 W
WThe 3,7cm ÚV vz. 38, manufacturer's designation Škoda A7, was a 37 mm tank gun designed by the Skoda Works in Czechoslovakia prior to World War II.
 W
WThe 8 cm kanon PL vz. 37 (Anti-aircraft Gun Model 37 was a Czech anti-aircraft gun used during the Second World War. Those weapons captured after the German occupation of Czechoslovakia in March 1939 were taken into Wehrmacht service as the 7.65 cm Flak M 37 . 97 were in service during the Munich Crisis in September 1938 of which Slovakia seized one when it declared independence six months later.
 W
WAM 50 is an automatically launched assault bridge used by combat engineers for crossing narrow obstacles such as rivers, canals, and ditches. It is mounted on heavy vehicles, and can bridge a gap up to 53 meters.
 W
WThe CZ 97B is a semi-automatic handgun introduced in 1997 in the .45 ACP caliber. The CZ 97B is essentially the CZ 75B in .45 ACP rather than 9mm, leading many gun enthusiasts to call the 97B the "big brother" to the very popular CZ 75B.
 W
WThe vz. 38 is a semi-automatic pistol manufactured from 1939 until 1945 chambered in .380 ACP. The barrel is attached to the frame by a hinge, allowing for very easy disassembly. Certain aspects of the pistol are covered by Czechoslovakian patent 65558 which may also be found as Finnish patent FI18533(A) from 1939.
 W
WThe Czechoslovak Army was the name of the armed forces of Czechoslovakia. It was established in 1918 following Czechoslovakia's declaration of independence from Austria-Hungary.
 W
WThe pistole vz. 24 was the standard Czech Army pistol of the inter-war period. It was an improved version of the pistole vz. 22, which had been licensed from Mauser. Slovakia seized over ten thousand vz. 24s when it declared its independence from Czechoslovakia in March 1939. The vz. 24 was succeeded in production by a simplified version chambered in .32 ACP, the vz. 27.
 W
WThe RPG-75 is a portable, disposable, single-shot anti-tank weapon, developed in the 1970s in Czechoslovakia. It fires a 68 mm grenade with an effective range of 300 meters and maximum range of 1000 meters. It resembles the American M72 LAW rocket launcher. This RPG is recommended to be used on light tanks and armoured track vehicles.
 W
WHolek is brand of revolvers made by Czech company ALFA - PROJ.
 W
WThe Skoda 105 mm Model 1939 was a mountain gun, manufactured by Skoda Works as a companion piece for the 75 mm M.39. This was a revised version of the 100 mm M.16 and 100 mm M.16/19. Like them it was broken down into three loads, each towed by a pair of horses, for transport.
 W
WThe Tatra 72 was an army off-road truck model made by Czech manufacturer Tatra between 1933 and 1937. It was mainly used for transporting military cargo, personnel and towing artillery pieces in Czech and later German armies. The design was also license-built in France by Lorraine-Dietrich.
 W
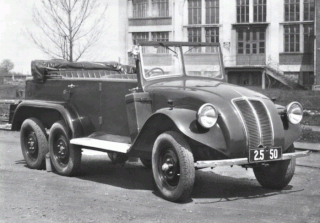
WThe Tatra 81 was heavy-duty truck model made by Czech manufacturer Tatra between 1940 and 1942. The development was ordered by German government in the aftermath of the German occupation of Czechoslovakia in 1939 and was complete the same year. It was mainly used in Germany by Ordnungspolizei, but few were utilized by Wehrmacht to ferry supplies. The vehicle had an 8-cylinder diesel engine with 12467 cc rated to 117.8 kW (158.0 hp) power. It had 4 gears and 1 reverse gear. The truck chassis, based on the Tatra backbone chassis conception, has 5700kg empty weight. The truck was rated for 6500 kg payload The Tatra 81 was capable of traveling at 65 km/h (40 mph).
 W
WThe Tatra 82 was a heavy-duty car model made by Czech manufacturer Tatra between 1935 and 1938. It was mainly used for military cargo and personnel.
 W
WThe Tatra 92 was an army off-road truck model made by Czech manufacturer Tatra between 1937 and 1941. It was mainly used for transporting military cargo and personnel in Czech and later German armies, but also ambulance and field kitchen lorry versions were made. The significant part of the production batch was exported to Kingdom of Romania.
 W
WThe TQ-Mi is an obsolete circular Czechoslovakian anti-tank blast mine. The mines body is made of cardboard impregnated with asphalt. A central pressure cap is made of glass, which sits on top of a chemical fuze, which is crushed open onto the booster charge. The booster charge is embedded in the TNT main charge, above which are a number of scrap metal fragments, giving a secondary anti-personnel effect.
 W
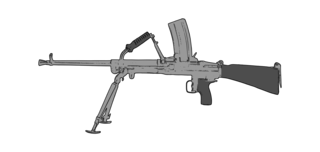
WThe vz. 52 is a Czechoslovak light machine gun developed after the Second World War for the Czechoslovak Armed Forces.
 W
WThe War College was a military staff college in Prague established by the government of Czechoslovakia in 1921 with the assistance of France. Originally called the War School, it was renamed the War College in 1934. It occupied the third floor of Tychonova 1 in Prague - as of 2017 the headquarters of the Czech Ministry of Defense.
 W
WThe ZB-30 and ZB-30J were Czechoslovakian light machine guns that saw extensive use during World War II.
 W
WThe ZB-60 was a heavy machine gun designed by Zbrojovka Brno in Czechoslovakia during the 1930s. Weapons acquired after the German occupation of Czechoslovakia in March 1939 were taken into Wehrmacht service as the 15 mm FlaMG 39(t); Former Yugoslav guns were designated as the 15 mm FlaMG 490(j). The Germans used them as light anti-aircraft guns during World War II. The British developed their 15 mm Besa Mk I from the ZB-60 for service on armored fighting vehicles.