 W
WThe Action of 14 December 1798 was a naval skirmish between the 32-gun British frigate HMS Ambuscade and the French 24-gun corvette Bayonnaise. Bayonnaise was vastly outgunned and outmanoeuvred, but was able to board and capture Ambuscade.
 W
WThe Action of 15 July 1798 was a minor naval battle of the French Revolutionary Wars, fought off the Spanish Mediterranean coast by the Royal Navy ship of the line HMS Lion under Captain Manley Dixon and a squadron of four Spanish Navy frigates under Commodore Don Felix O'Neil. Lion was one of several ships sent into the Western Mediterranean by Vice-Admiral Earl St Vincent, commander of the British Mediterranean Fleet based at the Tagus in Portugal during the late spring of 1798. The Spanish squadron was a raiding force that had sailed from Cartagena in Murcia seven days earlier, and was intercepted while returning to its base after an unsuccessful cruise. Although together the Spanish vessels outweighed the British ship, individually they were weaker and Commodore O'Neil failed to ensure that his manoeuvrees were co-ordinated. As a result, one of the frigates, Santa Dorotea, fell out of the line of battle and was attacked by Lion.
 W
WThe Action of 18 August 1798 was a minor naval engagement of the French Revolutionary Wars, fought between the British fourth rate ship HMS Leander and the French ship of the line Généreux. Both ships had been engaged at the Battle of the Nile three weeks earlier, in which a British fleet under Rear-Admiral Sir Horatio Nelson had destroyed a French fleet at Aboukir Bay on the Mediterranean coast of Egypt. Généreux was one of only four French ships to survive the battle, while Leander had been detached from the British fleet by Nelson on 6 August. On board, Captain Edward Berry sailed as a passenger, charged with carrying despatches to the squadron under Earl St Vincent off Cadiz. On 18 August, while passing the western shore of Crete, Leander was intercepted and attacked by Généreux, which had separated from the rest of the French survivors the day before.
 W
WThe Action of 24 October 1798 was a minor naval engagement of the French Revolutionary Wars, fought between a British Royal Navy frigate and two ships of the Batavian Navy. The Dutch ships were intercepted in the North Sea within hours of leaving port, 30 nautical miles (56 km) northwest of the Texel, by the British ship HMS Sirius. Both Dutch vessels were carrying large quantities of military supplies and French soldiers, reinforcements for the French and Irish forces participating in the Irish Rebellion of 1798. Although the rebellion had been defeated a month earlier, word of the British victory had not yet reached the European continent, and the Dutch force was intended to supplement a larger French squadron sent earlier in October. The French had already been defeated at the Battle of Tory Island and the Dutch suffered a similar outcome, both ships defeated in turn by the larger and better armed British vessel.
 W
WThe Action of 27 June 1798 was a minor naval engagement between British and French frigates in the Strait of Sicily in the Mediterranean Sea. The engagement formed part of a wider campaign, in which a major French convoy sailed from Toulon to Alexandria at the start of the Napoleonic campaign in Egypt. The French frigate Sensible had been detached from the convoy after the capture of Malta, under orders to carry wounded soldiers and looted treasure back to France while the main body continued to Egypt. The British frigate HMS Seahorse was one of a number of vessels detached from the main British Mediterranean Fleet in the Tagus River, sent to augment the fleet under Sir Horatio Nelson that was actively hunting the French convoy.
 W
WThe Action of 30 June 1798 was a minor naval engagement fought along the Biscay coast of France during the French Revolutionary Wars. The French Navy had been largely driven from the Atlantic Ocean early in the war following heavy losses in a series of failed operations. This had allowed the Royal Navy's Channel Fleet to institute a close blockade on the French naval ports of the Biscay coast, particularly Brest in Brittany. The blockade strategy included a constantly patrolling inshore squadron composed of frigates, tasked with preventing the passage of French ships into or out of the port. In the spring of 1798, several French frigates stationed in the Indian Ocean were sent back to France as the base at Île de France could no longer supply them effectively. One of these ships was the 40-gun frigate Seine, which departed Port Louis laden with 280 soldiers from the garrison.
