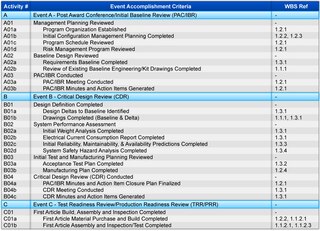
 W
WIn the United States Department of Defense, the Integrated Master Plan (IMP) and the Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) are important program management tools that provide significant assistance in the planning and scheduling of work efforts in large and complex materiel acquisitions. The IMP is an event-driven plan that documents the significant accomplishments necessary to complete the work and ties each accomplishment to a key program event. The IMP is expanded to a time-based IMS to produce a networked and multi-layered schedule showing all detailed tasks required to accomplish the work effort contained in the IMP. The IMS flows directly from the IMP and supplements it with additional levels of detail——both then form the foundations to implement an Earned Value Management System.The IMP is a bilateral agreement between the Government and a contractor on what defines the “event-driven” program. The IMP documents the key events, accomplishments, and the evaluation "criteria" in the development, production and/or modification of a military system; moreover, the IMS provides sequential events and key decision points to assess program progress. Usually the IMP is a contractual document. Supporting the IMP is the IMS that is made up of "tasks" depicting the work effort needed to complete the "criteria". It is a detailed time-driven plan for program execution that helps to ensure on-time delivery dates are achieved, and that tracking and status tool are used during program execution. These tools must show progress, interrelationships and dependencies.
 W
WMIL-DTL-5015 is a United States Military Standard which covers heavy-duty circular electrical connectors with soldered or crimped contacts. They are used for both digital and analog signals, as well as power distribution, and are common in various fields, including defense, aerospace, and industrial machinery. The connectors are particularly versatile and reliable, and due to their prevalence, relatively inexpensive.
 W
WMilitary Specification MIL-S-901D is a military specification for High Impact mechanical shock which applies to equipment mounted on ships. Two levels apply. Grade A items are items which are essential to the safety and continued combat capability of the ship. Grade B items are items whose operation is not essential to the safety and combat capability of the ship but which could become a hazard to personnel, to Grade A items, or to the ship as a whole as a result of exposure to shock. "Grade C", signifying that no shock qualification is required, is also sometimes referenced in acquisition documents even though the term has no official standing in the specification document.. Qualification testing is performed on a specified machine or on a barge floating in a pond where an explosive charge is detonated at various distances and depths in the pond to impart shock to the barges. See Barge Test.
 W
WMIL-STD-105 was a United States defense standard that provided procedures and tables for sampling by attributes based on Walter A. Shewhart, Harry Romig, and Harold Dodge sampling inspection theories and mathematical formulas. Widely adopted outside of military procurement applications.
 W
WMIL-STD-188 is a series of U.S. military standards relating to telecommunications.
 W
WMIL-STD-188 is a series of U.S. military standards relating to telecommunications.
 W
WMIL-STD-188 is a series of U.S. military standards relating to telecommunications.
 W
WMIL-STD-188 is a series of U.S. military standards relating to telecommunications.
 W
WMIL-STD-810, Environmental Engineering Considerations and Laboratory Tests, is a United States Military Standard that emphasizes tailoring an equipment's environmental design and test limits to the conditions that it will experience throughout its service life, and establishing chamber test methods that replicate the effects of environments on the equipment rather than imitating the environments themselves. Although prepared specifically for military applications, the standard is often used for commercial products as well.
 W
WAda is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level programming language, extended from Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for design by contract (DbC), extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international technical standard, jointly defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). As of 2020, the standard, called Ada 2012 informally, is ISO/IEC 8652:2012.
 W
WThe Picatinny rail, or Pic rail for short, also known as a MIL-STD-1913 rail or STANAG 2324 rail (canceled), is a military standard rail interface system that provides a mounting platform for firearm accessories. It was originally used for mounting scopes atop the receivers of larger caliber rifles. Once established, its use expanded to also attaching other accessories, such as: iron sights, tactical lights, laser aiming modules, night vision devices, reflex sights, foregrips, bipods, slings and bayonets.
 W
WNATO Joint Military Symbology is the NATO standard for military map marking symbols. Originally published in 1986 as Allied Procedural Publication 6 (APP-6), NATO Military Symbols for Land Based Systems, the standard has evolved over the years and is currently in its fifth version (APP-6D). The symbols are designed to enhance NATO's joint interoperability by providing a standard set of common symbols. APP-6 constituted a single system of joint military symbology for land, air, space and sea-based formations and units, which can be displayed for either automated map display systems or for manual map marking. It covers all of the joint services and can be used by them.
 W
WElectrical or fiber-optic connectors used by U.S. Department of Defense were originally developed in the 1930s for severe aeronautical and tactical service applications, and the Type "AN" (Army-Navy) series set the standard for modern military circular connectors. These connectors, and their evolutionary derivatives, are often called Military Standard, "MIL-STD", or (informally) "MIL-SPEC" or sometimes "MS" connectors. They are now used in aerospace, industrial, marine, and even automotive commercial applications.