 W
WThe Battle of Acapulco were a series of battles during the Second French intervention in Mexico. Acapulco was a key port of the Pacific trade routes and thus changed hands several times in the course of the Franco-Mexican war. In this period the population of the city had decreased from 6000 to 2000.
 W
WThe Great Siege of Acapulco was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred on 12 April 1813 at Acapulco de Juárez. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown, commanded by Pedro Antonio Vélez, and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire, commanded by José María Morelos. The prestigious battle resulted in a victory for the Mexican rebels.
 W
WThe Battle of Agua Dulce Creek was a skirmish during the Texas Revolution between Mexican troops and rebellious colonists of the Mexican province of Texas, known as Texians. As part of the Goliad Campaign to retake the Texas Gulf Coast, Mexican troops ambushed a group of Texians on March 2, 1836. The skirmish began approximately 26 miles (42 km) south of San Patricio, in territory belonging to the Mexican state of Tamaulipas.
 W
WThe Battle of Ambos Nogales, or as it is known in Mexico La batalla del 27 de agosto, was an engagement fought on 27 August 1918 between Mexican military and civilian militia forces and elements of U.S. Army troops of the 35th Infantry Regiment, who were reinforced by the Buffalo Soldiers of the 10th Cavalry Regiment, and commanded by Lt. Col. Frederick J. Herman. The American soldiers and militia forces were stationed in Nogales, Arizona, and the Mexican soldiers and armed Mexican militia were in Nogales, Sonora. This battle was notable for being a significant confrontation between U.S. and Mexican forces during the Border War, which took place in the context of the Mexican Revolution and the First World War.
 W
WThe Battle of Azcapotzalco,, was fought on August 19, 1821, in the town of Azcapotzalco, near Mexico City. It was to be the last major and decisive military action of the Mexican War of Independence. The insurgents, commanded by the colonels Anastasio Bustamante and Luis Quintanar, defeated the Spanish forces commanded by Manuel de la Concha.
 W
WThe Battle of Barranca Seca was a battle of the Second French intervention in Mexico and took place right after the Battle of Puebla on 18 May 1862. Contrary to the latter it was won by the unified reactionist Mexican-French forces. The battle was preceded by a coup de chef of the reactionist forces, which was heated by the intrigue of the Spanish high command against Almonte and Márquez and French pressure towards the replacement of Zuloaga. After the battle Almonte remained the only contender for the Commander-in-Chief office within the reactionist party and Márquez as acting General; both of them serving French interests.
 W
WThe Battle of Zacatecas in 1835 took place on 11 May 1835 in the immediate vicinity of the capital city in the state of Zacatecas, Mexico, between elements of the federal army under the command of Gen. Antonio López de Santa Anna and elements of the rebel army, which was commanded by General Francisco García Salinas during the Rebellion in Zacatecas of 1835.
 W
WThe Battle of Calderón Bridge was a decisive battle in the Mexican War of Independence. It was fought in January 1811 on the banks of the Calderón River 60 km (37 mi) east of Guadalajara in present-day Zapotlanejo, Jalisco.
 W
WThe Capture of Mexicali, or the Battle of Mexicali, was the first action of the Mexican Revolution taken by rebel Magonistas against the federal Mexican government of Porfirio Diaz. Under the direction of Ricardo Flores Magón, a group of rebels captured the border town of Mexicali with little resistance.
 W
WThe Capture of Tucson was an uncontested United States entry into the Mexican city of Tucson, Sonora, now the present day Tucson, Arizona. The would-be combatants were provisional Mexican Army troops and the American Army's "Mormon Battalion". Tucson temporarily 'fell' in December 1846 without resistance but was immediately reoccupied two days later by the Mexican forces once the US troops moved on.
 W
WThe Battle of Casas Grandes was fought in March 1911 between the federal Mexican Army loyal to President Porfirio Diaz and rebels under Gen. Francisco Madero. Rebel forces attacked the town of Casas Grandes, Chihuahua, but were driven back by the federal garrison.
