 W
WThe Angolan War of Independence, called in Angola the Luta Armada de Libertação Nacional, began as an uprising against forced cultivation of cotton, and it became a multi-faction struggle for the control of Portugal's overseas province of Angola among three nationalist movements and a separatist movement. The war ended when a leftist military coup in Lisbon in April 1974 overthrew Portugal's Estado Novo regime, and the new regime immediately stopped all military action in the African colonies, declaring its intention to grant them independence without delay.
 W
WThe Araguaia guerrilla was an armed movement in Brazil against its military dictatorship, active between 1967-1974 in the Araguaia river basin. It was founded by militants of the Communist Party of Brazil, the then Maoist counterpart to the Brazilian Communist Party (PCB), which aimed at establishing a rural stronghold from whence to wage a "people's war" against the Brazilian military dictatorship, which had been in power since the 1964 coup d'état. Its projected activities were based on the successful experiences led by the 26th of July Movement in the Cuban Revolution, and by the Communist Party of China during the Chinese Civil War.
 W
WThe Ballymurphy massacre was a series of incidents between 9 and 11 August 1971, in which the 1st Battalion, Parachute Regiment of the British Army killed eleven civilians in Ballymurphy, Belfast, Northern Ireland, as part of Operation Demetrius. The shootings were later referred to as Belfast's Bloody Sunday, a reference to the killing of civilians by the same battalion in Derry a few months later.
 W
WThe Battle of Basantar or the Battle of Barapind was one of the vital battles fought as part of the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 in the western sector of India. The Indian troops won a hard-fought battle that secured this area in the Punjab/Jammu sector. The name Battle of Basantar actually encompasses the entire gamut of battles and skirmishes fought in the Shakargarh sector.
 W
WThe Battle of Chamb, 1971 was a battle in the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971. The Pakistan Army invaded Chamb on the same principle as the Battle of Chamb (1965). The Pakistan Army's primary objective was to capture the town of Chamb and surrounding areas which had strategic importance for both Pakistan and India.
 W
WBlack September, also known as the Jordanian Civil War was a conflict fought in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan between the Jordanian Armed Forces (JAF), under the leadership of King Hussein, and the Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO), under the leadership of Yasser Arafat, primarily between 16 and 27 September 1970, with certain aspects of the conflict continuing until 17 July 1971.
 W
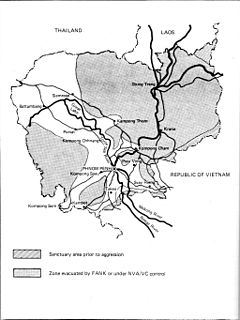
WOperation Chenla I or Chenla One was a major military operation conducted by the Khmer National Armed Forces (FANK) during the Cambodian Civil War. It began in late August 1970 and ended in February 1971, due to the FANK High Command's decision to withdraw some units from Tang Kauk to protect Phnom Penh after Pochentong airbase was attacked.
 W
WOperation Chenla II or Chenla Two was a major military operation conducted by the Khmer National Armed Forces (FANK) during the Cambodian Civil War from 20 August until 3 December 1971.
 W
WOperation Commando Hunt was a covert U.S. Seventh Air Force and U.S. Navy Task Force 77 aerial interdiction campaign that took place during the Vietnam War. The operation began on 15 November 1968 and ended on 29 March 1972. The objective of the campaign was to prevent the transit of People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) personnel and supplies on the logistical corridor known as the Ho Chi Minh Trail that ran from the southwestern Democratic Republic of Vietnam through the southeastern portion of the Kingdom of Laos and into the Republic of Vietnam.
 W
WThe Communist insurgency in Malaysia, also known as the Second Malayan Emergency, was an armed conflict which occurred in Malaysia from 1968 to 1989, between the Malayan Communist Party (MCP) and Malaysian federal security forces.
 W
WThe Communist insurgency in Sarawak occurred in Malaysia from 1962 to 1990, and involved the North Kalimantan Communist Party and the Malaysian Government. It was one of the two Communist insurgencies to challenge the former British colony of Malaysia during the Cold War. As with the earlier Malayan Emergency (1948–1960), the Sarawak Communist insurgents were predominantly ethnic Chinese, who opposed to British rule over Sarawak and later opposed the merger of the state into the newly created Federation of Malaysia. The insurgency was triggered by the 1962 Brunei Revolt, which had been instigated by the left-wing Brunei People's Party in opposition to the proposed formation of Malaysia.
 W
WThe Guinea-Bissau War of Independence was an armed independence conflict that took place in Portuguese Guinea between 1963 and 1974. Fought between Portugal and the African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde, an armed independence movement backed by Cuba and the Soviet Union, the war is commonly referred to as "Portugal's Vietnam" due to the large numbers of men and amounts of material expended in a long, mostly guerrilla war and the internal political turmoil it created in Portugal. The war ended when Portugal, after the Carnation Revolution of 1974, granted independence to Guinea-Bissau, followed by Cape Verde a year later.
 W
WThe Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 was a military confrontation between India and Pakistan that occurred during the liberation war in East Pakistan from 3 December 1971 to the fall of Dacca (Dhaka) on 16 December 1971. The war began with preemptive aerial strikes on 11 Indian air stations, which led to the commencement of hostilities with Pakistan and Indian entry into the war of independence in East Pakistan on the side of Bengali nationalist forces. Lasting just 13 days, it is one of the shortest wars in history.
