 W
WAnti-submarine warfare is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, and/or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations are typically carried out to protecting friendly shipping and coastal facilities from submarine attacks and to overcome blockades.
 W
WThe Advanced Combat Direction System (ACDS) is a centralized, automated command-and-control system, collecting and correlating combat information. It upgrades the Naval Tactical Data System (NTDS) for aircraft carriers and large-deck amphibious ships. A core component of non-Aegis combat systems, ACDS provides the capability to identify and classify targets, prioritize and conduct engagements, vector interceptor aircraft to targets, and exchange targeting information and engagement orders within the battle group and among different service components in the joint theater of operations. ACDS integrates the ship's sensors, weapons, and intelligence sources to allow command and control of battle group tactical operations.
 W
WThe Aegis Combat System is an American integrated naval weapons system developed by the Missile and Surface Radar Division of RCA, and now produced by Lockheed Martin. It uses powerful computer and radar technology to track and guide weapons to destroy enemy targets.
 W
WThe AN/AQS-13 series was a helicopter dipping sonar system for the United States Navy. These systems were deployed as the primary inner zone anti-submarine warfare (ASW) sensor on aircraft carrier based helicopters for over five decades. Companion versions with the AQS-18 designation were exported to various nations around the globe.
 W
WAn anti-submarine net or anti-submarine boom is a boom placed across the mouth of a harbour or a strait for protection against submarines.
 W
WAn anti-submarine missile is a standoff anti-submarine weapon. Often a variant of anti-ship missile designs an anti-submarine systems typically use a jet or rocket engine, to deliver: an explosive warhead aimed directly at a submarine; a depth charge, or; a homing torpedo that is carried from a launch ship, or other platform, to the vicinity of a target.
 W
WA depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon. It is intended to destroy a submarine by being dropped into the water nearby and detonating, subjecting the target to a powerful and destructive hydraulic shock. Most depth charges use high explosive charges and a fuze set to detonate the charge, typically at a specific depth. Depth charges can be dropped by ships, patrol aircraft, and helicopters.
 W
WA naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, any vessel. Naval mines can be used offensively, to hamper enemy shipping movements or lock vessels into a harbour; or defensively, to protect friendly vessels and create "safe" zones. Mines allow the minelaying force commander to concentrate warships or defensive assets in mine-free areas giving the adversary three choices: undertake an expensive and time-consuming minesweeping effort, accept the casualties of challenging the minefield, or use the unmined waters where the greatest concentration of enemy firepower will be encountered.
 W
WA nuclear depth bomb is the nuclear equivalent of the conventional depth charge, and can be used in anti-submarine warfare for attacking submerged submarines. The Royal Navy, Soviet Navy, and United States Navy had nuclear depth bombs in their arsenals at one point.
 W
WA modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive or fish torpedo; colloquially a fish. The term torpedo originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called mines. From about 1900, torpedo has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device.
 W
WThe anti-torpedo bulge is a form of defence against naval torpedoes occasionally employed in warship construction in the period between the First and Second World Wars. It involved fitting partially water-filled compartmentalized sponsons on either side of a ship's hull, intended to detonate torpedoes, absorb their explosions, and contain flooding to damaged areas within the bulges.
 W
WAutolycus or Sniffer was a method for detecting diesel-engined submarines from aircraft. It was designed to detect exhaust fumes from their diesel engines. Named after the mythical Greek, Autolycus, who took part in the search for the Golden Fleece, it was developed by the British during the early Cold War period. The first version of Autolycus was deployed on Shackleton aircraft in the mid-1950s, with an improved version re-appearing in the mid-1960s.
 W
WThe bathythermograph, or BT, also known as the Mechanical Bathythermograph, or MBT; is a small torpedo-shaped device that holds a temperature sensor and a transducer to detect changes in water temperature versus depth down to a depth of approximately 285 meters. Lowered by a small winch on the ship into the water, the BT records pressure and temperature changes on a coated glass slide as it is dropped nearly freely through the water. While the instrument is being dropped, the wire is paid out until it reaches a predetermined depth, then a brake is applied and the BT is drawn back to the surface. Because the pressure is a function of depth, temperature measurements can be correlated with the depth at which they are recorded.
 W
WBirth of a Giant is a 29-minute 1957 Canadian documentary film, directed by Hugh O'Connor and produced by the National Film Board of Canada (NFB) for the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC) television series, Perspective. The film depicts the role of story of the conception, construction and testing of the Canadair Argus aircraft, designed as a maritime patrol and anti-submarine aircraft for the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF). The title is an acknowledgement, that at the time, the Argus was the largest aircraft ever built in Canada.
