 W
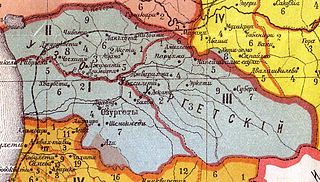
WThe 1841 rebellion in Guria was a conflict in the former Georgian principality of Guria, at that time part of the Georgia-Imeretia Governorate of the Russian Empire, that took place as a reaction to the government's newly introduced duties and taxes for the Georgian peasants. The rebels, joined by several nobles, were initially successful in overrunning much of Guria, but they were finally defeated by the Russian army and the allied Georgian nobility in September 1841.
 W
WThe Battle of Amoy was fought between British and Qing forces at Amoy on Xiamen Island, Fujian, in the Qing Empire on 26 August 1841 during the First Opium War. The British captured the forts at Xiamen and on nearby Gulangyu Island.
 W
WThe Broadway expedition was a British military expedition that explored the Broadway River in Guangdong province, China, on 13–15 March 1841 during the First Opium War. The river was also called the Inner Passage or Macao Passage as it served as an intricate channel from the Portuguese colony of Macao to the Chinese city of Canton (Guangzhou). The expedition was the first time a European vessel traversed the passage, and was believed by the Chinese to be inaccessible to foreigners due to the shallowness and intricacy of the channel as well as the forts along the banks. The iron steamship Nemesis had a shallow draught of 6 feet (1.8 m), which was a major advantage in navigating the river. Despite being over 600 tons burden, the ship was able to navigate through a river that frequently had less than 6 feet of water and through mud in areas of only 5 feet (1.5 m).
 W
WThe First Battle of Canton was fought between British and Chinese forces in Canton, Guangdong Province, China, on 18 March 1841 during the First Opium War. The capture led to the hoisting of the Union Jack on the British factory in Canton and the resumption of trade between the British and the Chinese.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Canton was fought between British and Chinese forces in Canton (Guangzhou), Guangdong province, China, in May 1841 during the First Opium War.
 W
WThe second capture of Chusan occurred on 1 October 1841 during the First Opium War when British forces captured the city of Dinghai, capital of the Chusan (Zhoushan) islands off the east Chinese coast.
 W
WThe Battle of Chinhai was fought between British and Chinese forces in Chinhai (Zhenhai), Zhejiang province, China, on the 10 October 1841 during the First Opium War. The Chinese force consisted of a garrison of Manchu and Mongol Bannermen. The British capture of this city allowed them to seize Ningpo unopposed on the 13 October.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Chuenpi was fought between British and Chinese forces in the Pearl River Delta, Guangdong province, China, on 7 January 1841 during the First Opium War. The British launched an amphibious attack at the Humen strait (Bogue), capturing the forts on the islands of Chuenpi and Taikoktow. Subsequent negotiations between British Plenipotentiary Charles Elliot and Chinese Imperial Commissioner Qishan resulted in the Convention of Chuenpi on 20 January. As one of the terms of the agreement, Elliot announced the cession of Hong Kong Island to the British Empire, after which the British took formal possession of the island on 26 January.
 W
WThe Dogra–Tibetan War or Sino-Sikh War was fought from May 1841 to August 1842, between the forces of the Dogra nobleman Gulab Singh of Jammu, under the suzerainty of the Sikh Empire, and Tibet under the suzerainty of Qing China. Gulab Singh's commander was the able general Zorawar Singh Kahluria, who, after the conquest of Ladakh, attempted to extend its boundaries in order to control the trade routes into Ladakh. Zorawar Singh's campaign, suffering from the effects of inclement weather, suffered a defeat at Minsar and Singh was killed. The Tibetans then advanced on Ladakh. Gulab Singh sent reinforcements under the command of his nephew Jawahir Singh. A subsequent battle near Leh in 1842 led to a Tibetan defeat. The Treaty of Chushul was signed in 1842 maintaining the status quo ante bellum.
