 W
WThe Battle of the Berlin Outposts and Bunker City was a battle fought between 7 and 27 July 1953 during the Korean War between United Nations Command (UN) and Chinese forces over several frontline outposts.
 W
WThe Battle of the Ch'ongch'on River, also known as the Battle of the Ch'ongch'on, was a decisive battle in the Korean War, and it took place from November 25 to December 2, 1950, along the Ch'ongch'on River Valley in the northwestern part of North Korea. In response to the successful Chinese First Phase Campaign against the United Nations (UN) forces, General Douglas MacArthur launched the Home-by-Christmas Offensive to expel the Chinese forces from Korea and to end the war. Anticipating this reaction, the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) Commander Peng Dehuai planned a counteroffensive, dubbed the "Second Phase Campaign", against the advancing UN forces.
 W
WThe Chinese Spring Offensive, also known as the Chinese Fifth Phase Offensive, was a military operation conducted by the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) during the Korean War. Mobilizing three field armies totaling 700,000 men for the operation, the Chinese command conducted their largest offensive operation since their Second Phase Offensive in November and December 1950. The operation took place in the summer of 1951 and aimed at permanently driving the United Nations Command (UN) forces off the Korean peninsula.
 W
WThe Battle of Chipyong-ni, also known as the Battle of Dipingli, was a decisive battle of the Korean War, that took place from 13–15 February 1951 between US and French units of the US 23rd Infantry Regiment and various units of the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) around the village of Chipyong-ni. The result was a United Nations Command victory. The battle, along with the Third Battle of Wonju, has been called "the Gettysburg of the Korean War," and represents the "high-water mark" of the Chinese invasion of South Korea. Due to the ferocity of the Chinese attack and the heroism of the defenders, the battle has also been called "one of the greatest regimental defense actions in military history."
 W
WThe Battle of Chosin Reservoir, also known as the Chosin Reservoir Campaign or the Battle of Jangjin Lake was an important battle in the Korean War. The name "Chosin" is derived from the Japanese pronunciation "Chōshin", instead of the Korean pronunciation.
 W
WThe Battle of Haktang-Ni was a skirmish in the Korean War fought between a largely Belgian United Nations Command (UN) contingent and Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) forces between 9–13 October 1951, just north of the city of Chorwon.
 W
WThe Naval Battle of the Han River was fought during the Korean War. The main fighting occurred after an Australian frigate was attacked by communist Chinese forces while transiting the Han River in Korea. Up until that time United Nations (UN) warships had operated on the river with only limited Chinese resistance. Following the engagement UN naval forces continued to operate on the Han, although riverine operations were suspended two months later. Four Australians were wounded during the engagement, while Chinese casualties have been estimated at around 40 killed and several guns destroyed.
 W
WThe Battle of Heartbreak Ridge, also known as the Battle of Wendengli, was a month-long battle in the Korean War which took place between 13 September and 15 October 1951. After withdrawing from Bloody Ridge, the Korean People's Army (KPA) set up new positions just 1,500 yards (1,400 m) away on a 7-mile (11 km) long hill mass. If anything, the defenses were even more formidable here than on Bloody Ridge.
 W
WThe Battle of Hill Eerie refers to several Korean War engagements between the United Nations Command (UN) forces and the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) in 1952 at Hill Eerie, a military outpost about 10 miles (16 km) west of Ch'orwon. It was taken several times by both sides; each sabotaging the others' position.
 W
WThe Battle of Hoengsong was a battle during the Korean War that took place between February 11 - 15, 1951. It was part of the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) Fourth Phase Offensive and was fought between the PVA and United Nations forces. After being pushed back northward by the UN's Operation Thunderbolt counteroffensive, the PVA was victorious in this battle, inflicting heavy casualties on the UN forces in the two days of fighting and temporarily regaining the initiative.
 W
WThe Third Battle of the Hook was a battle of the Korean War that took place between a United Nations Command (UN) force, consisting mostly of British troops, supported on their flanks by American and Turkish units against a predominantly Chinese force.
 W
WThe Second Battle of the Hook was a battle fought between 18 and 19 November 1952 during the Korean War between elements of United Nations Command (UN) troops consisting of British troops of the 1st Commonwealth Division and Chinese forces on a vital sector known as the "Hook" position which was the scene of much bitter fighting before and in the ensuing months. Attacking Chinese forces attempted to take the strategic position but were repelled by a combination of heavy firepower and effective counterattacks.