 W
WThe International Fincastle Competition is a contest of skills between the air forces of the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada and New Zealand. During the competition, crews compete in anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, and intelligence and surveillance gathering.
 W
WThe Great Underwater Wall is a People's Republic of China military program to monitor submarine, surface, and aerial vehicle activity in the seas adjacent to China. The submarine monitoring system in the South China Sea, is called the "Great Underwater Wall" and the "Underwater Monitoring System" in Chinese media.
 W
WUSNS Hayes (T-AGOR-16/T-AG-195) was a Hayes-class oceanographic research ship acquired by the U.S. Navy in 1971. In 1992 she was reconfigured as an acoustics research ship and assigned to the Navy's program of acoustic noise reduction for submarines.
 W
WHunter-killer Groups, also known as Convoy Support Groups, were groups of anti-submarine warships that were actively deployed to attack submarines during World War II. The advances in signals intelligence such as High-frequency direction finding, in cryptological intelligence such as Ultra, and in detection technologies such as radar and sonar/ASDIC enabled the Allied navies to form flotillas designed actively to hunt down submarines and sink them. Similar groups also existed during the Cold War. A hunter-killer group would typically be formed around an escort carrier to provide aerial reconnaissance and air cover, with a number of corvettes, destroyers, destroyer escorts, frigates, and/or United States Coast Guard Cutters armed with depth charges and Hedgehog anti-submarine mortars.
 W
WIn the first years of World War I submarines were fearful, one-sided weapons because they were invisible. In July 1915 Arthur Balfour replaced Winston Churchill as First Lord of the Admiralty. Balfour appreciated the importance of science, so he set up a Board of Invention and Research (BIR), made up of a three-man central committee supported by an eminent consulting panel. The remits of Section II of the panel included submarines, its members included the eminent physicists Ernest Rutherford and William Henry Bragg. The panel concluded that the most promising approach was to listen for submarines, so they pushed work to improve hydrophones. Soon Bragg moved to the hydrophone research center HMS Tarlair at Aberdour on the Firth of Forth.
 W
WConstructed using light steel nets, indicator nets were often anchored at various depths to the sea bed around Allied naval bases during both world wars. They were intended to entangle U-boat traffic of the enemy, even though the submarines often managed to disentangle themselves and escape before being blown up by depth charges.
 W
WLiberdade class blended wing bodies are autonomous underwater gliders developed by the US Navy Office of Naval Research which use a blended wing body hullform to achieve hydrodynamic efficiency. It is an experimental class whose models were originally intended to track quiet diesel electric submarines in littoral waters, move at 1–3 knots and remain on station for up to six months. The "Liberdade" was the name of a ship cobbled together by Joshua Slocum prior to the one he single-handedly piloted around the world.
 W
WProject Magnet was a major geomagnetic survey effort from 1951 through 1994. The project originated in the U.S. Navy Hydrographic Office, renamed the U.S. Naval Oceanographic Office (NAVOCEANO), supporting world magnetic modeling and charting. The project used aircraft flying magnetic surveys worldwide. Additional magnetic data were collected with geophysical survey ships in conjunction with other projects for combination into final products. Data was used to support navigation of ships and aircraft and to meet Naval requirements as well as scientific research.
 W
WA magnetic anomaly detector (MAD) is an instrument used to detect minute variations in the Earth's magnetic field. The term refers specifically to magnetometers used by military forces to detect submarines ; military MAD equipment is a descendant of geomagnetic survey or aeromagnetic survey instruments used to search for minerals by detecting their disturbance of the normal earth-field.
 W
WThe Mid-Atlantic Gap is a geographical term applied to an undefended area beyond the reach of land-based RAF Coastal Command antisubmarine (A/S) aircraft during the Battle of the Atlantic in the Second World War. It is frequently known as The Black Pit, as well as the Atlantic Gap, Air Gap, Greenland Gap, or just "the Gap". This resulted in heavy merchant shipping losses to U-boats. The gap was eventually closed in May 1943, as growing numbers of VLR Liberators and escort carriers became available, and as basing problems were addressed.
 W
WNaval Tactical Data System (NTDS) was a computerized information processing system developed by the United States Navy in the 1950s and first deployed in the early 1960s for use in combat ships. It took reports from multiple sensors on different ships and collated it to produce a single unified map of the battlespace. This information could then be relayed back to the ships and to the weapons operators.
 W
WNeptune Mission is a 1958 30-minute Canadian short documentary film produced by the National Film Board of Canada (NFB) for the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC) television series, Perspective. The film documents the submarine-hunting mission of the RCAF Neptune aircraft on Canada's Atlantic coastline during the Cold War. Neptune Mission is produced by David Bairstow, and directed by Walford Hewitson.
