 W
WAdvanced Extremely High Frequency (AEHF) is a series of communications satellites operated by the United States Space Force. They will be used to relay secure communications for the Armed Forces of the United States, the British Armed Forces, the Canadian Armed Forces, the Royal Netherlands Armed Forces and the Australian Defence Force. The system will consist of six satellites in geostationary orbits. The final satellite was launched on 26 March 2020. AEHF is backward compatible with, and will replace, the older Milstar system and will operate at 44 GHz Uplink and 20 GHz Downlink. The AEHF system is a joint service communications system that will provide survivable, global, secure, protected, and jam-resistant communications for high-priority military ground, sea and air assets.
 W
WAdvanced Extremely High Frequency (AEHF) is a series of communications satellites operated by the United States Space Force. They will be used to relay secure communications for the Armed Forces of the United States, the British Armed Forces, the Canadian Armed Forces, the Royal Netherlands Armed Forces and the Australian Defence Force. The system will consist of six satellites in geostationary orbits. The final satellite was launched on 26 March 2020. AEHF is backward compatible with, and will replace, the older Milstar system and will operate at 44 GHz Uplink and 20 GHz Downlink. The AEHF system is a joint service communications system that will provide survivable, global, secure, protected, and jam-resistant communications for high-priority military ground, sea and air assets.
 W
WAir Force Space Command (AFSPC) was a major command of the United States Air Force from September 1982 to December 2019. On 20 December 2019, concurrent with the signing of the National Defense Authorization Act for 2020, it was re-designated as the United States Space Force and became a new sixth service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for space warfare.
 W
WThe Boeing X-40A Space Maneuver Vehicle was a test platform for the X-37 Future-X Reusable Launch Vehicle.
 W
WThe Corona program was a series of American strategic reconnaissance satellites produced and operated by the Central Intelligence Agency Directorate of Science & Technology with substantial assistance from the U.S. Air Force. The Corona satellites were used for photographic surveillance of the Soviet Union (USSR), the People's Republic of China, and other areas beginning in June 1959 and ending in May 1972.
 W
WThe Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) monitors meteorological, oceanographic, and solar-terrestrial physics for the United States Department of Defense. The program is managed by the Air Force Space Command with on-orbit operations provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The mission of the satellites was revealed in March 1973. They provide cloud cover imagery from polar orbits that are Sun-synchronous at nominal altitude of 450 nautical miles (830 km).
 W
WThe Defense Satellite Communications System (DSCS) provides the United States with military communications to support globally distributed military users. Beginning in 2007, DSCS is being replaced by the Wideband Global SATCOM system. A total of 14 DSCS-III satellites were launched between the early 1980s and 2003. Two satellites were launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis in 1985 during the STS-51-J flight. As of 23 November 2015, seven DSCS-III satellites were still operational. DSCS operations are currently run by the 4th Space Operations Squadron out of Schriever Air Force Base.
 W
WThe Defense Support Program (DSP) is a program of the USAF that operated the reconnaissance satellites which form the principal component of the Satellite Early Warning System used by the United States.
 W
WDelta is an American versatile family of expendable launch systems that has provided space launch capability in the United States since 1960. More than 300 Delta rockets have been launched with a 95% success rate. Only the Delta IV Heavy rocket remains in use as of September 2020. Delta rockets are currently manufactured and launched by the United Launch Alliance.
 W
WDelta IV is a group of five expendable launch systems in the Delta rocket family introduced in the early 2000s. Originally designed by Boeing's Defense, Space and Security division for the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) program, the Delta IV became a United Launch Alliance (ULA) product in 2006. The Delta IV is primarily a launch vehicle for United States Air Force (USAF) military payloads, but has also been used to launch a number of United States government non-military payloads and a single commercial satellite.
 W
WThe Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) monitors meteorological, oceanographic, and solar-terrestrial physics for the United States Department of Defense. The program is managed by the Air Force Space Command with on-orbit operations provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The mission of the satellites was revealed in March 1973. They provide cloud cover imagery from polar orbits that are Sun-synchronous at nominal altitude of 450 nautical miles (830 km).
