 W
WThe Acoma Massacre refers to the punitive expedition by Spanish conquistadors at Acoma Pueblo in January 1599 that resulted in the deaths of around 500 Acoma men killed in a three-day battle, along with 300 women and children. Of the remaining Acoma who survived the attack, many were sentenced to 20-year enslavement and 24 suffered amputations.
 W
WThe Antelope Hills expedition was a campaign from January–May 1858 by the Texas Rangers and members of other allied Native American tribes against Comanche and Kiowa villages in the Comancheria. It began in western Texas and ended in a series of fights with the Comanche tribe on May 12, 1858, at a place called Antelope Hills by Little Robe Creek, a tributary of the Canadian River in what is now Oklahoma. The hills are also called the "South Canadians," as they surround the Canadian River. The fighting on May 12, 1858, is often called the Battle of Little Robe Creek.
 W
WThe Apalachee massacre was a series of raids by English colonists from the Province of Carolina and their Indian allies against a largely peaceful population of Apalachee Indians in northern Spanish Florida that took place in 1704, during Queen Anne's War. Against limited Spanish and Indian resistance, a network of missions was destroyed; most of the population either was killed or captured, fled to larger Spanish and French outposts, or voluntarily joined the English.
 W
WThe Battle of Ash Hollow, also known as the Battle of Blue Water Creek or the Harney Massacre, was an engagement of the First Sioux War, and fought on September 2 and 3, 1855 between United States Army soldiers under Brig. Gen. William S. Harney and a band of the Brulé Lakota along the Platte River in present-day Garden County, Nebraska. In the 20th century, the town of Lewellen, Nebraska, was developed here as a railroad stop.
 W
WThe Awa'uq Massacre or Refuge Rock Massacre, or, more recently, as the Wounded Knee of Alaska, was an attack and massacre of Koniag Alutiiq (Sugpiaq) people in April 1784 at Refuge Rock near Kodiak Island by Russian fur trader Grigory Shelekhov and 130 armed Russian men and cannoneers of his Shelikhov-Golikov Company.
 W
WThe Battle of Bad Axe, also known as the Bad Axe Massacre, was a battle between Sauk (Sac) and Fox Indians and United States Army regulars and militia that occurred on August 1–2, 1832. This final battle of the Black Hawk War took place near present-day Victory, Wisconsin in the United States. It marked the end of the war between white settlers and militia in Illinois and Michigan Territory, and the Sauk and Fox tribes under warrior Black Hawk.
 W
WThe Bear River Massacre, or the Battle of Bear River or Massacre at Boa Ogoi, took place in present-day Franklin County, Idaho on January 29, 1863. After years of skirmishes and food raids on farms and ranches, the United States Army attacked a Shoshone encampment, gathered at the confluence of the Bear River and Battle Creek in what was then southeastern Washington Territory, near the present-day city of Preston. Colonel Patrick Edward Connor led a detachment of California Volunteers as part of the Bear River Expedition against Shoshone tribal chief Bear Hunter. Hundreds of Shoshone men, women and children were killed near their lodges; the number of Shoshone victims reported by local settlers was higher than that reported by soldiers.
 W
WBear River Massacre Site, near Preston, Idaho, is the site of the Bear River Massacre, in which a village of Shoshone Native Americans were attacked by the California Volunteers on January 29, 1863. Estimates of Shoshone casualties are as high as 384. It is also known as Bear River Battleground or Massacre at Boa Ogoi. The incident has one of the highest recorded casualty counts of the American Indian Wars of the 19th century, but was overshadowed at the time by events of the ongoing American Civil War. The site was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1990.
 W
WThe Battle of Blanco Canyon was the decisive battle of Col. Ranald S. Mackenzie's initial campaign against the Comanche in West Texas, and marked the first time the Comanches had been attacked in the heart of their homeland. It was also the first time a large military force explored the heart of Comancheria. On 12 August 1871 Mackenzie and Colonel Benjamin Grierson were asked by Indian Agent Lawrie Tatum to begin an expedition against the Kotsoteka and Quahadi Comanche bands, both of whom had refused to relocate onto a reservation after the Warren Wagon Train Raid. Col. Mackenzie assembled a powerful force consisting of eight companies of the Fourth United States Cavalry, two companies of the Eleventh Infantry, and a group of twenty Tonkawa scouts.