 W
WThe Hungnam evacuation, also known as the Miracle of Christmas, was the evacuation of United Nations (UN) forces and North Korean civilians from the port of Hungnam, North Korea, between 15 and 24 December 1950 during the Korean War. Following the defeat of UN forces during the Battle of the Chosin Reservoir, by part of the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) in the Second Phase Campaign, UN forces had retreated to Hungnam from where they were evacuated to South Korea.
 W
WThe Battle of Hwacheon was a battle fought between 22 and 26 April 1951 during the Korean War between United Nations Command (UN) and Chinese forces during the Chinese Spring Offensive. The US 1st Marine Division successfully defended their positions and then withdrew under fire to the No-Name Line.
 W
WThe Battle of the Imjin River, also known as the Battle of Solma-ri or Battle of Gloster Hill in South Korea, or as Battle of Xuemali in China, took place 22–25 April 1951 during the Korean War. Troops from the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) attacked United Nations Command (UN) positions on the lower Imjin River in an attempt to achieve a breakthrough and recapture the South Korean capital Seoul. The attack was part of the Chinese Spring Offensive, the aim of which was to regain the initiative on the battlefield after a series of successful UN counter-offensives in January–March 1951 had allowed UN forces to establish themselves beyond the 38th Parallel at the Kansas Line.
 W
WThe Battle of Kapyong, also known as the Battle of Jiaping, was fought during the Korean War between United Nations Command (UN) forces—primarily Canadian, Australian, and New Zealand—and the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA). The fighting occurred during the Chinese Spring Offensive and saw the 27th British Commonwealth Brigade establish blocking positions in the Kapyong Valley, on a key route south to the capital, Seoul. The two forward battalions—3rd Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment and 2nd Battalion, Princess Patricia's Canadian Light Infantry —supported by an artillery battery from the Royal Regiment of New Zealand Artillery, occupied positions astride the valley and hastily developed defences. As thousands of soldiers from the Republic of Korea Army (ROK) began to withdraw through the valley, the PVA infiltrated the brigade position under the cover of darkness, and assaulted the Australians on Hill 504 during the evening and into the following day.
 W
WThe First Battle of Maryang-san, also known as the Defensive Battle of Maliangshan, was fought during the Korean War between United Nations Command (UN) forces—primarily Australian and British—and the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA). The fighting occurred during a limited UN offensive by US I Corps, codenamed Operation Commando. This offensive ultimately pushed the PVA back from the Imjin River to the Jamestown Line and destroyed elements of four PVA armies following heavy fighting. The much smaller battle at Maryang San took place over a five-day period, and saw the 3rd Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment dislodge a numerically superior PVA force from the tactically important Kowang san and Maryang san features, in conjunction with other units of the 1st Commonwealth Division.
 W
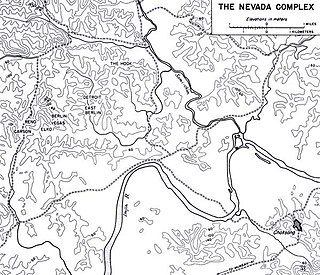
WThe Battle of the Nevada Complex was a battle fought between 25 and 29 May 1953 during the Korean War between United Nations Command (UN) and Chinese forces over several frontline outposts. After suffering heavy losses the UN abandoned the positions.
 W
WThe Battle of the Noris was a battle fought between 11 and 14 December 1952 during the Korean War between South Korean and Chinese forces on two adjacent hills known as Big Nori and Little Nori.
 W
WThe Battle of Old Baldy refers to a series of five engagements for Hill 266 in west-central Korea. They occurred over a period of 10 months in 1952–1953, though there was also vicious fighting both before and after these engagements.
 W
WThe Battle of Onjong, also known as the Battle of Wenjing, was one of the first engagements between Chinese and United Nations (UN) forces during the Korean War. It took place around Onjong in present-day North Korea from 25 to 29 October 1950. As the main focus of the Chinese First Phase Offensive, the People's Volunteer Army (PVA) 40th Corps conducted a series of ambushes against the Republic of Korea Army (ROK) II Corps, effectively destroying the right flank of the United States Eighth Army while stopping the UN advance north toward the Yalu River.
 W
WThe Battle of Outpost Kelly was a battle fought between 17 and 24 September 1952 during the Korean War between United Nations Command (UN) and Chinese forces for possession of a UN outpost position. The Chinese successfully seized the position and defended it against UN counterattacks. The battle is noted as the defending UN force had been largely composed of Spanish-speaking Puerto Ricans.