 W
WThe GEOSAT was a U.S. Navy Earth observation satellite, launched on March 12, 1985 into an 800 km, 108° inclination orbit, with a nodal period of about 6040 seconds. The satellite carried a radar altimeter capable of measuring the distance from the satellite to sea surface with a relative precision of about 5 cm. The initial phase was an 18-month classified Geodetic Mission (GM) have a ground-track with a near-23-day repeat with closure to within 50 kilometers. The effect of atmospheric drag was such that by fall 1986 GEOSAT was in an almost exact 23-day repeat orbit.
 W
WISAT is a spacecraft developed by the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory's Space Vehicles Directorate to test technology for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance spacecraft.
 W
WLacrosse or Onyx is a series of terrestrial radar imaging reconnaissance satellites operated by the United States National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). While not officially confirmed by the NRO or the Government of the United States prior to 2008, there was widespread evidence pointing to its existence, including one NASA website. In July 2008, the NRO itself declassified the existence of its synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite constellation.
 W
WThe Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) was part of the United States Air Force (USAF) human spaceflight program. The project was developed from early USAF concepts of crewed space stations to be used for satellite reconnaissance purposes, and was a successor to the canceled Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar military reconnaissance space plane. MOL evolved into a single-use laboratory, for which crews would be launched on 30-day missions, and return to Earth using a Gemini B spacecraft derived from NASA's Gemini spacecraft.
 W
WMilstar is a constellation of military communications satellites in geosynchronous orbit, which are operated by the United States Air Force, and provide secure and jam-resistant worldwide communications to meet the requirements of the Armed Forces of the United States. Six spacecraft were launched between 1994 and 2003, of which five are currently operational; the third launch failed, both damaging the satellite and leaving it in an unusable orbit.
 W
WThe Missile Defense Alarm System, or MIDAS, was a United States Air Force Air Defense Command system of 12 early-warning satellites that provided limited notice of Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile launches between 1960 and 1966. Originally intended to serve as a complete early-warning system working in conjunction with the Ballistic Missile Early Warning System, cost and reliability concerns limited the project to a research and development role. Three of the system's 12 launches ended in failure, and the remaining nine satellites provided crude infrared early-warning coverage of the Soviet Union until the project was replaced by the Defense Support Program. MiDAS represented one element of the United States's first generation of reconnaissance satellites that also included the Corona and SAMOS series. Though MIDAS failed in its primary role as a system of infrared early-warning satellites, it pioneered the technologies needed in successor systems.
 W
WThe Micro-satellite Technology Experiment (MiTEx) is a microsatellite-based mission launched into geosynchronous orbit 21 June 2006 aboard a Delta II rocket. The USAF described the mission as a "technology demonstration" for the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), the United States Air Force (USAF) and the United States Navy.
 W
WThe Mobile User Objective System is a narrowband military communications satellite system that supports a worldwide, multi-Service population of users in the ultra high frequency band. The system provides increased communications capabilities to newer, smaller terminals while still supporting interoperability with legacy terminals. MUOS is designed to support users who require greater mobility, higher bit rates and improved operational availability.
 W
WThe Naval Ocean Surveillance System (NOSS) is a series of signals intelligence satellites that have conducted electronic signals intelligence for the U.S. Navy since the early 1970s. The first series of satellites were codenamed "White Cloud" or "PARCAE", while second and third-generation satellites have used the codenames "Ranger" and "Intruder".
 W
WThe Naval Space Command (NSC) was a military command of the United States Navy and former component command of United States Space Command. It was headquartered at Dahlgren, Virginia, USA, and began operations on 1 October 1983. Naval Space Command used space capabilities to support naval forces through the operation of reconnaissance and communications satellites, as well as representing the Navy's space interests, both within the Navy and within U.S. Space Command.
 W
WOPS 0855, also designated OV4-3, was an American boilerplate Manned Orbiting Laboratory spacecraft launched in 1966. It was flown to demonstrate the launch configuration for future MOL missions. A number of research payloads, designated Manifold, were carried on board, which were intended to operate for 75 days. However, the spacecraft ceased operations after just 30. It was built from a decommissioned HGM-25A Titan I first stage oxidizer tank, bolted to a Transtage. It was part of the MOL and Orbiting Vehicle projects.