 W
WPassive Underwater Fire Control Feasibility System (PUFFS) was a passive sonar system for submarines. It was designated AN/BQG-4 and was primarily equipped on United States Navy conventional submarines built in the 1950s beginning with the Tang class, and also those converted to GUPPY III or otherwise modernized in the 1960s. It was also equipped on the nuclear-powered USS Tullibee (SSN-597). It was also installed on the USS Thomas Edison (SSBN610) but never achieved operational status. Its transducers can be seen on pictures of the vessel. A version known as "Micropuffs" was fitted on Oberon-class submarines for the Royal Australian Navy, and as Type 2041 on the Upholder-class for the British Royal Navy. This class still serves in the Royal Canadian Navy as the Victoria class, where Micropuffs is known as BQG-501. The system was notable for three tall, fin-like domes topside, except on Micropuffs installations. The system was retained on several submarines transferred by the US to foreign navies. It was associated with long-range passive detection of targets for the Mark 45 nuclear torpedo and other weapons. Most submarines backfitted with it were also lengthened 12-16 feet to accommodate additional electronics and plotting rooms. It was also planned for Thresher and Sturgeon class nuclear submarines, but was not fitted on them except Micropuffs experimentally on Barb and Haddock. With the exception of the four Canadian Victoria-class submarines, all PUFFS-equipped submarines have been disposed of or preserved as museum ships.
 W
WThe SACLANT ASW Research Centre was the predecessor to the NATO Undersea Research Centre. It was known as The SACLANT ASW Research Centre from 1959 through 1986, and the SACLANT Undersea Research Centre from 1987 through 2003. The Centre was commonly referred to as SACLANTCEN.
 W
WSIFOREX, Silent Force Exercise, is an advanced anti-submarine warfare (ASW) bilateral exercise hosted and administered by the Peruvian Navy with participation of the United States Navy. Its main purpose is to provide an advanced anti-submarine training against diesel-electric powered submarines. The event is held annually in July in Callao, Peru under the leadership of the Submarine Command of the Peruvian Navy, headquartered at the Base Naval del Callao.
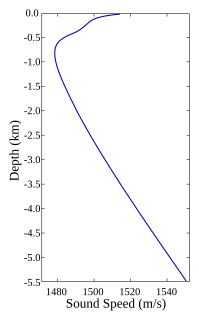 W
WThe SOFAR channel, or deep sound channel (DSC), is a horizontal layer of water in the ocean at which depth the speed of sound is at its minimum. The SOFAR channel acts as a waveguide for sound, and low frequency sound waves within the channel may travel thousands of miles before dissipating. An example was reception of coded signals generated by the Navy chartered ocean surveillance vessel Cory Chouest off Heard Island, located in the southern Indian Ocean, by hydrophones in portions of all five major ocean basins and as distant as the North Atlantic and North Pacific.
 W
WSonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. Two types of technology share the name "sonar": passive sonar is essentially listening for the sound made by vessels; active sonar is emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and SODAR is used for atmospheric investigations. The term sonar is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low (infrasonic) to extremely high (ultrasonic). The study of underwater sound is known as underwater acoustics or hydroacoustics.
 W
WA sonobuoy is a relatively small buoy expendable sonar system that is dropped/ejected from aircraft or ships conducting anti-submarine warfare or underwater acoustic research.
 W
WThe Sound Surveillance System (SOSUS) was a passive sonar system developed by the United States Navy to track Soviet submarines. The system's true nature was classified with the name and acronym SOSUS themselves classified. The unclassified name Project Caesar was used to cover the installation of the system and a cover story developed regarding the shore stations, identified only as a Naval Facility (NAVFAC), being for oceanographic research. In 1985, as the fixed bottom arrays were supplemented by the mobile Surveillance Towed Array Sensor System (SURTASS) and other new systems were coming on line, the name itself changed to Integrated Undersea Surveillance System (IUSS). The commands and personnel were covered by the "oceanographic" term until 1991 when the mission was declassified. As a result, the commands, Oceanographic System Atlantic and Oceanographic System Pacific became Undersea Surveillance Atlantic and Undersea Surveillance Pacific, and personnel were able to wear insignia reflecting the mission.
 W
WThe Sydney Harbour anti-submarine boom net was an anti-torpedo and submarine defence net that was in Sydney Harbour during World War II. It spanned the entire width of the harbour from Laing Point, Watsons Bay to Georges Head, on the northern side of Sydney Harbour. The boom formed part of the Sydney Harbour defences which also included artillery batteries and patrol boats.
 W
WA thermocline is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid in which temperature changes more drastically with depth than it does in the layers above or below. In the ocean, the thermocline divides the upper mixed layer from the calm deep water below.