selected for the raid was the Pas-de-Calais department on the French coast. The British Commandos had not long been formed and were not yet trained, so the operation was given to No. 11 Independent Company under the command of Major Ronnie Tod.
 W
WOperation Devon was the codeword given to an amphibious landing by British Commandos at Termoli on the Adriatic coast of Italy during the Italian Campaign of World War II. It was launched on 3 October 1943, as part of the attack on the Volturno Line, and was undertaken by No. 3 Commando, No. 40 Commando and other elements of the 2nd Special Service Brigade. It was later reinforced by two brigades of the British 78th Infantry Division.
 W
WOperation Jubilee or the Dieppe Raid was an Allied amphibious attack on the German-occupied port of Dieppe, northern France in the Second World War. Over 6,050 infantry, predominantly Canadian, supported by a regiment of tanks, were put ashore from a naval force operating under protection of Royal Air Force (RAF) fighters.
 W
WThe invasion of Elba, codenamed Operation Brassard, was part of the Italian campaign during the Second World War. The invasion was carried out by Free French Forces supported by British and American ships and aircraft.
 W
WOperation Flipper was a British commando raid during the Second World War, mainly by men from No. 11 (Scottish) Commando. The operation included an attack on the headquarters of Erwin Rommel, the commander of Panzergruppe Afrika in North Africa. It was timed for the night of 17/18 November 1941, just before the start of Operation Crusader. The operation failed as Rommel had left the target house weeks earlier and all but two of the commandos who landed were killed or captured. One member of the Special Boat Section team, who had secured the beach for the commando party, also escaped.
 W
WOperation Fritham was an Allied military operation during the Second World War to secure the coal mines on Spitsbergen, the main island of the Svalbard Archipelago, 650 mi (1,050 km) from the North Pole and about the same distance from Norway. The operation was intended to deny the islands to Nazi Germany.
 W
WThe Gallipoli campaign, also known as the Dardanelles campaign, the Battle of Gallipoli or the Battle of Çanakkale, was a military campaign in the First World War that took place on the Gallipoli peninsula, from 17 February 1915 to 9 January 1916. The Entente powers, Britain, France and Russia, sought to weaken the Ottoman Empire, one of the Central Powers, by taking control of the straits that provided a supply route to the Russian Empire. The Allied attack on Ottoman forts at the entrance of the Dardanelles in February 1915 failed and was followed by an amphibious landing on the Gallipoli peninsula in April 1915 to capture the Ottoman capital of Constantinople (Istanbul).
 W
WOperation Gauntlet was an Allied Combined Operation from 25 August until 3 September 1941, during the Second World War. Canadian, British and Free Norwegian Forces landed on the Norwegian island of Spitsbergen in the Svalbard Archipelago, 650 mi (1,050 km) south of the North Pole.
 W
WOperation Gearbox was a Norwegian and British operation on the Arctic island of Spitzbergen in the Svalbard Archipelago, during the Second World War. Operation Fritham, an earlier expedition in two ships, arrived on 13 May but met disaster after being spotted by a Luftwaffe Ju 88 bomber. Next day, four Fw 200 reconnaissance bombers attacked and killed fourteen men, including Einar Sverdrup, the commander. Eleven men were wounded, two mortally, one ship was sunk and the other set on fire.
 W
WOperation Gearbox II was a Norwegian and British operation during the Second World War on the Arctic island of Spitzbergen in the Svalbard Archipelago. Operation Fritham, the first attempt to establish a base had been defeated when the two ships carrying the force were sunk by Luftwaffe bombers on 14 May.
 W
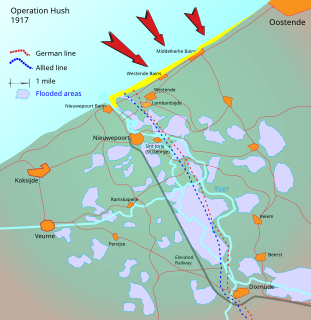
WOperation Hush was a British plan to make amphibious landings on the Belgian coast in 1917 during the First World War, supported by an attack from Nieuwpoort and the Yser bridgehead, positions which were a legacy of the Battle of the Yser in 1914. Several plans were considered in 1915 and 1916, then shelved due to operations elsewhere. Operation Hush was intended to begin when the Third Battle of Ypres, the main offensive at Ypres had advanced to Roulers, Koekelare and Thourout, linked by advances by the French and Belgian armies in between.
