 W
WThe 11 September 1922 Revolution was an uprising by the Greek army and navy against the government in Athens. The revolution took place on 11 September [N.S. 24 September] 1922.
 W
WThe 1922 Turin massacre refers to the attack by Italian Fascists against members of a local labour movement in Turin, Italy, during a three-day terror campaign from 18–20 December 1922, to break the resistance of the labour movement and working class to Fascism.
 W
WThe Battle of Dublin was a week of street battles in Dublin from 28 June to 5 July 1922 that marked the beginning of the Irish Civil War. Six months after the Anglo-Irish Treaty ended the recent Irish War of Independence, it was fought between the forces of the new Provisional Government and a section of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) that opposed the Treaty. The Irish Citizen Army also became involved in the Battle, supporting the anti-Treaty IRA in the O'Connell Street area. The fighting began with an assault by Provisional Government forces on the Four Courts building, and ended in a decisive victory for the Provisional Government.
 W
WThe Battle of Dumlupınar, or known as Field Battle of the Commander-in-Chief in Turkey, was the last battle in the Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922). The battle was fought from 26 to 30 August 1922 near Dumlupınar, Kütahya in Turkey.
 W
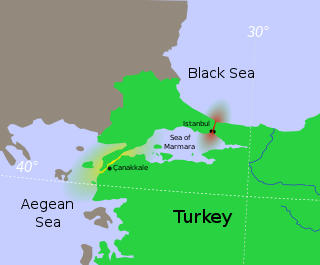
WThe Turkish capture of Smyrna was the final phase of the Great Offensive and last battle of the Turkish War of Independence. After the Turkish Army inflicted heavy losses on the Greek Army at Dumlupınar, on 30 August 1922, Greek forces were in continual retreat towards Smyrna as the Turkish Army's westward advance continued. On the eve of the Turkish arrival, Greek forces left the city, and on 8 September, at ten o'clock in the morning, the Greek administration ceased to exist in Smyrna. On 9 September 1922, the Turkish Army entered İzmir from Kemalpaşa to the east.
 W
WThe Chanak Crisis, also called the Chanak Affair and the Chanak Incident, was a war scare in September 1922 between the United Kingdom and Turkey. Chanak refers to Çanakkale, a city on the Anatolian side of the Dardanelles Strait. The crisis was caused by Turkish efforts to push the Greek armies out of Turkey and restore Turkish rule in the Allied-occupied territories, primarily in Constantinople and Eastern Thrace. Turkish troops marched against British and French positions in the Dardanelles neutral zone. For a time, war between Britain and Turkey seemed possible, but Canada refused to agree as did France and Italy. British public opinion did not want a war. The British military did not either, and the top general on the scene, Sir Charles Harington, refused to relay an ultimatum to the Turks because he counted on a negotiated settlement. The Conservatives in Britain's coalition government refused to follow Liberal Prime Minister David Lloyd George, who with Winston Churchill was calling for war.
 W
WThe Chauri Chaura incident took place on 4 February 1922 at Chauri Chaura in the Gorakhpur district of the United Province in British India, when a large group of protesters participating in the Non-cooperation movement, clashed with police who opened fire. In retaliation the demonstrators attacked and set fire to a police station, killing all of its occupants. The incident led to the death of three civilians and 23 policemen. Mahatma Gandhi, who was strictly against violence, halted the non-co-operation movement on the national level on 12 February 1922, as a direct result of this incident.
 W
WThe 18 of the Copacabana Fort revolt occurred on July 5, 1922, in the city of Rio de Janeiro, then the Federal District of Brazil. It was the first revolt of the tenentista movement, in the context of the Brazilian First Republic.
 W
WAntônio de Siqueira Campos was a leader and one of two survivors of a military revolt that occurred in July 1922 on Copacabana Beach in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, which became known as the 18 of the Copacabana Fort revolt. Following release from prison he took part in further rebellions including the so-called Prestes Column from 1925 to 1927. Siqueira Campos was born in Rio Claro in the Brazilian state of São Paulo on 18 May 1898 and died in Uruguay in a plane crash on 10 May 1930.
 W
WThe East Karelian Uprising and the Soviet–Finnish conflict 1921–1922 were an attempt by a group of East Karelian separatists to gain independence from the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. They were aided by a number of Finnish volunteers, starting from 6 November 1921. The conflict ended on 21 March 1922 with the Agreements between the governments of Soviet Russia and Finland about the measures of maintenance of the inviolability of the Soviet–Finnish border. The conflict is regarded in Finland as one of the heimosodat – "Kinship Wars".
 W
WThe Great Offensive was the largest and final military operation of the Turkish War of Independence, fought between the Turkish Armed Forces loyal to the government of the Grand National Assembly of Turkey, and the Kingdom of Greece, ending the Greco-Turkish War. The offensive began on 26 August 1922 with the Battle of Dumlupınar. The Turks amassed around 104,000 men, the largest number since the beginning of the war, to begin the offensive against the Greek army of approximately 130,000 men. From 31 August to 9 September, the front moved a distance of 300 km (190 mi) as the Greek troops retreated. The Turkish army lacked motorized vehicles; its forces consisted of infantry and cavalry units, and logistical support was provided by a supply system based on ox carts.
