 W
WThe presidency of Woodrow Wilson began on March 4, 1913 at noon when Woodrow Wilson was inaugurated as president of the United States, and ended on March 4, 1921. Wilson, a Democrat who previously served as the governor of New Jersey, took office as the 28th U.S. President after winning the 1912 presidential election, gaining a large majority in the Electoral College and a 42% plurality of the popular vote in a four–candidate field. Wilson was re-elected in 1916, defeating Republican Charles Evans Hughes by a fairly narrow margin. He was the first Southerner to be elected president since Zachary Taylor in 1848, and just the second Democrat to be elected president since 1860.
 W
WThe presidency of Woodrow Wilson began on March 4, 1913 when Woodrow Wilson was inaugurated as President of the United States, and ended on March 4, 1921.
 W
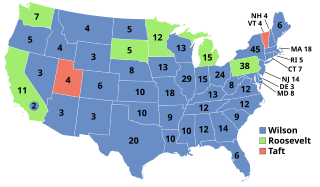
WThe 1912 United States presidential election was the 32nd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 5. Democratic Governor Woodrow Wilson unseated incumbent Republican President William Howard Taft and defeated former President Theodore Roosevelt, who ran under the banner of the new Progressive or "Bull Moose" Party. As of 2020, this is the most recent presidential election in which a top two finisher was neither a Democrat nor a Republican.
 W
WThe 1913 State of the Union Address was given by Woodrow Wilson, the 28th President of the United States, on Tuesday, December 2, 1913. It was given directly to the 63rd United States Congress by the president. Wilson was the first to do so since John Adams in 1800. With a few exceptions all addresses since then have been given directly following Wilson's lead.
 W
WThe 1916 Progressive National Convention was held in July 1916, in conjunction with the Republican national convention. This was to facilitate a possible reconciliation. Five delegates from each convention met to negotiate.
 W
WThe 1916 United States presidential election was the 33rd quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7. Incumbent Democratic President Woodrow Wilson defeated former Governor of New York Charles Evans Hughes, the Republican candidate.
 W
WThe 1917 State of the Union Address was given by Woodrow Wilson, the 28th President of the United States on Tuesday, December 4, 1917, during his turbulent second term. He spoke in the United States House of Representatives chamber, in the United States Capitol. He said, "I shall not go back to debate the causes of the war. The intolerable wrongs done and planned against us by the sinister masters of Germany have long since become too grossly obvious and odious to every true American to need to be rehearsed." He addressed the 65th United States Congress, and spoke of World War I. He ended with, "A supreme moment of history has come. The eyes of the people have been opened and they see. The hand of God is laid upon the nations. He will show them favor, I devoutly believe, only if they rise to the clear heights of His own justice and mercy." In the middle of the speech, he said this about the German Empire, "The worst that can happen to the detriment the German people is this, that if they should still, after the war is over, continue to be obliged to live under ambitious and intriguing masters interested to disturb the peace of the world, men or classes of men whom the other peoples of the world could not trust, it might be impossible to admit them to the partnership of nations which must henceforth guarantee the world's peace." He is saying that empires' do not promote world peace. A year after he gave this speech, on December 4, 1918, the United States military would swallow Germany in victory, and the saying that is written would come true, "Death has been swallowed up in victory."
 W
WThe Adamson Act was a United States federal law passed in 1916 that established an eight-hour workday, with additional pay for overtime work, for interstate railroad workers.
 W
WThe American Alliance for Labor and Democracy was an American political organization established in September 1917 through the initiative of the American Federation of Labor and making use of the resources of the United States government's Committee on Public Information. The group was dedicated to building support among American workers for that nation's participation in World War I in Europe. Following the victory of the Entente powers over the empires of Germany and Austria-Hungary the organization lost its raison d'être. It was finally terminated in November 1919 due to a lack of funding.
 W
WThe American Expeditionary Force, North Russia was a contingent of about 5,000 United States Army troops that landed in Arkhangelsk, Russia as part of the Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War. It fought the Red Army in the surrounding region during the period of September 1918 through to July 1919.
 W
WThe American Expeditionary Force, Siberia was a formation of the United States Army involved in the Russian Civil War in Vladivostok, Russia, after the October Revolution, from 1918 to 1920. The force was part of the larger Allied North Russia Intervention. As a result of this expedition, early relations between the United States and the Soviet Union were poor.