 W
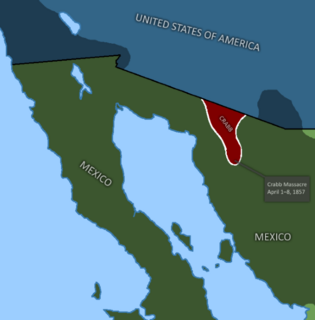
WThe Crabb massacre was the culmination of the eight-day Battle of Caborca. It was fought between Mexico and their O'odham allies against American forces in April 1857. Due to the outbreak of the Reform War in Mexico, the rebel Ygnacio Pesqueira invited the American politician Henry A. Crabb to colonize the northern frontier region in the state of Sonora, on the basis that the colonists would help Pesqueira fight in the civil war and against the Apache. However, when Crabb arrived in Mexico, his command was attacked and ultimately defeated. Some 50 survivors of the battle, out of about 85 men, were murdered by the Mexicans.
 W
WThe Crawford affair was a battle fought between Mexico and the United States in January 1886 during the Geronimo Campaign. Captain Emmet Crawford was commanding a company of Apache scouts, sixty miles southeast of Nacori Chico in Sonora, when his camp was attacked by Mexican Army militiamen. In the action, Crawford was shot and later died; his death nearly started a war between the United States and Mexico.
 W
WThe Battle of Cuautla was a battle between the forces of Emiliano Zapata and the federal army of the Mexican government that took place in the state of Morelos from May 11–19, 1911, during the Mexican Revolution. It has sometimes been described as "six of the most terrible days of battle in the whole Revolution". Eventually, the remains of the defending "Golden Fifth" regiment, the Fifth Cavalry Regiment of the Federal Army, withdrew and Zapata took control of the town. The Zapatista victory convinced Porfirio Díaz to come to terms with Francisco Madero, agree to the Treaty of Ciudad Juárez and resign as president.
 W
WThe Battle of El Maguey was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred on 2 May 1811 at El Maguey, in the State of Aguascalientes. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown, commanded by General Miguel Emparan, and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire, commanded by Ignacio López Rayón. The battle resulted in a victory for the Spanish royalists.
 W
WThe Battle of El Veladero was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred from 1810 through 30 April 1811 at Cerro El Veladero, Acapulco de Juárez. The battle was fought between royalist forces, loyal to the Spanish crown, commanded by Juan Antonio Fuentes, and Mexican rebels, commanded by José María Morelos and Rafael Valdovinos, fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. The rebels won.
 W
WThe Battle of Zitlala was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred on 26 October 1812 in the area around Escamela, Ixtaczoquitlán, Veracruz. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown, and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. The battle resulted in a victory for the Mexican rebels.
 W
WThe First Battle of Tijuana was an early engagement of the Mexican Revolution and the first significant victory for the Magonistas. Tijuana was captured and held by rebel forces on May 9, 1911 and was used as a haven for recruiting American volunteers from California.
 W
WThe Battle of Fortín was a minor clash between French and Mexican forces in the early stages of the Second French intervention in Mexico in 1862, and was the first outbreak of conflict between the two nations during the conflict. Following the breakdown of the French negotiations with the Mexican government both sides readied themselves for war. In the meantime, the French left 340 of their soldiers that had come done with illness and were recuperating in a French military hospital in Orizaba behind and marched towards Cordoba. The British and Spanish, unwilling to fight the Mexicans and having already negotiated a peaceful agreement with the Mexican government, began withdrawing on the same day of the skirmish. After the suspicious deaths of three French soldiers, General Charles de Lorencez became concerned about the fate of the sick in Orizaba. On the pretext that a letter from Mexican General Ignacio Zaragoza threatened their well-being, he sent his army to help them.