 W
WThe Battle for Outpost Vegas was a battle during the Korean War between the armed forces of the United Nations Command (UN) and China from 26 to 30 March 1953, four months before the end of the Korean War. Vegas was one of three outposts called the Nevada Cities north of the Main Line of Resistance (MLR), the United Nations defensive line which stretched roughly around the latitude 38th Parallel. Vegas, and the outposts it supported, Reno and Carson, were manned by elements of the 1st Marine Division. On 26 March 1953 the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) launched an attack on the Nevada Cities, including Vegas, in an attempt to better the position of China and North Korea in the Panmunjon peace talks which were occurring at the time, and to gain more territory for North Korea when its borders would be solidified. The battle raged for five days until PVA forces halted their advance after capturing one outpost north of the MLR on 30 March, but were repelled from Vegas. The battle for Outpost Vegas and the surrounding outposts are considered the bloodiest fighting to date in western Korea during the Korean War. It is estimated that there were over 1,000 American casualties and twice that number of Chinese during the Battle for Outpost Vegas. The battle is also known for the involvement of Sergeant Reckless, a horse in a USMC recoilless rifle platoon who transported ammunition and the wounded during the U.S. defense of outpost Vegas.
 W
WThe Battle of Pakchon, also known as the Battle of Bochuan, took place ten days after the start of the Chinese First Phase Offensive, following the entry of the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) into the Korean War. The offensive reversed the United Nations Command (UN) advance towards the Yalu River which had occurred after their intervention in the wake of the North Korean invasion of South Korea at the start of the war. The battle was fought between British and Australian forces from the 27th British Commonwealth Brigade with American armour and artillery in support, and the PVA 117th Division of the 39th Army, around the village of Pakchon on the Taeryong River. After capturing Chongju on 30 October the British and Australians had been ordered to pull back to Pakchon in an attempt to consolidate the western flank of the US Eighth Army. Meanwhile, immediately following their success at Unsan against the Americans, the PVA 117th Division had attacked southward, intending to cut off the UN forces as they withdrew in the face of the unexpected PVA assault. To halt the PVA advance, the 27th British Commonwealth Brigade was ordered to defend the lower crossings of the Taeryong and Chongchon rivers as part of a rearguard, in conjunction with the US 24th Infantry Division further upstream on the right.
 W
WThe Battle of Pork Chop Hill comprises a pair of related Korean War infantry battles during April and July 1953. These were fought while the United Nations Command (UN) and the Chinese and North Koreans negotiated the Korean Armistice Agreement. In the U.S., they were controversial because of the many soldiers killed for terrain of no strategic or tactical value, although the Chinese lost many times the number of US soldiers killed and wounded. The first battle was described in the eponymous history Pork Chop Hill: The American Fighting Man in Action, Korea, Spring 1953, by S.L.A. Marshall, from which the film Pork Chop Hill was drawn. The UN won the first battle but the Chinese won the second battle.
 W
WThe Battle of the Samichon River was fought during the final days of the Korean War between United Nations (UN) forces—primarily Australian and American—and the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA). The fighting took place on a key position on the Jamestown Line known as The Hook and saw the defending UN troops, including the 2nd Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment from the 28th British Commonwealth Brigade and the US 7th Marine Regiment, fight off numerous assaults by the PVA 137th Division during two concerted night attacks, inflicting numerous casualties on the PVA with heavy artillery and small arms fire. The action was part of a larger, divisional-sized PVA attack against the US 1st Marine Division, with diversionary assaults mounted against the Australians. With the peace talks in Panmunjom reaching a conclusion, the Chinese had been eager to gain a last-minute victory over the UN forces and the battle was the last of the war before the official signing of the Korean Armistice.
 W
WThe Second Phase Offensive or Second Phase Campaign of the Korean War was an offensive by the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) against United Nations Command (U.S./UN) forces, most of which were soldiers of South Korea and the United States. The two major engagements of the campaign were the Battle of the Ch'ongch'on River in the western part of North Korea and the Battle of Chosin Reservoir in the eastern part of North Korea.
 W
WThe Third Battle of Seoul, also known as the Chinese New Year's Offensive, the January–Fourth Retreat or the Third Phase Campaign Western Sector, was a battle of the Korean War, which took place from December 31, 1950, to January 7, 1951, around the South Korean capital of Seoul. In the aftermath of the major Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) victory at the Battle of the Ch'ongch'on River, the United Nations Command (UN) started to contemplate the possibility of evacuation from the Korean Peninsula. Chinese Communist Party chairman Mao Zedong ordered the Chinese People's Volunteer Army to cross the 38th Parallel in an effort to pressure the UN forces to withdraw from South Korea.
 W
WOperation Thunderbolt, also known in China as the Defensive Battle of the Han River Southern Bank, was a US offensive during the Korean War.
