 W
WThis is a list of wars involving the Kingdom of Sweden. There are legendary accounts of Swedish kings well into prehistory and they are mentioned by Tacitus in his Germania, but St. Olof Skötkonung (995–1022) was the first ruler documented to have been accepted by both the Swedes around Lake Mälaren and by the Geats around Lake Vättern. The modern state of Sweden considers itself to have been established on 6 June 1523 by the acclamation of Gustav Vasa as king which finally ended the Kalmar Union with Denmark, although the current Swedish constitution dates to 1974.
 W
WDuring the Napoleonic Wars until 1810, Sweden and Great Britain were allies in the war against Napoleon. As a result of Sweden's defeat in the Finnish War and the Pomeranian War, and the following Treaty of Fredrikshamn and Treaty of Paris, Sweden declared war on Great Britain. The bloodless war, however, existed only on paper, and Britain was still not hindered in stationing ships at the Swedish island of Hanö and trade with the Baltic states.
 W
WThe First Barbary War (1801–1805), also known as the Tripolitanian War and the Barbary Coast War, was the first of two Barbary Wars, in which the United States and Sweden fought against the four North African states known collectively as the "Barbary States". Three of these were autonomous, but nominally provinces of the Ottoman Empire: Tripoli, Algiers, and Tunis. The fourth was the independent Sultanate of Morocco.
 W
WThe Swedish Wars on Bremen were fought between the Swedish Empire and the Hanseatic town of Bremen in 1654 and 1666. Bremen claimed to be subject to the Holy Roman Emperor, maintaining Imperial immediacy, while Sweden claimed Bremen to be a mediatised part of her dominions of Bremen-Verden, themselves territories immediately beneath the emperor. Sweden was able to gain some territory, but despite forcing a formal oath of allegiance on Bremen, did not gain control of the town.
 W
WThe Campaign of Grodno was a plan developed by Johann Patkul and Otto Arnold von Paykull during the Swedish invasion of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, a part of the Great Northern War. Its purpose was to crush Charles XII's army with overwhelming force in a combined offensive of Russian and Saxon troops. The campaign, executed by Peter I of Russia and Augustus II of Saxony, began in July 1705 and lasted almost a year. In divided areas the allies would jointly strike the Swedish troops occupied in Poland, in order to neutralize the influence the Swedes had in the Polish politics. However, the Swedish forces under Charles XII successfully outmaneuvered the allies, installed a Polish king in favor of their own and finally won two decisive victories at Grodno and Fraustadt in 1706. This resulted in the Treaty of Altranstädt (1706) in which Augustus renounced his claims to the Polish throne, broke off his alliance with Russia, and established peace between Sweden and Saxony.
 W
WThe Congo Crisis was a period of political upheaval and conflict in the Republic of the Congo between 1960 and 1965. The crisis began almost immediately after the Congo became independent from Belgium and ended, unofficially, with the entire country under the rule of Joseph-Désiré Mobutu. Constituting a series of civil wars, the Congo Crisis was also a proxy conflict in the Cold War, in which the Soviet Union and the United States supported opposing factions. Around 100,000 people are believed to have been killed during the crisis.
 W
WThe Count's Feud, also called the Count's War, was a war of succession that raged in Denmark in 1534–36 and brought about the Reformation in Denmark. In the international context, it was part of the European wars of religion. The Count's Feud takes its name from the Protestant Count Christopher of Oldenburg, who supported the Catholic King Christian II, deposed in 1523, over the election of Christian III, a staunch Protestant who had already implemented Lutheranism as the state religion in Schleswig and Holstein in 1528.
 W
WThe Cudgel War was a 1596/97 peasant uprising in Finland. The name of the uprising derives from the fact that the peasants armed themselves with various blunt weapons, such as cudgels, flails and maces, as they were seen as the most efficient weapons against their heavily armoured enemies. The yeomen also had swords, some firearms and two cannons at their disposal. Their opponents, the troops of Clas Eriksson Fleming, were professional, heavily armed and armoured men-at-arms.
 W
WThe Dacke War was a peasant uprising led by Nils Dacke in Småland, Sweden, in 1542 against the rule of Gustav Vasa. Dacke and his followers were dissatisfied with the heavy tax burden, the introduction of Lutheranism, and the confiscation of Church property. In 1543 the uprising was defeated, and Nils Dacke was killed.
 W
WThe Dano-Hanseatic War from 1426–1435 was an armed trade conflict between the Danish-dominated Kalmar Union and the German Hanseatic League (Hansa) led by the Free City of Lübeck.
 W
WThe Dano-Swedish War was the first war between Denmark and Sweden. The Danes invaded Sweden by sea, but were defeated early at the Battle of Brunkeberg, in which King Christian I of Denmark was wounded by a cannonball. The Danish invasion was repelled, and the Swedes were independent from the Kalmar Union.