 W
WThe Battle of Goliad was the second skirmish of the Texas Revolution. In the early-morning hours of October 9, 1835, Texas settlers attacked the Mexican Army soldiers garrisoned at Presidio La Bahía, a fort near the Mexican Texas settlement of Goliad. La Bahía lay halfway between the only other large garrison of Mexican soldiers and the then-important Texas port of Copano.
 W
WEl Siege of Huajuapan de León was a battle of the Mexican War of Independence that was fought from 5 April to 23 July 1812 at Huajuapan de León, in the Mexican state of Oaxaca. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown, and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. This Spanish siege of the town, lasting 111 days, was the longest of the entire war. The battle resulted in a victory for the Mexican insurgents.
 W
WThe Battle of La Chincúa was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred from 19 April through 28 May 1813 at a ranch at Tonalá, Chiapas. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown, commanded by General Miguel Dambrini, and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire, commanded by Mariano Matamoros y Guridi. The battle resulted in a victory for the Mexican rebels.
 W
WThe Battle of Llanos de Santa Juana was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred on 12 July 1811 in the area around Cuauhtémoc, Colima known as Llanos de Santa Juana. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. The Mexican insurgents were commanded by General José Calixto Martínez y Moreno and the Spanish by Colonel Manuel del Río. The battle resulted in a victory for the Spanish royalists.
 W
WThe Battle of Lomas de Santa María was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred from 23–24 December 1813 in the area around Lomas de Santa María, in the municipality of Valladolid. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire.
 W
WThe Magonista Rebellion of 1911 was an early uprising of the Mexican Revolution organized by the Liberal Party of Mexico, which was only successful in northern Baja California. It is named after Ricardo Flores Magón, one of the leaders of the PLM. The Magonistas controlled Tijuana and Mexicali for about six months, beginning with the "liberation" of Mexicali on January 29, 1911. The rebellion was launched against the rule of Porfirio Díaz but was put down by forces loyal to Francisco I. Madero. Acting on a tip from Madero's agents, leaders of the Magonista movement were arrested in the United States.
 W
WThe Capture of Mazatlán was a Mexican victory during the Maximilian Affair. Mazatlán was a key port of the Pacific trade routes yielding between $4 and $5 million a year.
 W
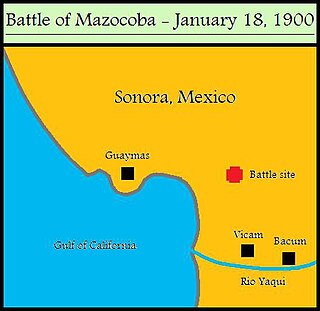
WThe Battle of Mazocoba, or the Mazocoba massacre, was a major engagement of the Yaqui Wars that was fought in Sonora, Mexico. On January 18, 1900, a Mexican Army expedition encountered hundreds of Yaqui renegades about twenty miles east of Guaymas. During the battle that followed, several hundred people were killed or wounded and over 1,000 Yaquis were taken prisoner.
 W
WThe Battle for Mexico City refers to the series of engagements from September 8 to September 15, 1847, in the general vicinity of Mexico City during the Mexican–American War. Included are major actions at the battles of Molino del Rey and Chapultepec, culminating with the fall of Mexico City. The U.S. Army under Winfield Scott scored a major success that ended the war.
 W
WThe Siege of Mexico City was an 1867 military engagement in the Second French intervention in Mexico between Mexican Republican forces, aided by the United States, and Emperor Maximilian's troops, aided by the French Empire and Austria-Hungary, encompassing in the siege of the city. It was the last armed conflict of the Second Mexican Empire and the fall of the city resulted in the transition of the Empire into the Republic led by Benito Juárez.
 W
WThe Mier expedition was an unsuccessful military operation launched in November 1842 by a Texian militia against Mexican border settlements; it was related to the Somervell expedition. It included a major battle at Ciudad Mier on December 26 and 27, 1842, which the Mexicans won. The Texian attack was launched partly in hopes of financial gain and partly in retaliation for the Dawson Massacre earlier that year, in which thirty-six Texas militia were killed by the Mexican Army. Both conflicts were part of continuing efforts by each side to control the land between the Rio Grande and Nueces River. The Republic of Texas believed that this territory had been ceded to it in the Treaties of Velasco, by which they gained independence; but Mexico did not agree.
