 W
WThe Battle of Camp Allegheny, also known as the Battle of Allegheny Mountain, took place on December 13, 1861, in Pocahontas County, Virginia, about 3 miles from the mountainous border of Highland County, Virginia, as part of the Operations in Western Virginia Campaign during the American Civil War. The battle was a small brigade-level conflict, and while the Confederates technically won with a Union withdrawal, it was considered militarily indecisive. However, it had critical implications for the future border of Virginia and West Virginia, ensuring Highland County remained in Confederate hands and would not be involved in the formation of the future state of West Virginia.
 W
WAntietam National Battlefield is a National Park Service-protected area along Antietam Creek in Sharpsburg, Washington County, northwestern Maryland. It commemorates the American Civil War Battle of Antietam that occurred on September 17, 1862.
 W
WThe Appomattox Court House National Historical Park is a preserved 19th century village in Appomattox County, Virginia. The village is famous for the site of the Battle of Appomattox Court House and contains the house of Wilmer McLean, where the surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia under Robert E. Lee to Union commander Ulysses S. Grant took place on April 9, 1865, effectively ending the American Civil War. The McLean House was the site of the surrender conference, but the village itself is named for the presence nearby of what is now preserved as the Old Appomattox Court House.
 W
WAuburn Battlefield, also known as Coffee Hill Battlefield, is a national historic district and American Civil War battlefield located near Catlett, Fauquier County, Virginia. It encompasses the areas of the two Auburn battles on October 13 and 14, 1863, and includes 18 contributing buildings, 23 contributing sites, and 8 contributing structures. The battles are referred to as the First Battle of Auburn and Second Battle of Auburn.
 W
WBall's Bluff Battlefield Regional Park and National Cemetery is a battlefield area and a United States National Cemetery, located 2 miles (3.2 km) northeast of Leesburg, Virginia. The cemetery is the third smallest national cemetery in the United States. Fifty-four Union Army dead from the Battle of Ball's Bluff are interred in 25 graves in the half-acre plot; the identity of all of the interred except for one, James Allen of the 15th Massachusetts, are unknown. Monuments to fallen Confederate Sergeant Clinton Hatcher and Union brigade commander Edward Dickinson Baker are located next to the cemetery, though neither is buried there. While the stone wall-enclosed cemetery itself is managed through the Culpeper National Cemetery and owned by the Department of Veterans Affairs, the balance of the 223-acre (0.90 km2) park is managed through the Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority.
 W
WThe Camp Bartow Historic District — centered on the historic inn called "Traveller's Repose" and the site of the Battle of Greenbrier River (1861) — is a national historic district located at Bartow, Pocahontas County, West Virginia, United States. It is situated at the foot of Burner Mountain, at a bend in the East Fork Greenbrier River, where U.S. Route 28 intersects U.S. Route 250.
 W
WCarnifex Ferry Battlefield State Park is an American Civil War battle site that commemorates the Battle of Carnifex Ferry. It is located on the rim of the Gauley River Canyon near Summersville, a town in Nicholas County, West Virginia. The 156-acre (0.63 km2) park features Patterson House Museum, three views of the Gauley River, hiking trails and picnic facilities. It is one of the oldest state parks in the United States. A Civil War reenactment takes place on a weekend after Labor Day. As Carnifex Ferry State Park, it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.
 W
WCedar Creek and Belle Grove National Historical Park became the 388th unit of the United States National Park Service when it was authorized on December 19, 2002. The National Historical Park was created to protect several historically significant locations in the Shenandoah Valley of Northern Virginia, notably the site of the American Civil War Battle of Cedar Creek and the Belle Grove Plantation.
 W
WDroop Mountain Battlefield State Park is a state park located on Droop Mountain in Pocahontas County, West Virginia. The park was the site of the Battle of Droop Mountain, the last major battle of the American Civil War in the state taking place on November 6, 1863. John D. Sutton, a West Virginia private in the Union Army at the battle, became the leader in the movement to create the park when he served in the West Virginia House of Delegates. Dedicated on July 4, 1928, Droop Mountain Battlefield became the first state park in West Virginia.
 W
WFive Forks Battlefield is a battlefield of the American Civil War, the location of the Battle of Five Forks, in which Union Army forces broke through Confederate Army lines, opening the way to gain control of the last rail line to besieged Petersburg. The Confederate loss caused them to abandon that city, which undermined the defense of Richmond, the Confederate capital. Final surrender of the Confederate forces would occur at Appomattox Courthouse eight days later.
 W
WFredericksburg and Spotsylvania National Military Park is a unit of the National Park Service in Fredericksburg, Virginia, and elsewhere in Spotsylvania County, commemorating four major battles in the American Civil War: Fredericksburg, Chancellorsville, The Wilderness, and Spotsylvania.
 W
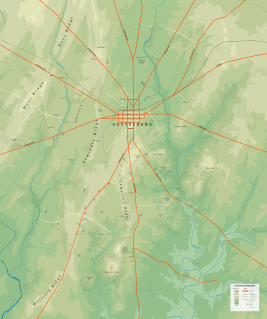
WThe Gettysburg Battlefield is the area of the July 1–3, 1863, military engagements of the Battle of Gettysburg within and around the borough of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Locations of military engagements extend from the 4-acre (1.6 ha) site of the first shot at Knoxlyn Ridge on the west of the borough, to East Cavalry Field on the east. A military engagement prior to the battle was conducted at the Gettysburg Railroad trestle over Rock Creek, which was burned on June 27.