 W
WThe Birth of a Nation, originally called The Clansman, is a 1915 American silent epic drama film directed by D. W. Griffith and starring Lillian Gish. The screenplay is adapted from the 1905 novel and play The Clansman, by Thomas Dixon Jr. Griffith co-wrote the screenplay with Frank E. Woods and produced the film with Harry Aitken.
 W
WThe Bisbee Deportation was the illegal kidnapping and deportation of about 1,300 striking mine workers, their supporters, and citizen bystanders by 2,000 members of a deputized posse, who arrested these people beginning on July 12, 1917. The action was orchestrated by Phelps Dodge, the major mining company in the area, which provided lists of workers and others who were to be arrested in Bisbee, Arizona, to the Cochise County sheriff, Harry C. Wheeler. These workers were arrested and held at a local baseball park before being loaded onto cattle cars and deported 200 miles (320 km) to Tres Hermanas in New Mexico. The 16-hour journey was through desert without food and with little water. Once unloaded, the deportees, most without money or transportation, were warned against returning to Bisbee.
 W
WLouis Freeland Post was a prominent Georgist and the Assistant United States Secretary of Labor during the closing year of the Wilson administration, the period of the Palmer Raids and the Red Scare, where he had responsibility for the Bureau of Immigration. Post considered the process to be a witch hunt and is credited with preventing many deportations and freeing many innocent people.
 W
WThe Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914, was a part of United States antitrust law with the goal of adding further substance to the U.S. antitrust law regime; the Clayton Act sought to prevent anticompetitive practices in their incipiency. That regime started with the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890, the first Federal law outlawing practices considered harmful to consumers. The Clayton Act specified particular prohibited conduct, the three-level enforcement scheme, the exemptions, and the remedial measures.
 W
WThe Committee on Public Information (1917–1919), also known as the CPI or the Creel Committee, was an independent agency of the government of the United States created to influence public opinion to support US participation in World War I.
 W
WThe Council of National Defense was a United States organization formed during World War I to coordinate resources and industry in support of the war effort, including the coordination of transportation, industrial and farm production, financial support for the war, and public morale.
 W
WThe Espionage Act of 1917 is a United States federal law passed on June 15, 1917, shortly after the U.S. entry into World War I. It has been amended numerous times over the years. It was originally found in Title 50 of the U.S. Code but is now found under Title 18. Specifically, it is 18 U.S.C. ch. 37
 W
WThe Evgenevka incident was an armed standoff between the American 27th Infantry Regiment (Wolfhounds) and the Japanese Military in Evgenevka, Siberia during the Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War.
 W
WThe Federal Employees' Compensation Act (FECA), is a United States federal law, enacted on September 7, 1916. Sponsored by Sen. John W. Kern (D) of Indiana and Rep. Daniel J. McGillicuddy (D) of Maine, it established compensation to federal civil service employees for wages lost due to job-related injuries. This act became the precedent for "disability insurance" across the country and the precursor to broad-coverage health insurance.
 W
WThe Federal Farm Loan Act of 1916 was a United States federal law aimed at increasing credit to rural family farmers. It did so by creating a federal farm loan board, twelve regional farm loan banks and tens of farm loan associations. The act was signed into law by President of the United States Woodrow Wilson.
 W
WThe Federal Reserve Act was passed by the 63rd United States Congress and signed into law by President Woodrow Wilson on December 23, 1913. The law created the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States.
 W
WThe First Red Scare was a period during the early 20th-century history of the United States marked by a widespread fear of far-left extremism, including but not limited to Bolshevism and anarchism, due to real and imagined events; real events included the October Revolution and anarchist bombings. At its height in 1919–1920, concerns over the effects of radical political agitation in American society and the alleged spread of communism and anarchism in the American labor movement fueled a general sense of concern.
 W
WThe Food and Fuel Control Act, Pub.L. 65–41, 40 Stat. 276, enacted August 10, 1917, also called the Lever Act or the Lever Food Act was a World War I era US law that among other things created the United States Food Administration and the United States Fuel Administration.
 W
WFreedom of the seas is a principle in the international law and sea. It stresses freedom to navigate the oceans. It also disapproves of war fought in water. The freedom is to be breached only in a necessary international agreement.
 W
WThe history of U.S. foreign policy from 1913–1933 concerns the foreign policy of the United States during World War I and much of the Interwar period. The administrations of Presidents Woodrow Wilson, Warren G. Harding, Calvin Coolidge, and Herbert Hoover successively handled U.S. foreign policy during this period.