 W
WThe Action of 30 May 1798 was a minor naval engagement between a small British squadron and a small French squadron off the coast of Normandy, France during the French Revolutionary Wars. A British blockading force, which had been conducting patrols in the region in the aftermath of the battle of St Marcou earlier in the month, encountered two French vessels attempting to sail unnoticed between Le Havre and Cherbourg. Closing with the French, the British commander Sir Francis Laforey sought to bring the French ships to battle as they attempted to turn back to Le Havre before the British squadron could attack. The French were unable to escape, and Laforey's ship, the fifth rate HMS Hydra, engaged the French corvette Confiante, while two smaller British ships chased the Vésuve.
 W
WThe Fourth Anglo–Mysore War was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore against the British East India Company and the Hyderabad Deccan in 1798–99.
 W
WThe Battle of Ballinamuck marked the defeat of the main force of the French incursion during the 1798 Rebellion in Ireland.
 W
WThe Revolt of Cairo was a revolt that occurred on 21-22 October 1798 by the citizens of Cairo against the French occupation of Egypt led by Napoleon Bonaparte.
 W
WThe Capture of La Croyable, or the Action of July 7, 1798, occurred when the French privateer schooner La Croyable was taken by the American sloop-of-war USS Delaware on 7 July 1798 during the Quasi-War. The engagement resulted in the first capture of any ship by the United States Navy, which had been formed just months before the action.
 W
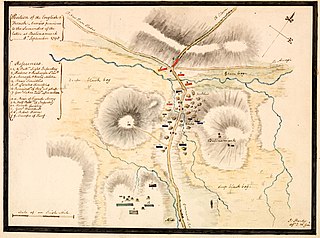
WThe Battle of Castlebar occurred on 27 August 1798 near the town of Castlebar, County Mayo, during the Irish Rising of that year. A combined force of 1,000 French troops and Irish patriots routed a force of 6,000 Protestant militia in what would later become known as the "Castlebar Races" or "Races of Castlebar".
 W
WThe Siege of Corfu was a military operation by a joint Russian and Turkish fleet against French troops occupying the island of Corfu.
 W
WThe East Indies theatre of the French Revolutionary Wars was a series of campaigns related to the major European conflict known as the French Revolutionary Wars, fought between 1793 and 1801 between the new French Republic and its allies and a shifting alliance of rival powers. Although the Indian Ocean was separated by vast distance from the principal theatre of the conflict in Western Europe, it played a significant role due to the economic importance of the region to Great Britain, France's most constant opponent, of its colonies in India and the Far Eastern trade.
 W
WThe French campaign in Egypt and Syria (1798–1801) was Napoleon Bonaparte's campaign in the Ottoman territories of Egypt and Syria, proclaimed to defend French trade interests, seek further direct alliances with Tipu Sultan, weaken Britain's access to India, and to establish scientific enterprise in the region. It was the primary purpose of the Mediterranean campaign of 1798, a series of naval engagements that included the capture of Malta. The campaign ended in defeat for Napoleon, and the withdrawal of French troops from the region.
 W
WThe French invasion of Malta was the successful invasion of the islands of Malta and Gozo, then ruled by the Order of St. John, by the French First Republic led by Napoleon in June 1798 as part of the Mediterranean campaign of the French Revolutionary Wars.
 W
WThe French invasion of Switzerland occurred from January until May 1798 as part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The independent Old Swiss Confederacy collapsed, both from this foreign invasion and simultaneous internal revolts, termed the "Helvetic Revolution". Its Ancien Régime institutions were abolished and replaced by the centralised pro-French Helvetic Republic.
 W
WThe Battle of Grauholz on 5 March 1798 was a battle between a Bernese army under Karl Ludwig von Erlach against the French Revolutionary Army under Balthazar Alexis Henri Schauenburg. The battle took place at Grauholz, a wooded hill in what is now the municipalities of Urtenen-Schönbühl and Moosseedorf in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. The government of Bern had already surrendered the previous day and the Bernese defeat at Grauholz ended their resistance to the French in the north of the canton.