 W
WOperation Lam Son 719 or 9th Route – Southern Laos Campaign was a limited-objective offensive campaign conducted in the southeastern portion of the Kingdom of Laos. The campaign was carried out by the armed forces of the South Vietnam between 8 February and 25 March 1971, during the Vietnam War. The United States provided logistical, aerial and artillery support to the operation, but its ground forces were prohibited by law from entering Laotian territory. The objective of the campaign was the disruption of a possible future offensive by the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN), whose logistical system within Laos was known as the Ho Chi Minh Trail.
 W
WThe Battle of Long Khanh was fought during the Vietnam War between elements of 1st Australian Task Force and the Viet Cong (VC) and People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) during Operation Overlord. The fighting saw Australian infantry from 3rd Battalion, Royal Australian Regiment attack a heavily fortified communist base camp in Long Khanh Province, while Centurion tanks providing close support crushed many bunkers and their occupants. Regardless, the VC fought hard to delay the Australian advance and although the bunker system was subsequently captured, along with a second system further south, the Australians suffered a number of casualties and the loss of a UH-1 Iroquois helicopter. With the Australians unable to concentrate sufficient combat power to achieve a decisive result, the bulk of the VC/PAVN force successfully withdrew intact, although they probably sustained heavy casualties in the process.
 W
WAnnette McGavigan was a 14-year-old girl fatally wounded by a gunshot in crossfire between British soldiers and the IRA on 6 September 1971. After three years of conflict in Northern Ireland, Annette became the 100th civilian to be killed in the Troubles. No individual has been charged with her death.
 W
WOperation Demetrius was a British Army operation in Northern Ireland on 9–10 August 1971, during the Troubles. It involved the mass arrest and internment of 342 people suspected of being involved with the Irish Republican Army (IRA), which was waging an armed campaign for a united Ireland against the British state. It was proposed by the Northern Ireland Government and approved by the British Government. Armed soldiers launched dawn raids throughout Northern Ireland, sparking four days of violence in which 20 civilians, two IRA members and two British soldiers were killed. All of those arrested were Irish nationalists, the vast majority of them Catholic. Due to faulty intelligence, many had no links with the IRA. Ulster loyalist paramilitaries were also carrying out acts of violence, which were mainly directed against Catholics and Irish nationalists, but no loyalists were included in the sweep.
Operation Gordian Knot was the largest and most expensive Portuguese military campaign in the Portuguese overseas province of Mozambique, East Africa. Carried out from 1970 to 1971, during the Portuguese Colonial War (1961–1974). The objectives of the campaign were to close down FRELIMO's infiltration routes across the Tanzanian border and to destroy permanent FRELIMO bases inside the liberated zones in Northern Mozambique. Gordian Knot was a seven-month long campaign ultimately employing thirty-five thousand men, and was almost successful since it destroyed most guerrilla camps located inside FRELIMO's liberated zones and captured large numbers of rebels and armaments, forcing FRELIMO to retreat from their bases and outposts in the provinces. The operation ultimately failed when FRELIMO forces regrouped and thrust further south into the province of Tete, opening a new front and overstretching the Portuguese Army. The failure of Gordian Knot helped fuel the discontent that led to the Carnation Revolution in April 1974.
 W
WOperation Shed Light was a crash development project in aerial warfare, initiated in 1966 by the United States Air Force to increase the ability to accurately strike at night or in adverse weather. During the 1960s the United States military worked hard to interdict the movement of men and materiel along the Ho Chi Minh trail. The North Vietnamese were experts in the use of weather and darkness to conceal their movement, and understanding the superiority of American air power put their skills immediately to good use. US forces seeking to impede the steady flow of supplies attempted to locate largely static targets during the day with poor results.
 W
WA Naxal or Naxalite is a member of any political organisation that claims the legacy of the Communist Party of India (Marxist–Leninist), founded in Calcutta in 1969. The Communist Party of India (Maoist) is the largest existing political group in that lineage today in India.
 W
WOperation Ranch Hand was a U.S. military operation during the Vietnam War, lasting from 1962 until 1971. Largely inspired by the British use of 2,4,5-T and 2,4-D during the Malayan Emergency in the 1950s, it was part of the overall chemical warfare program during the war called "Operation Trail Dust". Ranch Hand involved spraying an estimated 20 million U.S. gallons (76,000 m3) of defoliants and herbicides over rural areas of South Vietnam in an attempt to deprive the Viet Cong of food and vegetation cover. Areas of Laos and Cambodia were also sprayed to a lesser extent. Nearly 20,000 sorties were flown between 1961 and 1971.
 W
WThe seizure of Abu Musa and the Greater and Lesser Tunbs by Imperial Iranian Navy forces took place on 30 November 1971, after the withdrawal of British forces from the islands of Abu Musa and the Greater Tunb and Lesser Tunb, which are located in the Strait of Hormuz. The islands had been claimed by Iran and by the newly formed United Arab Emirates as a territory of the Emirate of Ras Al Khaimah. Iran has maintained military control of the islands since, while the UAE has made several attempts through international channels to regain control of the islands.
 W
W