 W
WThe first inauguration of Woodrow Wilson as the 28th President of the United States was held on Tuesday, March 4, 1913, at the East Portico of the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. This was the 32nd inauguration and marked the commencement of the first four-year term of Woodrow Wilson as President and Thomas R. Marshall as Vice President. Chief Justice Edward D. White administered the presidential oath of office to Wilson.
 W
WThe second inauguration of Woodrow Wilson as President of the United States was held privately on Sunday, March 4, 1917, at the President's Room inside the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. and publicly on Monday, March 5, 1917, at the East Portico of the Capitol. This was the 33rd inauguration and marked the commencement of the second and final four-year term of both Woodrow Wilson as President and Thomas R. Marshall as Vice President. Chief Justice Edward D. White administered the presidential oath of office to Wilson.
 W
WThe Keating–Owen Child Labor Act of 1916 also known as Wick's Bill, was a short-lived statute enacted by the U.S. Congress which sought to address child labor by prohibiting the sale in interstate commerce of goods produced by factories that employed children under fourteen, mines that employed children younger than sixteen, and any facility where children under fourteen worked after 7:00 p.m. or before 6:00 a.m. or more than eight hours daily. After its original failure to be enacted, the bill was revised and re-introduced to Congress, where it was finally accepted. The basis for the action was the constitutional clause giving Congress the task of regulating interstate commerce. The Act specified that the U.S. Attorney General, the Secretary of State and the Secretary of Agriculture would convene a caucus to publish from time to time uniform rules and regulations to comply with the Act. To enforce the Act, the Secretary of Labor would assign inspectors to perform inspections of workplaces that produce goods for commerce. The inspectors would have the authority to make unannounced visits and would be given full access to the facility in question. Anyone found in acceptance of this Act or who gave false evidence would be subject to fines and/or imprisonment.
 W
WDespite the United States never becoming an official member of the League of Nations, American individuals and organizations interacted with the League throughout its existence.
 W
WThe Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits the states and the federal government from denying the right to vote to citizens of the United States on the basis of sex. Initially introduced to Congress in 1878, several attempts to pass a women's suffrage amendment failed until passing the House of Representatives on May 21, 1919, followed by the Senate on June 4, 1919. It was then submitted to the states for ratification. On August 18, 1920, Tennessee was the last of the necessary 36 ratifying states to secure adoption. The Nineteenth Amendment's adoption was certified on August 26, 1920: the culmination of a decades-long movement for women's suffrage at both state and national levels.
 W
WThe North Russia intervention, also known as the Northern Russian expedition, the Archangel campaign, and the Murman deployment, was part of the Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War after the October Revolution. The intervention brought about the involvement of foreign troops in the Russian Civil War on the side of the White movement. The movement was ultimately defeated, while the Allied forces withdrew from Northern Russia after fighting a number of defensive actions against the Bolsheviks, such as the Battle of Bolshie Ozerki. The campaign lasted from March 1918, during the final months of World War I, to October 1919.
 W
WThe Overman Committee was a special subcommittee of the United States Senate Committee on the Judiciary chaired by North Carolina Democrat Lee Slater Overman. Between September 1918 and June 1919, it investigated German and Bolshevik elements in the United States. It was an early forerunner of the better known House Un-American Activities Committee, and represented the first congressional committee investigation of communism.
 W
WThe Palmer Raids were a series of raids conducted in November 1919 and January 1920 during the First Red Scare by the United States Department of Justice under the administration of President Woodrow Wilson to capture and arrest suspected leftists, mostly Italian and Eastern European immigrants and especially anarchists and communists, and deport them from the United States. The raids particularly targeted Italian immigrants and Eastern European Jewish immigrants with alleged leftist ties, with particular focus on Italian anarchists and immigrant leftist labor activists. The raids and arrests occurred under the leadership of Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer, with 3,000 arrested. Though 556 foreign citizens were deported, including a number of prominent leftist leaders, Palmer's efforts were largely frustrated by officials at the U.S. Department of Labor, which had authority for deportations and objected to Palmer's methods.
 W
WThe Paris Peace Conference was the formal meeting in 1919 and 1920 of the victorious Allies after the end of World War I to set the peace terms for the defeated Central Powers. Dominated by the leaders of Britain, France, the United States and Italy, it resulted in five controversial treaties that rearranged the map of Europe and imposed financial penalties. Germany and the other losing nations had no voice which gave rise to political resentments that lasted for decades.