 W
WThe Battle of the Îles Saint-Marcouf was an engagement fought off the Îles Saint-Marcouf near the Cotentin peninsula on the Normandy coast of France in May 1798 during the French Revolutionary Wars. Dislodging a British garrison on the islands was the main objective for French forces. The garrison allowed the islands to serve as a resupply base for Royal Navy ships patrolling northern French waters. Apart from expelling the British, the French sought to test new equipment and tactics, which had allegedly been developed with an intention of invading Britain.
 W
WThe Siege of Malta, also known as the Siege of Valletta or the French Blockade, was a two-year siege and blockade of the French garrison in Valletta and the Three Cities, the largest settlements and main port on the Mediterranean island of Malta, between 1798 and 1800. Malta had been captured by a French expeditionary force during the Mediterranean campaign of 1798, and garrisoned with 3,000 men under the command of Claude-Henri Belgrand de Vaubois. After the British Royal Navy destroyed the French Mediterranean Fleet at the Battle of the Nile on 1 August 1798, the British were able to initiate a blockade of Malta, assisted by an uprising among the native Maltese population against French rule. After its retreat to Valletta, the French garrison faced severe food shortages, exacerbated by the effectiveness of the British blockade. Although small quantities of supplies arrived in early 1799, there was no further traffic until early 1800, by which time starvation and disease was having a disastrous effect on health, morale, and combat capability of the French troops.
 W
WThe Raid on Manila of January 1798 was a Royal Navy false flag military operation during the French Revolutionary Wars intended to scout the strength of the defences of Manila, capital of the Spanish Philippines, capture a Manila galleon and assess the condition of the Spanish Navy squadron maintained in the port. Spain had transformed from an ally of Great Britain in the War of the First Coalition into an enemy in 1796. Thus the presence of a powerful Spanish squadron at Manila posed a threat to the China Fleet, an annual convoy of East Indiaman merchant ships from Macau in Qing Dynasty China to Britain, which was of vital economic importance to Britain. So severe was this threat that a major invasion of the Spanish Philippines had been planned from British India during 1797, but had been called off following the Treaty of Campo Formio in Europe and the possibility of a major war in India between the British East India Company and the Kingdom of Mysore.
 W
WThe Mediterranean campaign of 1798 was a series of major naval operations surrounding a French expeditionary force sent to Egypt under Napoleon Bonaparte during the French Revolutionary Wars. The French Republic sought to capture Egypt as the first stage in an effort to threaten British India and support Tipu Sultan, and thus force Great Britain to make peace. Departing Toulon in May 1798 with over 40,000 troops and hundreds of ships, Bonaparte's fleet sailed southeastwards across the Mediterranean Sea. They were followed by a small British squadron under Rear-Admiral Sir Horatio Nelson, later reinforced to 13 ships of the line, whose pursuit was hampered by a lack of scouting frigates and reliable information. Bonaparte's first target was the island of Malta, which was under the government of the Knights of St. John and theoretically granted its owner control of the Central Mediterranean. Bonaparte's forces landed on the island and rapidly overwhelmed the defenders, securing the port city of Valletta before continuing to Egypt. When Nelson learned of the French capture of the island, he guessed the French target to be Egypt and sailed for Alexandria, but passed the French during the night of 22 June without discovering them and arrived off Egypt first.
 W
WIn November 1798 a British expedition captured the island of Menorca from Spain. A large force under General Charles Stuart landed on the island and forced its Spanish garrison to surrender in eight days with only some bloodshed. The British occupied the island for four years, using it as a major naval base, before handing it back to Spain following the Treaty of Amiens.
 W
WPreveza is a city in the region of Epirus, northwestern Greece, located on the northern peninsula at the mouth of the Ambracian Gulf. It is the capital of the regional unit of Preveza, which is part of the region of Epirus. The Aktio-Preveza Immersed Tunnel – the first and so far only undersea tunnel in Greece – was completed in 2002 and connects Preveza in the north to Aktio in western Acarnania in Aetolia-Acarnania south of the mouth of the Ambracian Gulf. The ruins of the ancient city of Nicopolis lie 7 kilometres north of the city.