 W
WThe Dano-Swedish War from 1501 to 1512 was a military conflict between Denmark and Sweden within the Kalmar Union.
 W
WThe Dano-Swedish War of 1657–58 was a conflict between Sweden and Denmark–Norway during the Second Northern War. In 1657, Charles X of Sweden and his Swedish army were bogged down in Poland. Frederick III of Denmark saw an opportunity to recover the territories lost in 1645 and attacked Sweden. The outbreak of war with Denmark provided Charles with an excuse to withdraw from the Polish campaign and move against Denmark.
 W
WThe Dano-Swedish War of 1658–1660 was a war between Denmark–Norway and Sweden. It was a continuation of an earlier conflict between the two belligerents which had ended just months earlier, after Sweden and Denmark brokered a peace agreement in Roskilde in 1658. In the aftermath of that conflict, the Swedish king Charles X Gustav desired to add the province of Royal Prussia in Poland to the Swedish realm, but his position in the region was not strong enough with the opposition of Brandenburg and Austria. However, the Danes stalled and prolonged the fulfillment of some provisions of the earlier peace; the Swedish king decided to use this as a pretext to attack with an ambitious goal: to vanquish Denmark as a sovereign state and raze the capital of Copenhagen. A quick and decisive defeat of Denmark was however only seen as a means to a greater end. The long-term goal was to wage war in Europe without fearing Danish interference.
 W
WThe Dano-Swedish War of 1808–1809 was a war between Denmark–Norway and Sweden due to Denmark–Norway's alliance with France and Sweden's alliance with the United Kingdom during the Napoleonic Wars. Neither Sweden nor Denmark-Norway had wanted war to begin with but once pushed into it through their respective alliances, Sweden made a bid to acquire Norway by way of invasion while Denmark-Norway made ill-fated attempts to reconquer territories lost to Sweden in the 17th century. Peace was concluded on grounds of status quo ante bellum on 10 December 1809.
 W
WThe De la Gardie campaign was a joint military campaign by the Tsardom of Russia and Sweden during the Polish–Muscovite War from April 1609 to June 1610.
 W
WThe term Deluge denotes a series of mid-17th-century campaigns in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In a wider sense it applies to the period between the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648 and the Truce of Andrusovo in 1667, thus comprising the Polish theatres of the Russo-Polish and Second Northern Wars. In a stricter sense, the term refers to the Swedish invasion and occupation of the Commonwealth as a theatre of the Second Northern War (1655–1660) only; in Poland and Lithuania this period is called the Swedish Deluge, or less commonly the Russo–Swedish Deluge due to the Russo-Polish War. The term deluge was popularized by Henryk Sienkiewicz in his novel The Deluge (1886).
 W
WThe Engelbrekt rebellion (Engelbrektsupproret) was an uprising during 1434–1436 led by Swedish miner and nobleman Engelbrekt Engelbrektsson and directed against Eric of Pomerania, the king of the Kalmar Union. The uprising, with its center in Dalarna and Bergslagen, spread throughout Svealand and Götaland. The rebellion caused erosion within the unity of the Kalmar Union, leading to the temporary expulsion of Danish forces from Sweden.
 W
WThe English Wars were a series of conflicts between the United Kingdom and Sweden with Denmark-Norway as part of the Napoleonic Wars. It is named after England, the common name in Scandinavia of the United Kingdom, which declared war on Denmark-Norway due to disagreements over the neutrality of Danish trade and to prevent the Danish fleet falling into the hands of the First French Empire. It began with the first battle of Copenhagen in 1801 and its latter stage from 1807 onwards was followed by the Gunboat War, the Dano-Swedish War of 1808–09 and the Swedish invasion of Holstein in 1814.
 W
WThe Finnish War was fought between the Kingdom of Sweden and the Russian Empire from 21 February 1808 to 17 September 1809. As a result of the war, the eastern third of Sweden was established as the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland within the Russian Empire. Other notable effects were the Swedish parliament's adoption of a new constitution and the establishment of the House of Bernadotte, the new Swedish royal house, in 1818.
 W
WThe Franco-Dutch War, often simply called the Dutch War, fought from 1672 to 1678, was a major conflict which pitted France against the Dutch Republic. It also involved many other European states, including the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, England, Sweden, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Norway. It was the first of the major European wars that marked the reign of Louis XIV of France.
 W
WThe Gulf War, codenamed Operation Desert Shield for operations leading to the buildup of troops and defense of Saudi Arabia and Operation Desert Storm in its combat phase, was a war waged by coalition forces from 35 nations led by the United States against Iraq in response to Iraq's invasion and annexation of Kuwait arising from oil pricing and production disputes.