 W
WThe Railway Wage Commission was created in 1918 during World War I within the United States Railroad Administration.
 W
WRed Summer is the period from late winter through early autumn of 1919 during which white supremacist terrorism and racial riots took place in more than three dozen cities across the United States, as well as in one rural county in Arkansas. The term "Red Summer" was coined by civil rights activist and author James Weldon Johnson, who had been employed as a field secretary by the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) since 1916. In 1919, he organized peaceful protests against the racial violence which had occurred that summer.
 W
WThe Revenue Act of 1913, also known as the Underwood Tariff or the Underwood-Simmons Act, re-established a federal income tax in the United States and substantially lowered tariff rates. The act was sponsored by Representative Oscar Underwood, passed by the 63rd United States Congress, and signed into law by President Woodrow Wilson.
 W
WThe Sedition Act of 1918 was an Act of the United States Congress that extended the Espionage Act of 1917 to cover a broader range of offenses, notably speech and the expression of opinion that cast the government or the war effort in a negative light or interfered with the sale of government bonds.
 W
WThe Siberian intervention or Siberian expedition of 1918–1922 was the dispatch of troops of the Entente powers to the Russian Maritime Provinces as part of a larger effort by the western powers, Japan and China to support White Russian forces and the Czechoslovak Legion against Soviet Russia and its allies during the Russian Civil War. The Imperial Japanese Army continued to occupy Siberia even after other Allied forces withdrew in 1920.
 W
WThe Silent Sentinels, also known as the Sentinels of Liberty, were a group of women in favor of women's suffrage organized by Alice Paul and the National Woman's Party. They protested in front of the White House during Woodrow Wilson's presidency starting on January 10, 1917. They were the first group to picket the White House. They started their protest after a meeting with the president on January 9, 1917, during which he told the women to "concert public opinion on behalf of women's suffrage." The protesters served as a constant reminder to Wilson of his lack of support for suffrage. At first the picketers were tolerated, but they were later arrested on charges of obstructing traffic. The women protested at the White House gates and later in Lafayette Square until June 4, 1919 when the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution was passed both by the House of Representatives and the Senate.
 W
WThe Sixteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution allows Congress to levy an income tax without apportioning it among the states on the basis of population. It was passed by Congress in 1909 in response to the 1895 Supreme Court case of Pollock v. Farmers' Loan & Trust Co. The Sixteenth Amendment was ratified by the requisite number of states on February 3, 1913, and effectively overruled the Supreme Court's ruling in Pollock.
 W
WThe Smith–Lever Act of 1914 is a United States federal law that established a system of cooperative extension services, connected to the land-grant universities, in order to inform people about current developments in agriculture, home economics, public policy/government, leadership, 4-H, economic development, coastal issues, and many other related subjects. It helped farmers learn new agricultural techniques by the introduction of home instruction.
 W
WThe Treaty of the Danish West Indies, officially the Convention between the United States and Denmark for cession of the Danish West Indies, was a 1916 treaty transferring sovereignty of the Virgin Islands in the Danish West Indies from Denmark to the United States in exchange for a sum of US$25,000,000 in gold. It is, to date, one of the most recent permanent expansions of United States territory.
 W
WThe 1919 United States anarchist bombings were a series of bombings and attempted bombings carried out by followers of the Italian anarchist Luigi Galleani from April through June 1919.
 W
WOn April 2, 1917, President Woodrow Wilson asked a special joint session of the United States Congress for a declaration of war against the German Empire. Congress responded with the declaration on April 6.
 W
WThe U. S. Food Administration was the agency responsible for the administration of the U.S. army overseas and allies' food reserves during the United States participation in World War I. One of its important tasks was the stabilization of the price of wheat on the U.S. market. It was established by Executive Order 2679-A of August 10, 1917, pursuant to the Food and Fuel Control Act, and was abolished by another executive order, Executive Order 3320, on August 21, 1920.
 W
WThomas Woodrow Wilson was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of Princeton University and as the 34th governor of New Jersey before winning the 1912 presidential election. As president, he oversaw the passage of progressive legislative policies unparalleled until the New Deal in 1933. He also led the United States into World War I in 1917, establishing an activist foreign policy known as "Wilsonianism". He was the leading architect of the League of Nations.