 W
WThe Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre was a major theatre of operations during the Second World War. The vast size of the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre saw interconnected naval, land, and air campaigns fought for control of the Mediterranean, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Middle East and Southern Europe. The fighting in this theatre lasted from 10 June 1940, when Italy entered the war on the side of Germany, until 2 May 1945 when all Axis forces in Italy surrendered. However, fighting would continue in Greece – where British troops had been dispatched to aid the Greek government – during the early stages of the Greek Civil War.
 W
WThe East African campaign was fought in East Africa during the Second World War by Allies of World War II, mainly from the British Empire, against Italy and its colony of Italian East Africa, between June 1940 and November 1941. The British Middle East Command with troops from the United Kingdom, South Africa, British India, Uganda Protectorate, Kenya, Somaliland, West Africa, Northern and Southern Rhodesia, Sudan and Nyasaland participated in the campaign. These were joined by the Allied Force Publique of Belgian Congo, Imperial Ethiopian Arbegnoch and a small unit of Free French.
 W
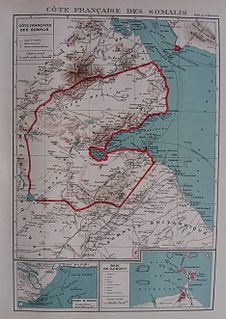
WFrench Somaliland, with its capital at Djibouti, was the scene of only minor skirmishing during World War II, principally between June and July 1940. After the fall of France the colony was briefly in limbo until a governor loyal to the Vichy government was installed on 25 July. It was the last French possession in Africa to remain loyal to Vichy, surrendering to Free French forces only on 26 December 1942. Pierre Nouailhetas governed the territory through most of the Vichy period. After aerial bombardment by the British, he instituted a reign of terror against Europeans and locals. Nouailhetas was eventually recalled and forced to retire. From September 1940, the colony was under an Allied blockade, and many of its inhabitants fled to neighbouring British Somaliland. After the territory's liberation, there were many governors and recovery from the deprivation of 1940–42 was only beginning when the war ended in 1945.
 W
WJungle Queen (1945) is a Universal movie serial.
 W
WThe involvement of the British Colony of Kenya in World War II began with the declaration of war on Nazi Germany by the British Empire in September 1939.
 W
WMadagascar, then officially known as French Madagascar, was a French colony at the outbreak of the Second World War, having been under French administration since 1885. It played an important role in the war due to the presence of critically important harbors, the contribution of Malagasy troops, and was also the scene of fighting between Allied and Vichy French forces in 1942. After the fall of France in 1940, Madagascar became a crucial flashpoint in contention between the Free French movement and Vichy France. The island was also consequential in the Pacific theater of the war as Imperial Japanese naval forces operated unopposed off the island for some time.
 W
WThe Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre was a major theatre of operations during the Second World War. The vast size of the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre saw interconnected naval, land, and air campaigns fought for control of the Mediterranean, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Middle East and Southern Europe. The fighting in this theatre lasted from 10 June 1940, when Italy entered the war on the side of Germany, until 2 May 1945 when all Axis forces in Italy surrendered. However, fighting would continue in Greece – where British troops had been dispatched to aid the Greek government – during the early stages of the Greek Civil War.
 W
WThe North African campaign of the Second World War took place in North Africa from 10 June 1940 to 13 May 1943. It included campaigns fought in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts and in Morocco and Algeria, as well as Tunisia.
 W
WThe Battle of Réunion or Liberation of Réunion was an amphibious landing and uprising which brought the island of Réunion onto the Allied side during the Second World War. The invasion was performed by the Free French Naval Forces (FNFL) destroyer Léopard on 28 November 1942, which toppled the administration loyal to the Vichy French regime and replaced it with a Free French administration.
 W
WSouthern Rhodesia, then a self-governing colony of the United Kingdom, entered World War II along with Britain shortly after the invasion of Poland in 1939. By the war's end, 26,121 Southern Rhodesians of all races had served in the armed forces, 8,390 of them overseas, operating in the European theatre, the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre, East Africa, Burma and elsewhere. The territory's most important contribution to the war is commonly held to be its contribution to the Empire Air Training Scheme (EATS), under which 8,235 British, Commonwealth and Allied airmen were trained in Southern Rhodesian flight schools. The colony's operational casualties numbered 916 killed and 483 wounded of all races.
 W
WDuring the Second World War (1939–1945), the Gambia was part of the British Empire as the Gambia Colony and Protectorate. At the outbreak of war between the British Empire and Nazi Germany in September 1939, the Gambia was home to the Gambia Company of the Royal West African Frontier Force (RWAFF).
 W
WIn World War II, French West Africa was not a major scene of major fighting. Only one large-scale action took place there: the Battle of Dakar. The region remained under the control of Vichy France after the fall of France and until the Allied invasion of North Africa. French Gabon, the only colony of French Equatorial Africa not to join Free France after the armistice, fell to invading Free French Forces from the neighbouring colonies after the Battle of Gabon, further isolating West Africa.