 W
WThe Invasion of Guadeloupe was a British amphibious operation fought between 28 January and 6 February 1810 over control of the Caribbean island of Guadeloupe during the Napoleonic Wars. The island was the final remaining French colony in the Americas, following the systematic invasion and capture of the others during 1809 by British forces. During the Napoleonic Wars, the French colonies had provided protected harbours for French privateers and warships, which could prey on the numerous British trade routes in the Caribbean and then return to the colonies before British warships could react. In response, the British instituted a blockade of the islands, stationing ships off every port and seizing any vessel that tried to enter or leave. With trade and communication made dangerous by the British blockade squadrons, the economies and morale of the French colonies began to collapse, and in the summer of 1808 desperate messages were sent to France requesting help.
 W
WThe Raid on Lorient was a British amphibious operation in the region around the town of Lorient from 29 September to 10 October 1746 during the War of the Austrian Succession. It was planned as an attempt to force the French to withdraw their forces from Flanders to reinforce their own coast. At the same time, as Lorient was used by the French East India Company as a base and supply depot, its destruction would serve British objectives in the East Indies.
 W
WThe Siege of Louisbourg was a pivotal operation of the Seven Years' War in 1758 that ended the French colonial era in Atlantic Canada and led to the subsequent British campaign to capture Quebec in 1759 and the remainder of French North America the following year.
 W
WThe Battle of Madagascar was the British campaign to capture the Vichy French-controlled island Madagascar during World War II. The seizure of the island by the British was to deny Madagascar's ports to the Imperial Japanese Navy and to prevent the loss or impairment of the Allied shipping routes to India, Australia and Southeast Asia. It began with Operation Ironclad, the seizure of the port of Diego-Suarez near the northern tip of the island, on 5 May 1942.
 W
WIn November 1798 a British expedition captured the island of Menorca from Spain. A large force under General Charles Stuart landed on the island and forced its Spanish garrison to surrender in eight days with only some bloodshed. The British occupied the island for four years, using it as a major naval base, before handing it back to Spain following the Treaty of Amiens.
 W
WOperation Musketoon was the codeword of a British–Norwegian commando raid in the Second World War. The operation was mounted against the German-held Glomfjord power plant in Norway from 11 to 21 September 1942.
 W
WThe Normandy landings were the landing operations and associated airborne operations on Tuesday, 6 June 1944 of the Allied invasion of Normandy in Operation Overlord during World War II. Codenamed Operation Neptune and often referred to as D-Day, it was the largest seaborne invasion in history. The operation began the liberation of German-occupied France and laid the foundations of the Allied victory on the Western Front.
 W
WOperation Corkscrew was the code name for the Allied invasion of the Italian island of Pantelleria on 11 June 1943, prior to the Allied invasion of Sicily during the Second World War. There had been an early plan to occupy the island in late 1940, but this was aborted when the Luftwaffe strengthened the Axis air threat in the region.
 W
WThe Siege of Petropavlovsk was a military operation in the Pacific Theatre of the Crimean War. The Russian casualties are estimated at 115 soldiers and sailors killed and seriously wounded, whilst the British suffered 105 casualties and the French 104.
 W
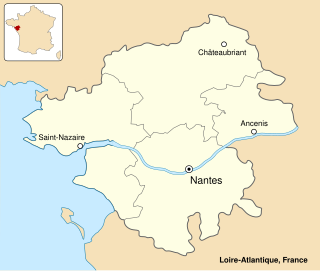
WThe St Nazaire Raid or Operation Chariot was a British amphibious attack on the heavily defended Normandie dry dock at St Nazaire in German-occupied France during the Second World War. The operation was undertaken by the Royal Navy and British Commandos under the auspices of Combined Operations Headquarters on 28 March 1942. St Nazaire was targeted because the loss of its dry dock would force any large German warship in need of repairs, such as Tirpitz, sister ship of Bismarck, to return to home waters by running the gauntlet of the Home Fleet of the Royal Navy and other British forces, via the English Channel or the GIUK gap.