 W
WThe Battle of Monte de las Cruces was one of the pivotal battles of the early Mexican War of Independence, in October 1810.
 W
WThe Battle of Naco, or the First Battle of Naco due to a later siege was a battle of the Mexican Revolution between Constitutionalist forces and Mexican government forces. Rebel forces under General Alvaro Obregon defeated the Mexican Army garrison and captured Naco, Sonora.
 W
WThe Capture of Oaxaca was a battle during the War of Mexican Independence that occurred on 25 November 1812 at Oaxaca, Oaxaca. It was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown, commanded by General Antonio Pío González-Saravia Mollinedo, and the Mexican insurgents fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire, commanded by José María Morelos y Pavón. The battle resulted in a victory for the Mexican insurgents.
 W
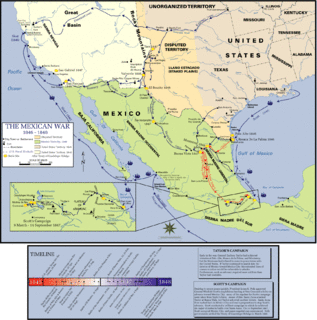
WThe Pacific Coast Campaign refers to United States naval operations against targets along Mexico's Pacific Coast during the Mexican–American War. It excludes engagements of the California Campaign in areas of The Californias north of the Baja California Peninsula. The objective of the campaign was to secure the Baja Peninsula of Mexico, and to blockade/capture west-coast ports of Mexico--especially Mazatlan, a major port-of-entry for imported supplies. The resistance of Mexican forces to the north in the Los Angeles area and the lack of ships, soldiers and logistical support prevented an early occupation of the peninsula and the west-coast Mexican seaports. The U.S. Navy attempted blockades of the ports three times before being able to successfully blockade and/or occupy them.
 W
WThe Battle of Puerto de Piñones was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred on 1 April 1811 at Puerto de Piñones, Coahuila. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown, commanded by José Manuel de Ochoa, and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire, commanded by Ignacio López Rayón. The battle resulted in a victory for the Mexican rebels.
 W
WThe Bombardment of Punta Sombrero was an American naval bombardment in response to a Mexican attack on a United States Navy warship during the Mexican–American War, on October 31, 1847.
 W
WThe Battle of Puruarán was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred on 5 January 1814 in the area around Puruarán, Michoacán. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. The Mexican insurgents were commanded by Mariano Matamoros y Guridi and the Spanish by Agustín Cosme Damián de Iturbide y Arámburu who would later go on to become the Mexican emperor, and by Ciriaco del Llano. The battle lasted approximately one hour and resulted in a victory for the Spanish Royalists.
 W
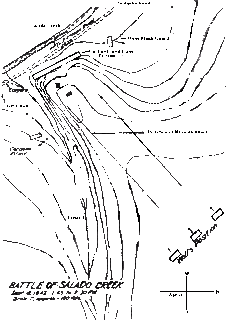
WThe Battle of Salado Creek was a decisive engagement in 1842 which repulsed the final Mexican invasion of the Republic of Texas. Colonel Mathew Caldwell of the Texas Rangers led just over 200 militia against an army of 1,600 Mexican Army soldiers and Cherokee warriors, and defeated them outside of San Antonio de Bexar along Salado Creek. As a result of this action, French-Mexican commander General Adrián Woll retreated south and back into Mexico.
 W
WThe Battle of San Juan Bautista was a battle in the Second French intervention in Mexico fought on February 27, 1864. Mexican Republicans were victorious and retook control of the city. The Republican forces consisted only of the Tabasquian militia from the surrounding areas ranging between 300 and 1,100 men, only half of whom were equipped with firearms the others fought with machetes.