 W
WBrodhead's Coshocton Expedition was a campaign in April, 1781, by the United States against the Delaware Indians near Coshocton, Ohio. Led by Daniel Brodhead IV, the Americans massacred the Delawares as well as peaceful Moravian converts.
 W
WThe Camp Grant massacre, on April 30, 1871, was an attack on Pinal and Aravaipa Apaches who surrendered to the United States Army at Camp Grant, Arizona, along the San Pedro River. The massacre led to a series of battles and campaigns fought between the Americans, the Apache, and their Yavapai allies, which continued into 1875, the most notable being General George Crook's Tonto Basin Campaign of 1872 and 1873.
 W
WThe Council House Fight, often referred to as the Council House Massacre, was a decidedly lopsided fight between soldiers and officials of the Republic of Texas and a delegation of Comanche chiefs during a peace conference in San Antonio on March 19, 1840. The meeting took place under an observed truce with the purpose of negotiating the exchange of captives and ultimately facilitating peace after two years of war. The Comanches sought to obtain recognition of the boundaries of the Comancheria, their homeland, while the Texians wanted the release of Texian and Mexican citizens held prisoner by the Comanches.
 W
WThe Crow Creek massacre occurred around the mid 1300s CE between Native American groups at a site along the Missouri River in the South Dakota area; it is now within the Crow Creek Indian Reservation. Crow Creek Site, the site of the massacre near Chamberlain, is an archaeological site and a U.S. National Historic Landmark, located at coordinates 43°58′48″N 99°19′54″W. An excavation of part of the site was done in the 1950s, with additional excavations in 1978 and later.
 W
WThe Cutthroat Gap massacre occurred in 1833, "The Year the Stars Fell" in Oklahoma. A group of Osage warriors charged into a Kiowa camp and brutally slaughtered the women, children and elderly there. Most of the warriors of this group of Kiowas, headed by Chief A'date or "Islandman" had left to raid a band of Utes or had gone bison hunting. The camp was left mainly unguarded and when the Osage came, the Kiowas had no choice but to flee. The Osage killed approximately 150 Kiowa people and took their sacred Tai-me medicine bundle and two children captive.
 W
WThe Fairfield Swamp Fight was the last engagement of the Pequot War and marked defeat of the Pequot tribe in the war and the loss of their recognition as a political entity in the 17th century. The participants in the conflict were the Pequot and the English with their allied tribes. The Fairfield Swamp Fight occurred July 13–14, 1637 in what is present-day Fairfield, Connecticut. The town of Fairfield was founded after the battle in 1639.
 W
WThe Fall Creek massacre refers to the slaughter of 9 Native Americans—two men, three women, two boys, and two girls—of uncertain tribal origin on March 22, 1824 by seven white settlers in Madison County, Indiana. The tribal band was living in an encampment along Deer Lick Creek, near the falls at Fall Creek, the site of present-day Pendleton, Indiana. The incident sparked national attention as details of the massacre and trial were reported in newspapers of the day. It was the first documented case in which white Americans were convicted, sentenced to capital punishment, and executed for the murder of Native Americans under U.S. law. Of the seven white men who participated in the crime, six were captured. The other white man, Thomas Harper, was never apprehended. Four of the men were charged with murder and the other two testified for the prosecution. The four accused men were convicted and sentenced to death by hanging. James Hudson was hanged on January 12, 1825, in Madison County, and Andrew Sawyer and John Bridge Sr. were hanged on June 3, 1825. James B. Ray, the governor of Indiana, pardoned John Bridge Jr., the eighteen-year-old son of John Bridge Sr., due to his age and the influence the others may have had on his involvement in the murders.
 W
WFort Neoheroka, or Nooherooka, is the name of a stronghold constructed in what is now Greene County, North Carolina by the Tuscarora tribe during the Tuscarora War of 1711–1715. In March 1713, the fort was besieged and ultimately attacked by a colonial force consisting of an army from the neighboring Province of South Carolina, under the command of Colonel James Moore and made up mainly of Indians including Yamasee, Apalachee, Catawba, and Cherokee. The 1713 siege lasted for more than three weeks, from around March 1 to March 22, 1713. Hundreds of men, women and children were burned to death in a fire that destroyed the fort. Approximately 170 more were killed outside the fort while approximately 400 were taken to South Carolina where they were sold into slavery. The defeat of the Tuscaroras, once the most powerful Indian tribe in the Province of North Carolina, opened up North Carolina's interior to further settlement. The supremacy of the Tuscaroras in the colony was broken forever, and most moved north to live among the Iroquois. On July 17, 2009, the Fort Neoheroka Site was added to the National Register of Historic Places.
