 W
WThe American-led intervention in the Syrian Civil War refers to the United States-led support of the Syrian rebels and the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) during the course of the Syrian Civil War, including Combined Joint Task Force - Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF-OIR), the active military operation led by the United States, and involving the militaries of the United Kingdom, France, Jordan, Turkey, Canada, Australia, and others against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and al-Nusra Front since 2014. Since early 2017, the U.S. and its partners have also targeted the Syrian government and its allies via airstrikes and aircraft shoot-downs.
 W
WThe American-led intervention in the Syrian Civil War refers to the United States-led support of Syrian opposition and the Federation of Northern Syria during the course of the Syrian Civil War and active military involvement led by the United States and its allies — the militaries of the United Kingdom, France, Jordan, Turkey, Canada, Australia and more — against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and al-Nusra Front since 2014. Since early 2017, the U.S. and other Coalition partners have also targeted the Syrian government and its allies via airstrikes and aircraft shoot-downs.
 W
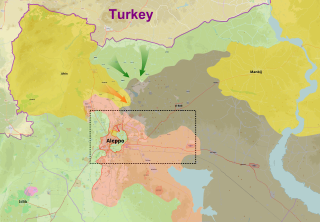
WThe 2016 Dabiq offensive was a military offensive and part of the third phase of Operation Euphrates Shield launched by the Turkish Armed Forces and factions from the Free Syrian Army and allied groups, with the goal of capturing the town of Dabiq, north of Aleppo from Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant (ISIL). It began in September and resulted in the capture of Dabiq by Turkish/FSA-allied forces on 16 October.
 W
WThe Battle of al-Hasakah (2016) was a battle between the paramilitary police of the Asayish and the People's Protection Units (YPG), against the pro-government National Defence Forces and the Syrian Arab Army, backed by the Syrian Arab Air Force, in the city of al-Hasakah, Syria.
 W
WOn 16 March 2017, an airstrike by the United States Armed Forces killed up to 49 people in the rebel-held village of al-Jinah near Aleppo, Syria. The US military claimed the people targeted in the strike were militants belonging to the terrorist group al-Qaeda. However, the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights (SOHR), local residents and local officials have claimed that the building struck was a mosque filled with worshipers. At the time, US military claimed that the structure bombed was not a mosque itself but was next to a mosque, which was undamaged. However, on May 5, 2017, a US Central Command investigation determined that the building was indeed part of a mosque-complex. Rami Abdel Rahman, head of SOHR, claimed the structure was a mosque which held over 300 people at the time of the strike. In September 2017, the United Nations Commission of Inquiry on Syria concluded that "United States forces failed to take all feasible precautions to avoid or minimize incidental loss of civilian life, injury to civilians and damage to civilian objects, in violation of international humanitarian law." The UN commission's findings did not support the U.S. claim that an al-Qaeda meeting was taking place.
 W
WThe al-Shaddadi offensive (2016), also known as Operation Wrath of Khabur, was an offensive launched by the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) during the Syrian Civil War, in February 2016. The main goal of this offensive was to capture the strategic city of Al-Shaddadi and the remainder of the southern al-Hasakah Governorate from the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL). During the offensive, the US-led coalition conducted more than 86 airstrikes in Al-Shaddadi and the nearby areas, in support of the SDF advances.
 W
WOn 7 February 2018, the U.S.-led coalition, established in 2014 to counter the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), delivered massive air and artillery strikes on the Syrian pro-government forces near the town of Khasham, or Al Tabiyeh, both in the Deir ez-Zor Governorate. The United States explained the attack by stating that the pro-government forces had ″initiated an unprovoked attack against well-established Syrian Democratic Forces headquarters" in the area, while Coalition service members were ″co-located with SDF partners during the attack eight kilometers east of the agreed-upon Euphrates River de-confliction line″. The Russian defence ministry's statement released on 8 February 2018 referred to the incident at the village of Salihiyah and said that it was caused by reconnaissance actions of Syrian militia that had not been cleared with the Russian operations command; the statement stressed that there were no Russian service members in the ″designated district of the Deir ez-Zor province of Syria".
 W
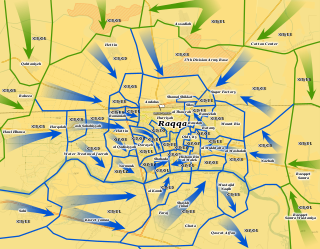
WThe Battle of Raqqa (2017) was the fifth and final phase of the Raqqa campaign (2016–17) launched by the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) against the Islamic State (ISIL) with an aim to seize the city of Raqqa, the de facto capital of ISIL since 2014. The battle began on 6 June 2017, and was supported by airstrikes and ground troops from the US-led coalition. The operation was named the "Great Battle" by the SDF. It concluded on 17 October 2017, with the SDF fully capturing the city of Raqqa.