 W
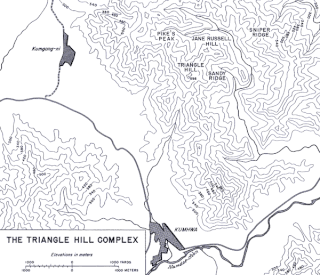
WThe Battle of Triangle Hill, also known as Operation Showdown or the Shangganling Campaign, was a protracted military engagement during the Korean War. The main combatants were two United Nations (UN) infantry divisions, with additional support from the United States Air Force, against elements of the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) 15th and 12th Corps. The battle was part of UN attempts to gain control of "The Iron Triangle", and took place from 14 October to 25 November 1952.
 W
WThe Battle of Uijeongbu, also known as the Battle of Uijongbu, was a battle fought between 1–4 January 1951, at Uijeongbu, South Korea, as part of the United Nations Command (UN) retreat after the third Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) offensive after entering the Korean War. The 3rd Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment had been defending the approaches north of Seoul, as part of the withdrawal of the United Nations forces and tasked with slowing the Chinese advance to allow the withdrawal of the United States 8th Army.
 W
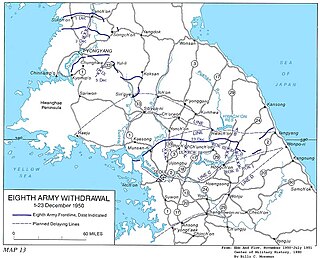
WThe UN retreat from North Korea was the withdrawal of United Nations (UN) forces from North Korea that took place from 2–25 December 1950.
 W
WThe Battle of Unsan, also known as the Battle of Yunshan, was a series of engagements of the Korean War that took place from 25 October to 4 November 1950 near Unsan, North Pyongan province in present-day North Korea. As part of the People's Republic of China's First Phase Campaign, the People's Volunteer Army (PVA) made repeated attacks against the Republic of Korea Army (ROK) 1st Infantry Division near Unsan beginning on 25 October, in an attempt to take advancing United Nations forces by surprise. In an accidental first encounter with the United States military during the Korean War, the PVA 39th Corps attacked the unprepared US 8th Cavalry Regiment in Unsan on 1 November, resulting in one of the most devastating US losses of the Korean War.
 W
WThe Battle of Wawon(Korean: 군우리 전투; hanja: 軍隅里戰鬪; rr: Gunuri Jeontu; Turkish: Kunuri Muharebeleri), also known as the Battle of Wayuan, was a series of delay actions of the Korean War that took place from 27-29 November 1950 near Wawon in present-day North Korea. After the collapse of the US Eighth Army's right flank during the Battle of the Ch'ongch'on River, the Chinese People's Volunteer Army (PVA) 38th Corps advanced rapidly towards the critical road junction at Kunu-ri in an effort to cut off United Nations forces' retreat route. In what was considered to be Turkey's first real combat action since the aftermath of World War I, the Turkish Brigade attempted to delay the Chinese advances at Wawon. Although during the battle the Turkish Brigade was crippled after being encircled by Chinese forces with superior numbers, they were still be able to breach the Chinese trap and rejoin the US 2nd Infantry Division. Delay of the PVA advance after meeting with heavy Turkish resistance helped the other United Nations forces to withdraw without suffering many casualties and reassemble later in December.
 W
WThe Battle of White Horse, was a battle during the Korean War hill in the Iron Triangle, formed by Pyonggang at its peak and Gimhwa-eup and Cheorwon-eup at its base, a strategic transportation route in the central region of the Korean peninsula.
 W
WThe First and Second Battles of Wonju, also known as the Wonju Campaign or the Third Phase Campaign Eastern Sector, was a series of engagements between North Korean and United Nations (UN) forces during the Korean War. The battle took place from December 31, 1950 to January 20, 1951 around the South Korean town of Wonju. In coordination with the Chinese capture of Seoul on the western front, the North Korean Korean People's Army (KPA) attempted to capture Wonju in an effort to destabilize the UN defenses along the central and the eastern fronts.
 W
WThe Third Battle of Wonju, was a series of engagements between North Korean and United Nations (UN) forces during the Korean War. The battle took place from 13 to 18 February 1951 north of the South Korean town of Wonju.
 W
WThe Battle of Yultong, also known as the Battle of Meiluodong, Battle of Yuldong, or Battle of Yuldong-ri, was a battle of the Korean War. It was fought between elements of the Chinese People's Volunteer Army 34th Division and the Filipino 10th Battalion Combat Team (BCT), north of Yeoncheon during April 22–23, 1951. The battle was part of the Chinese Spring Offensive.