 W
WOrbital Express was a space mission managed by the United States Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and a team led by engineers at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Orbital Express program was aimed at developing "a safe and cost-effective approach to autonomously service satellites in orbit". The system consisted of two spacecraft: the ASTRO servicing satellite, and a prototype modular next-generation serviceable satellite; NEXTSat. The mission launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on 8 March 2007, aboard an Atlas V expendable launch vehicle. The launch was part of the United States Air Force Space Test Program STP-1 mission.
 W
WRepair Satellite Prototype (RSat-P) is a microsatellite built by the United States Naval Academy (USNA) in Annapolis, Maryland. The small spacecraft is a 3U CubeSat intended to demonstrate capabilities for minor in-orbit repair of a much larger, conventional spacecraft.
 W
WThe Seal of the United States Space Force is the official seal of the U.S. Space Force, the space warfare service branch of the U.S. Armed Forces. The seal itself was approved on 15 January 2020.
 W
WThe Space Force Delta is the official logo of the U.S. Space Force, the space warfare service branch of the U.S. Armed Forces. The delta itself was unveiled on 22 July 2020.
 W
WThe Space-Based Infrared System (SBIRS) is a consolidated system intended to meet the United States' infrared space surveillance needs through the first two to three decades of the 21st century. The SBIRS program is designed to provide key capabilities in the areas of missile warning, missile defense and battlespace characterization via satellites in geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO), sensors hosted on satellites in highly elliptical orbit (HEO), and ground-based data processing and control. SBIRS ground software integrates infrared sensor programs of the U.S. Air Force (USAF) with new IR sensors.
 W
WThe Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), nicknamed the "Star Wars program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons. The concept was first announced on March 23, 1983 by President Ronald Reagan, a vocal critic of the doctrine of mutually assured destruction (MAD), which he described as a "suicide pact", and called upon US scientists and engineers to develop a system that would render nuclear weapons obsolete.
 W
WThor was a US space launch vehicle derived from the PGM-17 Thor intermediate-range ballistic missile. The Thor rocket was the first member of the Delta rocket family of space launch vehicles. The last launch of a direct derivative of the Thor missile occurred in 2018 as the first stage of the final Delta II.
 W
WThor-Agena was a series of orbital launch vehicles. The rockets used Thor first stages and Agena second stages. They are thus cousins of the more-famous Thor-Deltas, which founded the Delta rocket family. The first attempted launch of a Thor-Agena was in January 1959. The first successful launch was on February 28, 1959, launching Discoverer 1. It was the first two-stage rocket to place a satellite into orbit.
 W
WTitan was a family of United States expendable rockets used between 1959 and 2005. Titan I and Titan II were part of the US Air Force's intercontinental ballistic missile fleet until 1987. The space launch vehicle versions contributed the majority of the 368 Titan launches, including all the Project Gemini crewed flights of the mid-1960s. Titan vehicles were also used to lift US military payloads as well as civilian agency intelligence-gathering satellites and to send highly successful interplanetary scientific probes throughout the Solar System.
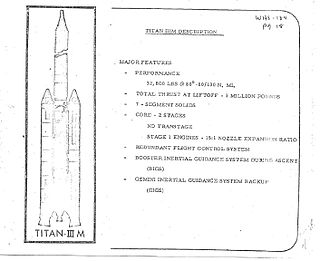 W
WThe Titan IIIM was a planned American expendable launch system, intended to launch the Manned Orbiting Laboratory and other payloads. Development was cancelled in 1969. The projected UA1207 solid booster rockets were eventually used on the Titan IV.
 W
WThe Transit system, also known as NAVSAT or NNSS, was the first satellite navigation system to be used operationally. The system was primarily used by the U.S. Navy to provide accurate location information to its Polaris ballistic missile submarines, and it was also used as a navigation system by the Navy's surface ships, as well as for hydrographic survey and geodetic surveying. Transit provided continuous navigation satellite service from 1964, initially for Polaris submarines and later for civilian use as well.