 W
WThe Gnadenhutten massacre, also known as the Moravian massacre, was the killing of 96 Christian Lenape by U.S. militiamen from Pennsylvania on March 8, 1782 at the Moravian missionary village of Gnadenhutten, Ohio during the American Revolutionary War. More than a century later, Theodore Roosevelt called the massacre "a stain on frontier character that the lapse of time cannot wash away".
 W
WThe Indian massacre of 1622, popularly known as the "Jamestown massacre", took place in the English Colony of Virginia, in what is now the United States, on Friday, 22 March 1622.
 W
WThe Battle of Little Robe Creek, also called the Battle of Antelope Hills, took place on May 12, 1858. It actually was a series of three distinct encounters that took place on a single day, between the Comanches on the one side, and Texas Rangers, militia, and allied Tonkawas attacking them. It was undertaken against the laws of the United States at the time, which strictly forbade such an incursion into the Indian Territories of Oklahoma, and marked a significant escalation of the Indian Wars. It also marked the first time American or Texas Ranger forces had penetrated the Comancheria as far as the Wichita Mountains, and Canadian River, and it marked a decisive defeat for the Comanches.
 W
WThe Massacre Canyon battle took place in Nebraska on August 5, 1873 near the Republican River. It was one of the last hostilities between the Pawnee and the Sioux and the last battle/massacre between Great Plains Indians in North America. The massacre occurred when a large Oglala/Brulé Sioux war party of over 1,500 warriors led by Two Strike, Little Wound, and Spotted Tail attacked a band of Pawnee during their summer buffalo hunt. In the ensuing rout more than 150 Pawnees were killed, men with mostly women and children, the victims suffering mutilation and some set on fire.
 W
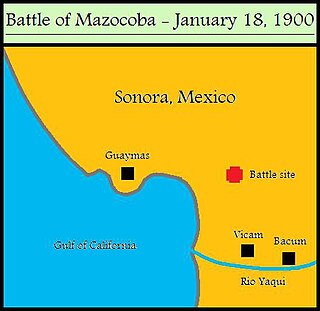
WThe Battle of Mazocoba, or the Mazocoba massacre, was a major engagement of the Yaqui Wars that was fought in Sonora, Mexico. On January 18, 1900, a Mexican Army expedition encountered hundreds of Yaqui renegades about twenty miles east of Guaymas. During the battle that followed, several hundred people were killed or wounded and over 1,000 Yaquis were taken prisoner.
 W
WThe Mendocino War was the genocide of the Yuki between July 1859 to January 18, 1860 by white settlers in Mendocino County, California. It was caused by settler intrusion and slave raids on native lands and subsequent native retaliation, resulting in the deaths of hundreds of natives. In 1859, a band of locally sponsored rangers led by Walter S. Jarboe, called the Eel River Rangers, raided the countryside in an effort to remove natives from settler territory and move them onto the Nome Cult Farm, an area near the Mendocino Indian Reservation. By the time the Eel River Rangers were disbanded in 1860, Jarboe and his men had killed 283 warriors, captured 292, killed countless women and children, and only suffered 5 casualties themselves in just 23 engagements. The bill to the state for the rangers' services amounted to $11,143.43. Scholars, however, state that the damage to the area and natives in particular was even higher than reported, especially given the vast number of raiding parties formed outside of the Eel River Rangers. Frustrated with the inadequacy of federal protection, settlers formed their own raiding parties against the natives, joining Jarboe in his mission to rid Round Valley of its native population. Those that survived were moved to the Nome Cult Farm, where they experienced hardships typical of the reservation system of the day. After the conflict, contemporaries claimed that the conflict was more of a slaughter than a war, and later historians have labeled it a genocide.
 W
WMountain Chief was a South Piegan warrior of the Blackfoot Tribe. Mountain Chief was also called Big Brave (Omach-katsi) and adopted the name Frank Mountain Chief. Mountain Chief was involved in the 1870 Marias Massacre, signed the Treaty of Fort Laramie in 1868, and worked with anthropologist Frances Densmore to interpret folksong recordings.
 W
WThe Mystic massacre took place on May 26, 1637 during the Pequot War, when Connecticut colonists under Captain John Mason and their Narragansett and Mohegan allies set fire to the Pequot Fort near the Mystic River. They shot anyone who tried to escape the wooden palisade fortress and killed most of the village in retaliation for previous Pequot attacks. The only Pequot survivors were warriors who had been with their sachem Sassacus in a raiding party outside the village.
