 W
WThis is a list of corvette and sloop classes of the Royal Navy. The original term for ships of fewer than 28 (carriage) guns, but at least 20 guns, was "post ship"; the term 'corvette' was not introduced into the Royal Navy until the 1830s, and at that time its use replaced both the larger sloops and also what had previously been categorised officially as 'post ships', i.e. ships of 20, 22 or 24 guns which were so-called because they were the lowest grade of warship which could be commanded by a 'post captain'; as such, they formed the lower portion of the sixth rate.
 W
WHMS Active was a Volage-class corvette built for the Royal Navy in the late 1860s. Launched in 1869, she entered service in 1873, and was the Commodore's ship on the Cape of Good Hope and West Africa Station. Her crew served ashore in both the Third Anglo-Ashanti and Zulu Wars. From 1885 to 1898, the ship was the flagship of the Training Squadron. Active was sold for scrap in 1906.
 W
WHMS Amethyst was a gaff rigged three mast sailing boat. She was a Spartan-class 26-gun sixth rate launched in 1844 and sold in 1869 for use as a cable vessel.
 W
WThe Amethyst-class corvettes were a class of the last wooden warships to be built for the British Royal Navy; each was built at a Royal Dockyard. Three were ordered under the 1871-72 Programme and two under the 1872-73 Programme. Built in the early and middle 1870s, they mostly served overseas and were retired early as they were regarded as hopelessly obsolete by the late 1880s.
 W
WHMS Andromache was a 28-gun sixth rate launched in 1832. She was converted to a powder hulk in 1854 and was broken up in 1875.
 W
WHMS Juno was a 26-gun Spartan-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy launched in 1844 at Pembroke. As HMS Juno, she carried out the historic role in 1857 of annexing the Cocos (Keeling) Islands to the British Empire. She was renamed HMS Mariner in January 1878 and then HMS Atalanta two weeks later.
 W
WHMS Calliope was a 28-gun sixth rate launched in October 1837 and broken up in November 1883.
 W
WHMS Conway was a Conway-class sixth rate of the Royal Navy, built by Chatham Dockyard and launched on 2 February 1832. She was lent to the Mercantile Marine Association of Liverpool in February 1859 to act as a training ship for boys, and gave her name to HMS Conway, a series of ships and a shore-based school. When Winchester took her place as the training ship in 1861, the two ships swapped names. Under her new name of Winchester she became the Aberdeen Royal Naval Reserve ship on 28 August 1861.
 W
WHMS Cossack was a Cossack-class corvette which was laid down as Witjas for the Imperial Russian Navy. She was seized due to the Crimean War breaking out whilst she was under construction and taken into service with the Royal Navy.
 W
WHMS Daphne was a Royal Navy corvette, the name ship of her class, commissioned in 1839
 W
WHMS Druid was a Briton-class wooden screw corvette built for the Royal Navy in the late 1860s. She spent her service life overseas on the Cape of Good Hope and North America and West Indies Stations and was sold for scrap in 1886.
 W
WHMS Eurydice was a 26-gun Royal Navy corvette which was the victim of one of Britain's worst peacetime naval disasters when she sank in 1878.
 W
WHMS Imogene was a Conway-class sixth rate of the Royal Navy, built by Pembroke Dockyard and launched on 24 June 1831. She served in the East Indies, China and South America, but was accidentally burnt while out of commission on 27 September 1840.
 W
WHMS Iris was a 26-gun sixth-rate frigate launched on 14 July 1840 from Devonport Dockyard. She spent some time with the West Africa Squadron suppressing the slave trade and later with the East Indies Station was involved in operations in Borneo. Iris was the first flagship of the Australia Station between 1859 and 1861 during which time she participated in the First Taranaki War. In 1864 she was extensively modified to allow her to ferry transatlantic telegraph cable to the cable-laying ship Great Eastern. She was decommissioned and sold off in 1869.
 W
WHMS Juno was a 26-gun Spartan-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy launched in 1844 at Pembroke. As HMS Juno, she carried out the historic role in 1857 of annexing the Cocos (Keeling) Islands to the British Empire. She was renamed HMS Mariner in January 1878 and then HMS Atalanta two weeks later.
 W
WHMS Malacca was a 17-gun sloop of the Royal Navy, launched in 1853. She later served as the Tsukuba of the Imperial Japanese Navy.
 W
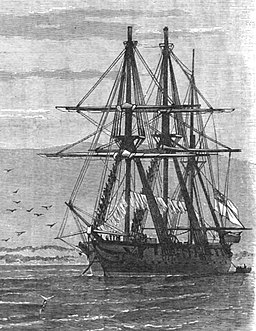
WHMS Modeste was a British Royal Navy corvette commissioned in 1838 and sold in 1866.
 W
WHMS Niger was an 8-gun screw sloop launched on 18 November 1846 from Woolwich Dockyard. She had been intended as a sailing sloop but her design was lengthened to fit a steam engine, and she was fitted with screw propulsion at Deptford Dockyard in 1847-48 prior to completion. She was reclassified as a corvette in 1852.
 W
WHMS Rover was an 18-gun iron screw corvette built for the Royal Navy in the 1870s, the sole ship of her class. The ship was initially assigned to the North America and West Indies Station until she returned home in 1879. She was transferred to the Training Squadron when it formed in 1885. Rover was not really suitable for such a role and she was placed in reserve four years later and then sold for scrap in 1893.
 W
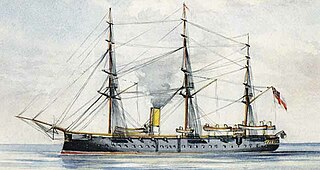
WHMS Tartar was a wooden screw corvette of the Royal Navy. Originally built for the Russian Empire, she was seized by British forces on 5 April 1854, shortly before her launch.
 W
WHMS Thetis was a Briton-class wooden screw corvette built for the Royal Navy in the late 1860s.
 W
WHMS Volage was a Volage-class corvette built for the Royal Navy in the late 1860s. She spent most of her first commission assigned to the Flying Squadron circumnavigating the world and later carried a party of astronomers to the Kerguelen Islands to observe the transit of Venus in 1874. The ship was then assigned as the senior officer's ship in South American waters until she was transferred to the Training Squadron during the 1880s. Volage was paid off in 1899 and sold for scrap in 1904.
 W
WThe Volage class was a group of two screw corvettes built for the Royal Navy in the late 1860s. Both ships spent the bulk of their active service abroad. Volage spent most of her first commission assigned to the Detached or Flying Squadron circumnavigating the world and then carried a party of astronomers to the Kerguelen Islands to observe the Transit of Venus in 1874. The ship was then assigned as the senior officer's ship in South American waters until she was transferred to the Training Squadron during the 1880s.