 W
WThe Greco-Turkish War of 1919–1922 was fought between Greece and the Turkish National Movement during the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire in the aftermath of World War I, between May 1919 and October 1922.
 W
WThe Herrin massacre took place on June 21–22, 1922 in Herrin, Illinois, in a coal mining area during a nationwide strike by the United Mineworkers of America (UMWA). Although the owner of the mine originally agreed with the union to observe the strike, when the price of coal went up, he hired non-union workers to produce and ship out coal, as he had high debt in start-up costs. After an exchange of gunfire by armed guards and union miners, three miners and 20 non-miners were killed, including the superintendent and 19 strikebreakers.
 W
WIkhwan raids on Transjordan were a series of plunders by the Ikhwan, irregular Arab tribesmen of Najd, on Transjordan between 1922 and 1924. The repeated Wahhabi incursions from Najd into southern parts of his territory were the most serious threat to emir Abdullah's position in Transjordan. The emir was powerless to repel those raids by himself, thus the British maintained a military base, with a small air force, at Marka, close to Amman. The British military force was the primary obstacle against the Ikhwan, helping emir Abdullah to secure his rule over Transjordan.
 W
WMahmud Barzanji revolts were a series of armed uprisings by Kurdish Sheykh Mahmud Barzanji against the Iraqi authority in newly conquered British Mesopotamia and later the British Mandate in Iraq. Following his first insurrection in May 1919, Sheykh Mahmud was imprisoned and eventually exiled to India for a one-year period. When returning, he was once again appointed a governor, but shortly revolted again declaring himself as the ruler of the Kingdom of Kurdistan. The Kingdom of Kurdistan lasted from September 1922 – July 1924. With British forces greatly exceeding his in ammunition and training, the defeat finally subdued the region to central British Iraqi rule in 1924. Sheykh Mahmud retreated into mountains, and eventually reached terms with the independent Kingdom of Iraq in 1932, over his return from the underground. Sheykh Mahmud revolts are considered the first chapter of the modern Iraqi–Kurdish conflict.
 W
WThe March on Rome was an organized mass demonstration in October 1922, which resulted in Benito Mussolini's National Fascist Party (PNF) ascending to power in the Kingdom of Italy. In late October 1922, Fascist Party leaders planned an insurrection, to take place on 28 October. When fascist troops entered Rome, Prime Minister Luigi Facta wished to declare a state of siege, but this was overruled by King Victor Emmanuel III. On the following day, 29 October 1922, the King appointed Mussolini as Prime Minister, thereby transferring political power to the fascists without armed conflict.
 W
WOperation Nemesis was a covert operation and an assassination campaign by the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (Dashnaktsutyun) carried out between 1920 and 1922, during which a number of former Ottoman political and military figures were assassinated for their role in the Armenian Genocide, as well as Azerbaijani figures for the 1918 massacre of Armenians in Baku. Shahan Natalie and Armen Garo are considered its masterminds. It was named after the Greek goddess of divine retribution, Nemesis.
 W
WThe Paraguayan Civil War (1922), took place between 27 May 1922 and 10 July 1923, within the borders of Paraguay. It started when supporters of candidate Adolfo Chirife attempted to forcefully restore the implementation of presidential elections canceled by President Eusebio Ayala. Chirife represented the so-called Constitutionalist or Schaererist side ideologically supporting liberal politician Eduardo Schaerer, while troops under Ayala were named Loyalists or Gondrists ideologically pledging allegiance to former President Manuel Gondra. The conflict concluded when Gondrist forces defeated the remnants of the Schaererist army in Asunción.
 W
WThe Rand Rebellion was an armed uprising of white miners in the Witwatersrand region of South Africa, in March 1922. Jimmy Green, a prominent politician in the Labour Party, was one of the leaders of the strike.
 W
WThe Rif War was an armed conflict fought from 1920 to 1927 between the colonial power Spain and the Berber tribes of the Rif mountainous region of Morocco. Led by Abd el-Krim, the Riffians at first inflicted several defeats on the Spanish forces by using guerrilla tactics and captured European weapons. After France's military intervention against Abd el-Krim's forces and the major landing of Spanish troops at Al Hoceima, considered the first amphibious landing in history to involve the use of tanks and aircraft, Abd el-Krim surrendered to the French and was taken into exile.
 W
WSheikh Khazal rebellion refers to the 1924 Arab separatist uprising by Khazal al-Kabi, the Sheikh of Mohammerah, in Iranian Khuzestan. The rebellion was quickly and efficiently suppressed by Reza Pahlavi with minimal casualties, subduing the Bakhtiari tribes allied with Sheikh Khazal and resulting in his surrender.
 W
WThe Simko Shikak revolt refers to an armed Ottoman-backed tribal Kurdish uprising against the Qajar dynasty of Iran from 1918 to 1922, led by Kurdish chieftain Simko Shikak from the Shekak tribe. The revolt is often referred as the first modern conflict involving Iranian Kurds with separatist ambitions.