 W
WThe Norridgewock Raid occurred in contested lands being fought over by England, France, and the Wabanaki Confederacy, during the colonial frontier conflict referred to as Governor Dummer's War. Despite being called a 'battle' by some, the raid was essentially a massacre of Indians by colonial British troops. Captains Johnson Harmon, Jeremiah Moulton, and Richard Bourne (Brown) led a force of two hundred colonial New Englanders, which attacked the Abenaki village of Narantsouak, or Norridgewock, on the Kennebec River; the current town of Norridgewock, Maine developed near there. The village was led by, among others, the sachems Bomazeen and Welákwansit, known to the English as Mog. The village's Catholic mission was run by a French Jesuit priest, Father Sébastien Râle.
 W
WThe Battle of North Fork or the Battle of the North Fork of the Red River occurred on September 28, 1872, near McClellan Creek in Gray County, Texas, United States. A monument on that spot marks the site of the battle between the Comanche Indians under Kai-Wotche and Mow-way and a detachment of cavalry and scouts under U.S. Army Colonel Ranald S. Mackenzie. There was an accusation that the battle was really an attempt "to make a massacre," as during the height of battle some noncombatants were wounded while mixed in with warriors.
 W
WPavonia was the first European settlement on the west bank of the North River that was part of the seventeenth-century province of New Netherland in what would become the present Hudson County, New Jersey.
 W
WThe Battle of Pease River occurred on December 18, 1860, near the present-day town of Margaret, Texas in Foard County, Texas, United States. The town is located between Crowell and Vernon within sight of the Medicine Mounds just outside present-day Quanah, Texas.
 W
WThe Sand Creek massacre was a massacre of Cheyenne and Arapaho people by the U.S. Army in the American Indian Wars that occurred on November 29, 1864, when a 675-man force of the Third Colorado Cavalry under the command of U.S. Army Colonel John Chivington attacked and destroyed a village of Cheyenne and Arapaho people in southeastern Colorado Territory, killing and mutilating an estimated 70–500 Native Americans, about two-thirds of whom were women and children. The location has been designated the Sand Creek Massacre National Historic Site and is administered by the National Park Service. This was part of a series of events known as the Colorado War and was preceded by the Hungate massacre.
 W
WSand Creek Massacre National Historic Site is a National Historic Site in Kiowa County, Colorado, near Eads and Chivington in Kiowa County commemorating the Sand Creek Massacre that occurred here on November 29, 1864. The site is about 170 miles (270 km) southeast of Denver and about 125 miles (200 km) east of Pueblo. A few basic park facilities have been opened at this site.
 W
WThe St. Francis Raid was an attack in the French and Indian War by Robert Rogers on St. Francis, near the southern shore of the Saint Lawrence River in what was then the French province of Canada, on October 4, 1759. Rogers and about 140 men entered the village, which was reportedly occupied primarily by women, children, and the elderly, early that morning, slaughtered many of the inhabitants where they lay, shot down many who attempted to flee, and then burned the village. Rogers reported killing as many as 300 people, while French reports placed the number closer to thirty, mainly women and children. One of Rogers' men was killed, and seven were wounded.
 W
WThe Fall of Tenochtitlan, the capital of the Aztec Empire, was a decisive event in the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. It occurred in 1521 following extensive manipulation of local factions and exploitation of pre-existing divisions by Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés, who was aided by the support of his indigenous allies and his interpreter and companion La Malinche.
 W
WThe Wounded Knee Massacre, also known as the Battle of Wounded Knee, was a domestic massacre of nearly three hundred Lakota people, by soldiers of the United States Army. It occurred on December 29, 1890, near Wounded Knee Creek on the Lakota Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in the U.S. state of South Dakota, following a botched attempt to disarm the Lakota camp. The previous day, a detachment of the U.S. 7th Cavalry Regiment commanded by Major Samuel M. Whitside intercepted Spotted Elk's band of Miniconjou Lakota and 38 Hunkpapa Lakota near Porcupine Butte and escorted them 5 miles (8.0 km) westward to Wounded Knee Creek, where they made camp. The remainder of the 7th Cavalry Regiment, led by Colonel James W. Forsyth, arrived and surrounded the encampment. The regiment was supported by a battery of four Hotchkiss mountain guns.