 W
WThe Dorr Rebellion (1841–1842) was an attempt by middle-class residents to force broader democracy in the U.S. state of Rhode Island, where a small rural elite was in control of government. It was led by Thomas Wilson Dorr, who mobilized the disenfranchised to demand changes to the state's electoral rules. The state was still using its 1663 colonial charter as a constitution; it required that voters own land as qualification to vote. A later legislative rule required that a man had to be white and own $134 in property in order to vote.
 W
WThe Battle of Famaillá, was a Federal Party victory, under the command of former Uruguayan president Manuel Oribe, over the army of the Unitarian Party under general Juan Lavalle, during the Argentine Civil War.
 W
WThe Battle of First Bar was fought between British and Chinese forces at First Bar Island and its surrounding area in the Pearl River, Guangdong province, China, on 27 February 1841 during the First Opium War.
 W
WThe Battle of Jellalabad in 1842 was an Afghan siege of the isolated British outpost at Jellalabad about 80 miles (130 km) east of Kabul. The siege was lifted after five months when a British counterattack routed the Afghans, driving them back to Kabul.
 W
WThe Nerbudda incident was the execution of 197 personnel of the British transport ship Nerbudda and brig Ann in Taiwan on 10 August 1842 during the First Opium War. An additional 87 prisoners died from ill-treatment in captivity. In September 1841, the Nerbudda became shipwrecked off northern Taiwan near Keelung. In March 1842, the Ann became shipwrecked at Da'an harbour. Survivors from both ships—primarily Indian camp followers and lascars—were captured and marched south to the capital of Taiwan Prefecture, where they were imprisoned before being beheaded. Out of the nearly 300 castaways who landed or attempted to land in Taiwan, only 11 survived captivity and execution. The Daoguang Emperor ordered the execution on 14 May 1842, after the Chinese defeat in Zhejiang.
 W
WThe Rufus River Massacre was a massacre of 30–40 Aboriginal people that took place in 1841 along the Rufus River, in the Central Murray region, after three consecutive ambushes with "overlanders" on the recently opened overland stock route, which followed an old Aboriginal route. The massacre occurred after an official party, including Protector of Aborigines, Matthew Moorhouse, along with police, was sent out by the Governor of South Australia, George Grey.
 W
WThe Sanyuanli incident was a military conflict between regular troops of the British Army and an irregular force made up of Chinese militia and local citizens that took place around Sanyuanli village on the outskirts of Canton on the 29 May 1841 after the Second Battle of Canton at the time of the First Opium War (1839–1842). Regarded by the British as a minor skirmish, to the Chinese it is regarded as a live example of a spontaneous uprising by the indigenous Chinese people in response to the actions of an actively aggressive invading foreign power since 1644.
 W
WThe Second Seminole War, also known as the Florida War, was a conflict from 1835 to 1842 in Florida between various groups of Native Americans collectively known as Seminoles and the United States, part of a series of conflicts called the Seminole Wars. The Second Seminole War, often referred to as the Seminole War, is regarded as "the longest and most costly of the Indian conflicts of the United States".
 W
WThe Battle of the Bogue was fought between British and Chinese forces in the Pearl River Delta, Guangdong province, China, on 23–26 February 1841 during the First Opium War. The British launched an amphibious attack at the Humen strait (Bogue), capturing the forts on the islands of Anunghoy and North Wangtong. This allowed the fleet to proceed further up the Pearl River towards the city of Canton (Guangzhou), which they captured the following month.
 W
WThe Battle of Village Creek occurred on May 24, 1841, on the embankments of Village Creek. The battle, which evolved into a running gunfight between the Republic of Texas militia and the Village Creek tribes, was attributed to the increased Native American raids on Anglo settlements in the Red River counties.
 W
WThe Battle of Whampoa was fought between British and Chinese forces at Whampoa Island on the Pearl River near the city of Canton (Guangzhou), Guangdong, China, on 2 March 1841 during the First Opium War.