 W
WThe Ultra High Frequency Follow-On (UFO) system is a United States Department of Defense (DOD) program sponsored and operated by the U.S. Navy to provide communications for airborne, ship, submarine and ground forces. The UFO constellation replaced the U.S. DOD Fleet Satellite Communications System (FLTSATCOM) constellation and will consist of eleven satellites. The ground terminal segment consists of equipment and resident personnel at existing satellite communication stations. The spacecraft are controlled by the Naval Satellite Operations Center (NAVSOC) located at the Naval Base Ventura County, Point Mugu, CA.
 W
WThe United States Space Force (USSF) is the space service branch of the U.S. Armed Forces, and is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services. Initially formed as Air Force Space Command on 1 September 1982, the Space Force was established as an independent military branch on 20 December 2019, with the signing of the United States Space Force Act, part of the National Defense Authorization Act for 2020.
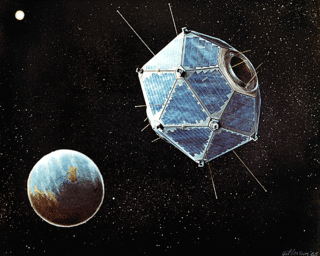 W
WVela was the name of a group of satellites developed as the Vela Hotel element of Project Vela by the United States to detect nuclear detonations to monitor compliance with the 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty by the Soviet Union.
 W
WVela 1A was a military satellite developed to detect nuclear detonations to monitor compliance with the 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty by the Soviet Union.
 W
WVela 1B was a military satellite developed to detect nuclear detonations to monitor compliance with the 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty by the Soviet Union.
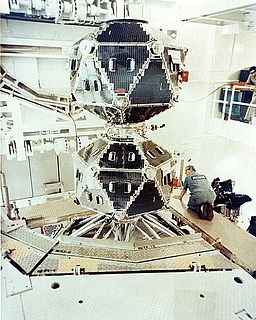 W
WVela 2A, also known as Vela 3, Vela Hotel 3 and OPS 3662, was a U.S. military satellite developed to detect nuclear detonations to monitor compliance with the 1963 Partial Test Ban Treaty by the Soviet Union. The secondary task of the ship was space research.
 W
WVela 2B was a U.S. reconnaissance satellite for detecting explosions and nuclear tests on land and in space, the first of the second pair of Vela series satellites, taken together with Vela 2A and ERS 13 satellites. The secondary task of the ship was space research.
 W
WVela 3A was a U.S. reconnaissance satellite to detect explosions and nuclear tests on land and in space; the first of the third pair of Vela series satellites; taken together with Vela 3B and ERS 17 satellites.
 W
WVela 3B was a U.S. reconnaissance satellite to detect explosions and nuclear tests on land and in space; the first of the third pair of Vela series satellites; taken together with Vela 3A and ERS 17 satellites.
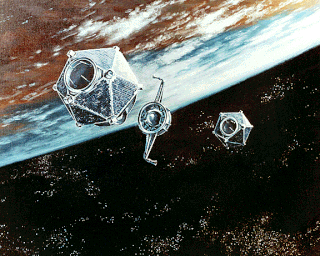 W
WVela 5A was an American reconnaissance satellite to detect explosions and nuclear tests on land and in space. It was released together with Vela 5B, OV5 5, OV5 6 and OV5 9.
 W
WThe Wideband Global SATCOM system (WGS) is a high capacity satellite communications system planned for use in partnership by the United States Department of Defense (DoD), Canadian Department of National Defence (DND) and the Australian Department of Defence. The system is composed of the Space Segment satellites, the Terminal Segment users and the Control Segment operators.
 W
WThe Boeing X-37, also known as the Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV), is a reusable robotic spacecraft. It is boosted into space by a launch vehicle, then re-enters Earth's atmosphere and lands as a spaceplane. The X-37 is operated by the United States Space Force for orbital spaceflight missions intended to demonstrate reusable space technologies. It is a 120-percent-scaled derivative of the earlier Boeing X-40. The X-37 began as a NASA project in 1999, before being transferred to the United States Department of Defense in 2004.