 W
WThe Ingrian War between Sweden and Russia lasted between 1610 and 1617. It can be seen as part of Russia's Time of Troubles and is mainly remembered for the attempt to put a Swedish duke on the Russian throne. It ended with a large Swedish territorial gain in the Treaty of Stolbovo, which laid an important foundation to Sweden's Age of Greatness.
 W
WThe Kalmar War (1611–1613) was a war between Denmark–Norway and Sweden. Though Denmark soon gained the upper hand, it was unable to defeat Sweden entirely. The Kalmar War was the last time Denmark successfully defended its dominium maris baltici against Sweden, and it also marked the increasing influence of the two countries on Baltic politics.
 W
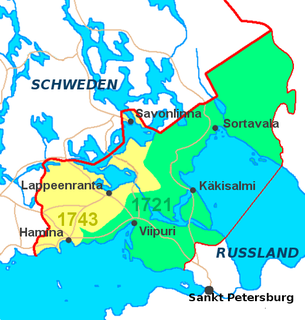
WThe attempt to create a Kingdom of Finland in 1742 is a little-known chapter in the history of Finland. Following the Russian occupation in the Russo-Swedish War (1741–1743) and vague promises of making the country independent, Finns elected the then Duke Peter of Holstein-Gottorp as the King of Finland. However, the political situation had outgrown the idea of Finnish independence and it quickly evaporated.
 W
WThe First Libyan Civil War was an armed conflict in 2011 in the North African country of Libya fought between forces loyal to Colonel Muammar Gaddafi and foreign supported groups seeking to oust his government. It erupted with the Libyan Revolution, also known as the 17 February Revolution. The war was preceded by protests in Zawiya on 8 August 2009 and finally ignited by protests in Benghazi beginning on Tuesday, 15 February 2011, which led to clashes with security forces that fired on the crowd. The protests escalated into a rebellion that spread across the country, with the forces opposing Gaddafi establishing an interim governing body, the National Transitional Council.
 W
WThe Livonian Crusade refers to the various Christianization campaigns in the area constituting modern Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia during the Papal-sanctioned Northern Crusades. It was conducted mostly by Germans from the Holy Roman Empire and Danes. It ended with the creation of the Terra Mariana and Duchy of Estonia. The lands on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea were the last corners of Europe to be Christianized.
 W
WThe Livonian War (1558–1583) was fought for control of Old Livonia, when the Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of Denmark–Norway, the Kingdom of Sweden, and the Union of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland.
 W
WThe Franco-Swedish War or Pomeranian War was the first involvement by Sweden in the Napoleonic Wars. The country joined the Third Coalition in an effort to defeat France under Napoleon Bonaparte.
 W
WThe Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire, the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, Savoy and Portugal. It was fought in Europe and the surrounding seas, in North America, and in India. It is sometimes considered the first global war. The conflict encompassed the Williamite war in Ireland and Jacobite risings in Scotland, where William III and James II struggled for control of England and Ireland, and a campaign in colonial North America between French and English settlers and their respective Indigenous allies, today called King William's War by Americans.
 W
WThe Northern Seven Years' War was fought between the Kingdom of Sweden and a coalition of Denmark–Norway, Lübeck, and Poland-Lithuania between 1563 and 1570. The war was motivated by the dissatisfaction of King Frederick II of Denmark with the dissolution of the Kalmar Union, and the will of King Eric XIV of Sweden to break Denmark's dominating position. The fighting continued until both armies had been exhausted, and many men died. The resulting Treaty of Stettin was a stalemate, with neither party gaining any new territory.
 W
WThe Great Northern War was the war fought between a coalition of Denmark–Norway, Russia and Saxony-Poland on one side and Sweden on the other side from 1700 to 1721. It started by a coordinated attack on Sweden by the coalition in 1700, and ended 1721 with the conclusion of the Treaty of Nystad, and the Stockholm Treaties. As a result of the war, Russia supplanted Sweden as the dominant power on the shores of the Baltic Sea, becoming a major player in European politics.
 W
WThe Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Saxony–Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715.
 W
WThe Polish–Swedish War (1600–1611) was a continuation of struggle between Sweden and Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth over control of Livonia and Estonia, as well as the dispute over the Swedish throne between Charles IX of Sweden and Sigismund III of Poland.
 W
WThe Polish–Swedish War (1617–18) was a phase of the longer Polish–Swedish War (1600–29). It continued the war of 1600–11 and was an attempt by Sweden to take Polish pressure off Russia. The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was then also fighting Tartars and the Ottoman Empire. Russia and Sweden were at that stage allied, prior to the Ingrian War, part of Russia's Time of Troubles. The 1617–18 war's cause was a dispute over Livonia and Estonia, and a dispute between Sigismund III Vasa and Gustavus Adolphus over the Swedish throne.