 W
WThe Battle of the Nile was a major naval battle fought between the British Royal Navy and the Navy of the French Republic at Aboukir Bay on the Mediterranean coast off the Nile Delta of Egypt from the 1st to the 3rd of August 1798. The battle was the climax of a naval campaign that had raged across the Mediterranean during the previous three months, as a large French convoy sailed from Toulon to Alexandria carrying an expeditionary force under General Napoleon Bonaparte. The British fleet was led in the battle by Rear-Admiral Sir Horatio Nelson; they decisively defeated the French under Vice-Admiral François-Paul Brueys d'Aigalliers.
 W
WThe Peasants' War was a peasant revolt in 1798 against the French occupiers of the Southern Netherlands, a region which now includes Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Germany. The French had annexed the region in 1795 and control of the region was officially ceded to the French after the Treaty of Campo Formio in 1797. The revolt is considered part of the French Revolutionary Wars.
 W
WThe Battle of the Pyramids, also known as the Battle of Embabeh, was a major engagement fought on 21 July 1798 during the French Invasion of Egypt. The French army, under Napoleon Bonaparte, scored a decisive victory against the forces of the local Mamluk rulers, wiping out almost the entire Ottoman army located in Egypt. It was the battle where Napoleon employed the divisional square tactic to great effect. Actually a rectangle, the deployment of the French brigades into these massive formations repeatedly threw back multiple cavalry charges by the Mamluks.
 W
WThe Quasi-War was an undeclared war fought from 1798 to 1800 between the United States and France. Most of the fighting took place in the Caribbean and off the Atlantic coast.
 W
WThe Battle of the Raz de Sein was a single-ship naval engagement of the blockade of Brest during the French Revolutionary Wars between a French and Royal Navy ships of the line on 21 April 1798. The British blockade fleet under Admiral Lord Bridport had sailed from St Helens on 12 April and on the morning of 21 April was crossing the Iroise Passage when sails were spotted to the east. Three ships were detached in pursuit, led by the 74-gun ship of the line HMS Mars under Captain Alexander Hood. As the British ships approached their quarry a third sail was sighted to the southeast close to the coastline and moving north towards Brest.
 W
WThe Battle of Shubra Khit, also known as the Battle of Chobrakit, was the first major engagement of Napoleon's campaign in Egypt that took place on 13 July, 1798. On their march to Cairo, the French army encountered an Ottoman army consisting of Mamluk cavalry and drafted Fellahins under Murad Bey. Napoleon lined his forces up into infantry squares, a tactic which helped repel the Mamluk cavalry, largely due to their inability to penetrate them without suffering severe casualties. A naval battle also occurred, with an Ottoman flotilla being repelled by a French flotilla.
 W
WThe Battle of the Nile was a significant naval action fought during 1–3 August 1798. The battle took place in Aboukir Bay, near the mouth of the River Nile on the Mediterranean coast of Egypt and pitted a British fleet of the Royal Navy against a fleet of the French Navy. The battle was the climax of a three-month campaign in the Mediterranean during which a huge French convoy under General Napoleon Bonaparte had sailed from Toulon to Alexandria via Malta. Despite close pursuit by a British fleet of thirteen ships of the line, one fourth rate and a sloop under Sir Horatio Nelson, the French were able to reach Alexandria unscathed and successfully land an army, which Bonaparte led inland. The fleet that had escorted the convoy, consisting of thirteen ships of the line, four frigates and a number of smaller vessels under Vice-amiral François-Paul Brueys D'Aigalliers, anchored in Aboukir Bay as Alexandria harbour was too narrow, forming a line of battle that was protected by shoals to the north and west.
 W
WThe War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802) was the second war on revolutionary France by most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, various German monarchies and Sweden, though Prussia did not join this coalition and Spain supported France.