 W
WThe Battle of Sarrin refers to a military operation during 2015 in the northeastern Aleppo Governorate, during the Syrian Civil War, conducted by Kurdish YPG and allied forces against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant in the town of Sarrin, in an effort to capture the town and the surrounding region.
 W
WOn October 26–27, 2019, the United States conducted Operation Kayla Mueller, a military operation named after Kayla Mueller, that resulted in the death of Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, the then-leader and self-proclaimed caliph of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) terrorist organization. The operation took place in the outskirts of Barisha, Idlib Governorate, Syria. According to General Kenneth "Frank" McKenzie, the United States Central Command (CENTCOM) commander who oversaw the operation, Baghdadi killed himself along with two children when he detonated a suicide belt while seeking to evade the U.S. forces during the raid.
 W
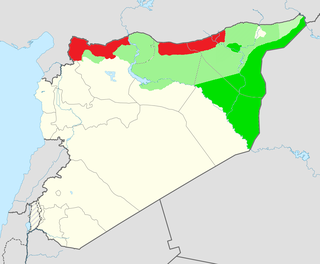
WThe Deir ez-Zor campaign (2017–2019), codenamed the al-Jazeera Storm campaign, was a military operation launched by the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) in Syria's Deir ez-Zor Governorate in 2017. It took place during the Rojava conflict of the Syrian Civil War, with the goal of capturing territory in eastern Syria, particularly east and north of the Euphrates river. The U.S.-led Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF–OIR) anti-ISIL coalition provided extensive air support while SDF personnel composed the majority of the ground forces; CJTF-OIR special forces and artillery units were also involved in the campaign. The ground campaign stalled and was paused in early 2018 due to the Turkish-led invasion of Afrin, but resumed on 1 May 2018 with the new phase named by the anti-ISIL Coalition as Operation Roundup. The third phase started on 10 September 2018 but was once again halted due to Turkish artillery attacks on SDF positions near the Syria-Turkey border on 31 October. The SDF and the Coalition announced the resumption of the offensive on 11 November. After a string of steady successes following the capturing of ISIL's Hajin stronghold and a ten-day pause for civilian evacuations, the SDF launched its final assault on the remainder of the Middle Euphrates River Valley (MERV) pocket on 9 February 2019.
 W
WThe Eastern Syria insurgency is an armed insurgency being waged by remnants of the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and both pro and anti-Syrian government Arab nationalist insurgents, against the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria, its military, and their allies in the US-led Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF–OIR) coalition.
 W
WOperation Euphrates Shield was a cross-border military operation conducted by the Turkish Armed Forces and Turkey-aligned Syrian opposition groups in the Syrian civil war which led to the Turkish occupation of northern Syria. Operations were carried out in the region between the Euphrates river to the east and the Syrian rebel-held area around Azaz to the west. The Turkish military and Turkey-aligned Syrian rebel groups, some of which used the Free Syrian Army label, fought against both the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) and the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), from 24 August 2016. On 29 March 2017, the Turkish military officially announced that Operation Euphrates Shield was "successfully completed".
 W
WThe Ja'Din shootdown incident occurred on 18 June 2017, when a United States Navy F/A-18E, shot down a Syrian Air Force Su-22 Fitter with an AIM-120 AMRAAM missile after it reportedly attacked U.S. backed Syrian Democratic Forces positions in the town of Ja'Din. It was the first time the US shot down a manned aircraft since 1999 and the first with the F/A-18E variant.
 W
WThe Siege of Kobanî was launched by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant on 13 September 2014, in order to capture the Kobanî Canton and its main city of Kobanî in northern Syria, in the de facto autonomous region of Rojava.
 W
WThe Kobanî massacre was a combination of suicide missions and attacks on Kurdish civilians by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant on the Kurdish-held city of Kobanî, beginning on Thursday, 25 June, and culminating on Friday, 26 June 2015. The attacks continued into 28 June, with the last remaining ISIL militant being killed on the following day. The attacks resulted in 223–233 civilians dead, as well as 35–37 Kurdish militiamen and at least 79 ISIL assailants. It was the second-largest massacre committed by ISIL since it declared a caliphate in June 2014.
 W
WThe Manbij offensive, code-named Operation Martyr and Commander Faysal Abu Layla by the SDF, was a 2016 military offensive operation by the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) to capture the city of Manbij from the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), and eventually, the ISIL-held areas through Al-Bab to Herbel, in the area referred to as the "Manbij Pocket" in the northern Aleppo Governorate. The main goal of the offensive was to cut off ISIL's last supply routes from Turkey, and to prevent ISIL fighters from escaping across the Syria-Turkey border. For the first five days of the offensive, the US-led coalition conducted over 55 airstrikes in support of the SDF. After capturing Manbij city on 12 August, the SDF announced that the offensive would continue until the whole countryside around Manbij was captured, though the offensive effectively ended shortly after the Turkish Armed Forces initiated Operation Euphrates Shield to prevent the SDF uniting the regions of Rojava.