 W
WThe Polish–Swedish War of 1621 to 1625 was a war in a long-running series of conflicts between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Swedish Empire. It began with a Swedish invasion of the Polish–Lithuanian fiefdom Livonia. Swedish forces succeeded in taking the city of Riga after a siege. The Commonwealth, focussed on war with the Ottoman Empire, was unable to send significant forces to stop Gustav Adolf, and signed a truce favorable to Sweden. The Commonwealth ceded Livonia north of the Dvina (Düna) river, and retained only nominal control over Riga. The new truce in Mitau was signed and lasted from November 1622 to March 1625.
 W
WThe Swedish invasion of Poland (1701–1706), also known as Charles XII's invasion of Poland or the Polish front of the Great Northern War, was a conflict in eastern Europe overshadowed by the ongoing Great Northern War fought between the Swedish Empire against the Russian Empire, Denmark-Norway, Saxony and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Polish front was a major part of the greater conflict, and it included some decisive battles in favor of the Swedes that contributed to the length of the war.
 W
WThe Pomeranian War was a theatre of the Seven Years' War. The term is used to describe the fighting between Sweden and Prussia between 1757 and 1762 in Swedish Pomerania, Prussian Pomerania, northern Brandenburg and eastern Mecklenburg-Schwerin.
 W
WThe Russo-Swedish War of 1788–1790, known as Gustav III's Russian War in Sweden, Gustav III's War in Finland and Catherine II's Swedish War in Russia, was fought between Sweden and Russia from June 1788 to August 1790.
 W
WThe Scanian War was a part of the Northern Wars involving the union of Denmark–Norway, Brandenburg and Sweden. It was fought from 1675 to 1679 mainly on Scanian soil, in the former Danish and Norway provinces along the border with Sweden, and in Northern Germany. While the latter battles are regarded as a theater of the Scanian war in English, Danish, Norwegian and Swedish historiography, they are seen as a separate war in German historiography, called the Swedish-Brandenburgian War.
 W
WSecond Danish-Hanseatic War was a war between Denmark and the Hanseatic League from August 1361 to May 1370. The Hanseatic League, supported by Sweden, Mecklenburg, Holstein and some Danish nobles, attacked Valdemar IV. In 1368, the Hanseatic League invaded Copenhagen and finally forced Denmark to sign Treaty of Stralsund.
 W
WThe Second Northern War was fought between Sweden and its adversaries the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1655–60), the Moscow Tsardom (1656–58), Brandenburg-Prussia (1657–60), the Habsburg Monarchy (1657–60) and Denmark–Norway. The Dutch Republic often intervened against Sweden in an informal trade war but was not a recognized part of the Polish–Danish alliance.
 W
WThe Swedish War of Liberation, also known as Gustav Vasa's Rebellion and the Swedish War of Secession, was a rebellion and a civil war in which the nobleman Gustav Vasa successfully deposed King Christian II from the throne of Sweden, ending the Kalmar Union between Sweden, Norway, and Denmark.
 W
WThe Swedish–Norwegian War, also known as the Campaign against Norway, War with Sweden 1814, or the Norwegian War of Independence, was a war fought between Sweden and Norway in the summer of 1814. The war was a Swedish victory and led to Norway being forced into the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway, a union with Sweden under the Swedish king Charles XIII but with Norway having its own constitution and parliament.
 W
WThe Theatre War, Cowberry War, Cranberry War or Lingonberry War, was a brief war between Denmark–Norway and Sweden, starting on 24 September 1788, formally lasting until 9 July 1789. Although the decision to launch the attack was taken in Denmark, the majority of the attacking soldiers were Norwegians from the Danish-Norwegian army.
 W
WThe Torstenson war, Hannibal controversy or Hannibal War was a short period of conflict between Sweden and Denmark–Norway from 1643 to 1645 towards the end of the Thirty Years' War. The names refer to Swedish general Lennart Torstenson and Norwegian governor-general Hannibal Sehested.
 W
WThe war against Sigismund was a war between Duke Charles, later King Charles IX and Sigismund, King of Sweden and Poland. Lasting from 1598 to 1599, it is also called War of Deposition against Sigismund, since the focus of the conflicts was the attempt to depose the latter from the throne of Sweden. The war eventually resulted in the deposition of Sigismund, with Duke Charles taking over the government and later also acceding to the throne.
 W
WThe War of Deposition against King Hans was a war in which Swedish separatists under the leadership of the Swedish regent Sten Sture the Elder rebelled against the newly elected king of the Kalmar Union, John, King of Denmark.