 W
WHarpers Ferry National Historical Park is located at the confluence of the Potomac and Shenandoah rivers in and around Harpers Ferry, West Virginia. The park includes land in the Shenandoah Valley in Jefferson County, West Virginia; Washington County, Maryland and Loudoun County, Virginia. The park is managed by the National Park Service, an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior. Originally designated Harpers Ferry National Monument in 1944, the park was declared a National Historical Park by the U.S. Congress in 1963. The park includes the historic town of Harpers Ferry, notable as a center of 19th-century industry and as the scene of John Brown's failed abolitionist uprising. Consisting of almost 4,000 acres (16 km2), it includes the site of which Thomas Jefferson once wrote, "The passage of the Potomac through the Blue Ridge is perhaps one of the most stupendous scenes in Nature" after visiting the area in 1783. Due to a mixture of historical events and ample recreational opportunities, all within 50 miles (80 km) of Washington, D.C., the park was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on October 15, 1966. The Park's Superintendent is presently Tyrone Brandyburg.
 W
WManassas National Battlefield Park is a unit of the National Park Service located in Prince William County, Virginia, north of Manassas that preserves the site of two major American Civil War battles: the First Battle of Bull Run, also called the First Battle of Manassas, and the Second Battle of Bull Run or Second Battle of Manassas. It was also where Confederate General Thomas J. Jackson acquired his nickname "Stonewall". The park was established in 1940 and listed on the National Register of Historic Places on October 15, 1966.
 W
WMonocacy National Battlefield is a unit of the National Park Service, the site of the Battle of Monocacy in the American Civil War fought on July 9, 1864. The battlefield straddles the Monocacy River southeast of the city of Frederick, Maryland. The battle, labeled "The Battle That Saved Washington," was one of the last the Confederates would carry out in Union territory. The two opposing leaders were General Jubal Early, fighting for the South, and General Lew Wallace, fighting for the North.
 W
WNew Market Battlefield State Historical Park is a historic American Civil War battlefield and national historic district located near New Market, Shenandoah County, Virginia. The district encompasses the site of the Battle of New Market, a battle fought on May 15, 1864, during Valley Campaigns of 1864. In the middle of the battlefield stands the Bushong House, used by both sides as a hospital during the battle and now the visitor center for the 300-acre park.
 W
WOx Hill Battlefield Park is a site in Fairfax, Virginia, where the Battle of Ox Hill was fought during the American Civil War. It was the only major battle of the war fought in Fairfax County. The battlefield is now a public park adjacent to suburban developments and the Fairfax Towne Center shopping center, and is maintained by the Fairfax County Park Authority.
 W
WThe Petersburg Breakthrough Battlefield is a historic district in Dinwiddie County, near Petersburg, Virginia. It was the location of the Third Battle of Petersburg, in which the Union Army broke through Confederate Army lines protecting Petersburg and Richmond on April 2, 1865, during the American Civil War. The success of the breakthrough led to abandonment of Richmond by General Robert E. Lee, a general retreat, and surrender at Appomattox Court House one week later. Portions of the area were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2003, and a different portion was designated a National Historic Landmark in 2006. Much of the battlefield area is part of Pamplin Historical Park, a private park open to the public that interprets the battle. The park includes a full-service visitor center, trails, displays, interpretive signs and history programs. The Civil War Trust and its partners have acquired and preserved 407 acres (1.65 km2) of the Breakthrough battlefield in five transactions since 2004.
 W
WPetersburg National Battlefield is a National Park Service unit preserving sites related to the American Civil War Siege of Petersburg (1864–65). The Battlefield is centered on the city of Petersburg, Virginia, and also includes outlying components in Hopewell, Prince George County, and Dinwiddie County. Over 140,000 people visit the park annually.
 W
WThe Richmond National Battlefield Park commemorates 13 American Civil War sites around Richmond, Virginia, which served as the capital of the Confederate States of America for most of the war. The park connects certain features within the city with defensive fortifications and battle sites around it.
 W
WSailor's Creek Battlefield Historical State Park is a 321-acre (130 ha) state park in Rice, Virginia,. It includes a portion of the landmarked Sayler's Creek Battlefield, an area of 1,022 acres (414 ha) that was the site of the April 6th, 1865 Battle of Sayler's Creek, one of the last major engagements in the Eastern Theater of the war during Confederate General-in-Chief Robert E. Lee (1807-1870), during his week-long retreat to the southwest in the final Appomattox campaign from the fallen Confederate capital at Richmond and nearby Petersburg, before his subsequent surrender three days later at Appomattox Court House to pursuing Union Army General-in-Chief Ulysses S. Grant (1822-1885), on April 9, 1865, effectively ending the American Civil War (1861-1865).
 W
WSayler's Creek Battlefield near Farmville, Virginia was the site of the Battle of Sayler's Creek of the American Civil War. Robert E. Lee's army was retreating from the Richmond to Petersburg line. Here, on April 6, 1865, Union General Philip Sheridan cut off and beat back about a quarter of Lee's army. Eight Confederate generals surrendered, and 7,700 men were lost. Confederate Major General George Washington Custis Lee, eldest son of Robert E. Lee, was forcibly captured on the battlefield by Private David Dunnels White of the 37th Massachusetts Regiment. This was the last major engagement of the war in Virginia; Lee's surrender at Appomattox occurred three days later. A portion of the landmarked battlefield area is included in Sailor's Creek Battlefield Historical State Park. The Civil War Trust and its partners have acquired and preserved 885 acres (3.58 km2) of the battlefield in five transactions since 1996.
 W
WThoroughfare Gap Battlefield is a historic American Civil War battlefield located at Thoroughfare Gap, Broad Run, Prince William County, Virginia. It was the site of the Battle of Thoroughfare Gap. The property includes a number of resources present at the time of the battle including the separately listed Beverley Mill, a five-story, coursed-rubble stone building set into the north side of Thoroughfare Gap. Meadowlands, the Chapman's house and the second Upper Mill are clearly visible on the landscape, as well as an important ice pit and a walled cemetery associated with the Chapman family.