 W
WThe Raid on Saint-Paul was an amphibious operation conducted by a combined British Army, Royal Navy and Royal Marines force against the fortified French port of Saint Paul on Île Bonaparte during the Napoleonic Wars. The operation was launched on 20 September 1809 as both a precursor to a future full-scale invasion of Île Bonaparte and in order to capture the French frigate Caroline and the East Indiamen she had seized in the Action of 31 May 1809 which were sheltering in the harbour. The operation was a complete success, with British storming parties capturing the batteries overlooking the port, which allowed a naval squadron under Commodore Josias Rowley to enter the bay and capture the shipping in the harbour.
 W
WThe Raid on Santorini took place on 24 April 1944 as part of the Mediterranean Campaign in World War II. It was conducted by the British Special Boat Service, against the mixed German and Italian garrison on the island of Santorini (Thera) in the Aegean Sea. The raid was made in tandem with similar operations at the islands of Ios, Mykonos and Amorgos that aimed to destroy Axis naval observation posts and radio stations on the Cycladic islands.
 W
WThe Allied invasion of Sicily, codenamed Operation Husky, was a major campaign of World War II, in which the Allies took the island of Sicily from the Axis powers. It began with a large amphibious and airborne operation, followed by a six-week land campaign, and initiated the Italian Campaign.
 W
WThe Raid on Symi also known as Operation Tenement took place from 13 to 15 July 1944 as part of the Mediterranean Campaign in World War II. The action was a combined operation conducted by two Allied special forces, the British Special Boat Service and the Greek Sacred Band, who raided the German and Italian garrisons at the island of Symi in the Aegean Sea.
 W
WThe Battle of Tanga, sometimes also known as the Battle of the Bees, was the unsuccessful attack by the British Indian Expeditionary Force "B" under Major General A.E. Aitken to capture German East Africa during the First World War in concert with the invasion Force "C" near Longido on the slopes of Mount Kilimanjaro. It was the first major event of the war in Eastern Africa and saw the British defeated by a significantly smaller force of German Askaris and colonial volunteers under Lieutenant Colonel Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck. It was the beginning of the East African Campaign of World War I, and is considered as one of greatest victories of the Schutztruppe in Africa. The British retreat enabled the Schutztruppe to salvage modern equipment, medical supplies, tents, blankets, food and a number of Maxim Machine Guns which allowed them to successfully resist the allies for the rest of the War.
 W
WOperation Torch was an Allied invasion of French North Africa during the Second World War. The French colonies in the area were dominated by the French, formally aligned with Germany but of mixed loyalties. Reports indicated that they might support the Allies. American General Dwight D. Eisenhower, supreme commander of the Allied forces in the European Theater, planned a three-pronged attack on Casablanca (Western), Oran (Center) and Algiers (Eastern), then a rapid move on Tunis.
 W
WThe Walcheren Campaign was an unsuccessful British expedition to the Netherlands in 1809 intended to open another front in the Austrian Empire's struggle with France during the War of the Fifth Coalition. Sir John Pitt, 2nd Earl of Chatham, was the commander of the expedition. with the missions of capturing Flushing and Antwerp in the Netherlands and enabling navigation of the Scheldt River. Some 40,000 soldiers, 15,000 horses together with field artillery and two siege trains crossed the North Sea and landed at Walcheren on 30 July. This was the largest British expedition of that year, larger than the army serving in the Peninsular War in Portugal. Nevertheless it failed top achieve any of the goals. The Walcheren Campaign involved little fighting, but heavy losses from the sickness popularly dubbed "Walcheren Fever". Although more than 4,000 British troops died during the expedition, only 106 died in combat; the survivors withdrew on 9 December.