 W
WOn 14 April 2018, beginning at 04:00 Syrian time (UTC+3), the United States, France, and the United Kingdom carried out a series of military strikes involving aircraft and ship-based missiles against multiple government sites in Syria during the Syrian Civil War. They said it was in reprisal for the Douma chemical attack against civilians on 7 April, which they attributed to the Syrian government. The Syrian government denied involvement in the Douma attacks and called the airstrikes a violation of international law.
 W
WThe northern al-Bab offensive was a military offensive and part of the third phase of Operation Euphrates Shield launched by the Turkish Armed Forces and factions from the Free Syrian Army and allied groups, with the goal of capturing the city of al-Bab located north of Aleppo from the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant.
 W
WOperation Inherent Resolve (OIR) is the U.S. military's operational name for the International military intervention against ISIL, including both a campaign in Iraq and a campaign in Syria, with a closely-related campaign in Libya. Since 18 September 2018, the U.S. Army's III Armored Corps has been responsible for Combined Joint Task Force – Operation Inherent Resolve (CJTF—OIR). The campaign is primarily waged by American air forces in support of local allies, most prominently the Iraqi security forces and Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF). Combat ground troops, mostly special forces and artillery, have also been deployed, especially in Iraq. 75-80% of the airstrikes have been conducted by the military of the United States, with the other 20-25% by the United Kingdom, France, Turkey, Canada, the Netherlands, Denmark, Belgium, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Jordan.
 W
WOn the morning of 7 April 2017, the United States launched 59 Tomahawk cruise missiles from the Mediterranean Sea into Syria, aimed at Shayrat Airbase controlled by the Syrian government. The strike was executed under responsibility of U.S. President Donald Trump, as a direct response to the Khan Shaykhun chemical attack that occurred on 4 April.
 W
WThe Syrian Desert campaign was a large-scale military operation of the Syrian Army that initially started along the highway from Damascus to the border with Iraq against rebel forces during the Syrian Civil War. Its first intended goal was to capture both the highway and the al-Tanf border crossing, thus securing the Damascus countryside from a potential rebel attack. Later, multiple other fronts were opened as part of the operation throughout the desert, as well as operation "Grand Dawn" against ISIL with the aim of reopening the Damascus-Palmyra highway and preparing for an offensive towards Deir ez-Zor.
 W
WThe Rojava-Islamist conflict, a major theater in the Syrian Civil War, started after fighting erupted between the Kurdish-majority People's Protection Units (YPG) and Islamist rebel factions in the city of Ras al-Ayn. The YPG launched a campaign in an attempt to take control of the Islamist-controlled areas in the governorate of al-Hasakah and parts of Raqqa and Aleppo governorates after al-Qaeda in Syria used those areas to attack the YPG. The Kurdish groups and their allies' goal was also to capture Kurdish areas from the mainly Arab Islamist rebels, and strengthen the autonomy of the region of Rojava. The Syrian Democratic Forces would go on to take substantial territory from Islamist groups, in particular the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, provoking a strong reaction from Turkey, ruled by the Islamist Justice and Development Party.
 W
WThe Syrian Train and Equip Program was a United States-led military operation launched in 2014 that identified and trained selected Syrian opposition forces inside Syria as well as in Turkey and other US-allied states who would then return to Syria to fight the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. The program reportedly cost the US $500 million. It was a covert program, run by U.S. Special Operations Forces, separate from Timber Sycamore, the parallel covert program run by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). As of July 2015, only a group of 54 trained and equipped fighters had been reported to have been deployed, which was quickly routed by al-Nusra, and a further 75 were reported in September 2015.
 W
WTimber Sycamore was a classified weapons supply and training program run by the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) and supported by some Arab intelligence services, such as the security service in Saudi Arabia. Launched in 2012 or 2013, it supplied money, weaponry and training to rebel forces fighting Syrian President Bashar al-Assad in the Syrian Civil War. According to US officials, the program was run by the CIA's Special Activities Division and has trained thousands of rebels. President Barack Obama secretly authorized the CIA to begin arming Syria's embattled rebels in 2013.
 W
WThe Tokhar Massacre, occurred on 19 July 2016 in the village of Tokhar, during an offensive by United States-backed forces near the city of Manbij in Aleppo Governorate, and carried out by the United States Air Force. The operation was carried out as part of the American-led intervention in Syria. Reports of the death toll varied, ranging from 56 to 212 civilians being killed with "entire families" pulverized.
 W
WThe western al-Bab offensive was a military operation launched by the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant in the countryside of northwestern Aleppo Governorate, south of the towns of Mare' and Tel Rifaat.