 W
WThe Battle of San Pablo del Monte took place on May 5, 1863 during the Siege of Puebla (1863).
 W
WThe Battle of San Pedro was fought between the French and Mexican imperial forces and the Mexican Republicans during the Second French intervention in Mexico on 22 December 1864. The liberals achieved a decisive victory over the invading forces and captured the majority of the survivors.
 W
WThe Battle of Tacámbaro was a battle of the French Intervention in Mexico which took place on 11 April 1865 in the state of Michoacán in western Mexico. The battle, named after the town in which it was fought, pitted 300 members of the Belgian Legion supporting the Mexican Empire against approximately 3,000 Mexican republicans.
 W
WThe Battle of Tecualoya was a military action of the Mexican War of Independence fought between 17–20 January 1812 in the canyons of Tecualoya, Mexico. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. The Mexican insurgents were commanded by General Hermenegildo Galeana and the Spanish by Rosendo Porlier y Asteguieta. The battle resulted in a victory for Spanish loyalists.
 W
WThe Battle of Tenancingo was a military action of the Mexican War of Independence fought on 22 January 1812 on the outskirts of Tenancingo de Degollado, Mexico. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. The Mexican insurgents were commanded by General José María Morelos y Pavón and the Spanish by Rosendo Porlier y Asteguieta. The battle resulted in a victory for the Mexican rebels.
 W
WThe Battle of Temalaca was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred on 5 November 1815 in the area around Temalaca, Puebla. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. The Mexican insurgents were commanded by José María Morelos and the Spanish by Manuel de la Concha. The battle resulted in a victory for the Spanish Royalists.
 W
WThe Battle of Tenango del Valle was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred in May 1812 on the outskirts of Tenango del Valle, State of Mexico. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown, and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Tijuana was fought during the Mexican Revolution in June 1911. The opposing sides were rebel Magonistas and federal Mexican troops of President Francisco León de la Barra with American militia volunteers from Los Angeles, California. Tijuana was retaken by federal forces after a short battle just south of the town.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Topolobampo was a bloodless naval engagement during the Mexican Revolution. In March 1914, a rebel Constitutionalist gunboat attempted to break the blockade of Topolobampo, Sinaloa in Mexico. The attack forced federal gunboats to a further distance but failed to lift the blockade.
 W
WThe United States occupation of Veracruz began with the Battle of Veracruz and lasted for seven months, as a response to the Tampico Affair of April 9, 1914. The incident came in the midst of poor diplomatic relations between Mexico and the United States, and was related to the ongoing Mexican Revolution.
 W
WThe Yaqui Uprising, also called the Nogales Uprising, was an armed conflict that took place in the Mexican state of Sonora and the American state of Arizona over several days in August 1896. In February, the Mexican revolutionary Lauro Aguirre drafted a plan to overthrow the government of President Porfirio Díaz. Aguirre's cause appealed to the local Native Americans, such as the Yaqui, who organized an expedition to capture the customs house in the border town of Nogales on August 12.
 W
WThe Battle of Zacatecas was a military action of the Mexican War of Independence fought on 15 April 1811 at Zacatecas, Zacatecas. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. The Mexican insurgents were commanded by General Ignacio López Rayón and the Spanish by José Manuel de Ochoa. The battle resulted in a victory for rebel forces.
 W
WThe Battle of Zitácuaro was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred on 2 January 1812 in the area around Zitácuaro, Michoacán. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. The Mexican insurgents were commanded by General Ignacio López Rayón and the Spanish by Félix María Calleja. The battle resulted in a victory for the Spanish Royalists even in the face of overwhelming odds.
 W
WThe Battle of Zitlala was a battle of the War of Mexican Independence that occurred on 4 July 1812 on the outskirts of Zitlala, Guerrero. The battle was fought between the royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown, and the Mexican rebels fighting for independence from the Spanish Empire. The battle resulted in a victory for the Mexican rebels.