 W
WThe Avignon Papacy, also known as the Babylonian Captivity, was the period from 1309 to 1376 during which seven successive popes resided in Avignon rather than in Rome. The situation arose from the conflict between the papacy and the French crown, culminating in the death of Pope Boniface VIII after his arrest and maltreatment by Philip IV of France. Following the further death of Pope Benedict XI, Philip forced a deadlocked conclave to elect the French Clement V as pope in 1305. Clement refused to move to Rome, and in 1309 he moved his court to the papal enclave at Avignon, where it remained for the next 67 years. This absence from Rome is sometimes referred to as the "Babylonian captivity of the Papacy".
 W
WThe 1304–05 papal conclave, held in Perugia, was the protracted papal conclave that elected non-cardinal Raymond Bertrand de Got as Pope Clement V. This immediately preceded the beginning of the Avignon Papacy.
 W
WThe 1314–16 papal conclave, held in the apostolic palace of Carpentras and then the Dominican house in Lyon, was one of the longest conclaves in the history of the Roman Catholic Church and the first conclave of the Avignon Papacy. The length of the conclave was due to the division of the cardinals into three factions: Italian, Gascon, and French/Provençal.
 W
WThe 1334 papal conclave elected Jacques Fournier as Pope Benedict XII to succeed Pope John XXII.
 W
WThe 1342 papal conclave – the papal conclave convened after the death of Pope Benedict XII, it elected Cardinal Pierre Roger, who became the fourth Pope of the period of Avignon Papacy under the name Clement VI.
 W
WThe 1352 papal conclave convened after the death of Pope Clement VI, elected as his successor cardinal Etienne Aubert, who became the fifth Pope of the period of Avignon Papacy under the name Innocent VI. This conclave is remarkable because during its celebration Cardinals for the first time in history subscribed the electoral capitulation, which limited the power of elect.
 W
WThe 1362 papal conclave elected William Grimoard as Pope Urban V to succeed Pope Innocent VI in the Palais des Papes of Avignon, continuing the Avignon Papacy.
 W
WThe 1370 papal conclave, held after the death of Pope Urban V, elected as his successor cardinal Pierre Roger de Beaufort, who under the name Gregory XI became seventh and the last pope of the period of Avignon Papacy.
 W
WThe 1378 papal conclave which was held from April 7 to 9, 1378, was the papal conclave which was the immediate cause of the Western Schism in the Catholic Church. The conclave was one of the shortest in the history of the Catholic Church. The conclave was also the first since 1159 held in the Vatican and in Old St. Peter's Basilica.
 W
WBernard d'Albi, was born at Saverdun in the diocese of Pamiers in the Pyrenees foothills, south of Toulouse, and died on 23 November 1350 at Avignon. He was a French cardinal of the 14th century.
 W
WL'Anneau du pêcheur is a 1995 novel by the French writer Jean Raspail. The narrative has two timelines: the time of Benedict XIII, the last antipope of the Avignon Papacy, and contemporary times, when the Catholic Church tries to discover Benedict's successor, as it turns out that his line of papacy has continued in secret throughout the centuries. The book received the Prix Maison de la Presse and the Prince Pierre Foundation's Literary Prize.
 W
WGuillaume d'Aure, OSB, was born in Toulouse, and died on 3 December 1353 in Avignon. He was a French Benedictine monk and Cardinal. He was the son of Bernard VII Dodon, Count of Comminges, and Bertrande, Countess d'Aure, daughter of Arnaud, Vicomte de l'Arboust. He had a brother Raymond Roger d'Aure.
 W
WAvignon Cathedral is a Roman Catholic church located next to the Palais des Papes in Avignon, France. The cathedral is the seat of the Archbishop of Avignon.
 W
WThe Avignon Exchange was one of the first foreign exchange markets in history, established in the Comtat Venaissin during the Avignon Papacy. The Exchange was composed of the agents (factores) of the great Italian banking-houses, who acted as money-changers as well as financial intermediaries between the Apostolic Camera and its debtors and creditors. The most prosperous quarter of the city of Avignon, where the bankers settled, became known simply as the Exchange. According to de Roover, "Avignon can be considered an Italian colony, since the papal bankers were all Italians".
 W
WThe Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Avignon is an archdiocese of the Latin Rite of the Roman Catholic Church in France. The diocese exercises jurisdiction over the territory embraced by the department of Vaucluse, in the Region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur. The current archbishop is Jean-Pierre Marie Cattenoz, who was appointed in 2002.
 W
WPope Benedict XII, born Jacques Fornier, was head of the Catholic Church from 30 December 1334 to his death in April 1342. He was the third Avignon pope. Benedict was a careful pope who reformed monastic orders and opposed nepotism. Unable to remove his capital to Rome or Bologna, he started the great palace at Avignon. He decided against a notion of Pope John XXII by saying that souls may attain the "fulness [sic] of the beatific vision" before the Last Judgment. Whilst being a stalwart reformer, he attempted unsuccessfully to reunite the Orthodox Church and Catholic Church, almost 3 centuries after the Great Schism; he also failed to come to an understanding with Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor.
 W
WPedro Martínez de Luna y Pérez de Gotor, known as el Papa Luna in Spanish and Pope Luna in English, was an Aragonese nobleman, who as Benedict XIII, is considered an antipope by the Catholic Church.
 W
WNicolas de Besse was born in the diocese of Limoges, in 1322. He was a French bishop and Cardinal. He was the son of Jacques de Besse, Seigneur de Bellefaye and Almodie (Delphine) Roger, sister of Pope Clement VI. He had a brother Pierre de Besse, who became Seigneur de Bellefaye and who married Margueritte de Thiers. Nicolas de Besse died in Rome on 5 November 1369.
 W
WNiccolò Brancaccio was born in the Kingdom of Naples, perhaps in Naples itself. He was Archbishop of Bari and then Archbishop of Cosenza, while serving in the Roman Curia in Avignon. He became a cardinal of the Avignon Obedience in 1378, and was Cardinal Priest of Santa Maria in Trastevere and then Cardinal Bishop of Albano. He participated in the Council of Pisa in 1409, and was one of the electors of Pope Alexander V and of Pope John XXIII.
 W
WRaymond de Canillac was a French lawyer, bishop, and cardinal. He was born at Roche de Canilhac, the family castle, in the diocese of Mende in the Gevaudan in central France, the son of Guillaume de Canillac and a sister of Cardinal Bertrand de Déaulx. Both of his uncles, Pons and Guy, were successively abbots of Aniane, as was a nephew of the Cardinal, also called Pons. In 1345 his niece Garine, the daughter of his brother Marquis and of Alixène de Poitiers-Valentinois, married Guillaume Roger, Vicount of Beaufort, the brother of Cardinal Pierre Roger de Beaufort, who became Pope Clement VI. Raymond became a member of the Canons Regular of Saint Augustine (CRSA). He studied law at the University of Montpellier, and obtained the degree of Doctor in utroque iure.
 W
WPope Clement V, born Raymond Bertrand de Got, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 5 June 1305 to his death. He is remembered for suppressing the order of the Knights Templar and allowing the execution of many of its members, and as the pope who moved the Papacy from Rome to Avignon, ushering in the period known as the Avignon Papacy.
 W
WPope Clement VI, born Pierre Roger, was head of the Catholic Church from 7 May 1342 to his death in 1352. He was the fourth Avignon pope. Clement reigned during the first visitation of the Black Death (1348–1350), during which he granted remission of sins to all who died of the plague.
 W
WRobert of Geneva was elected to the papacy as Clement VII by the cardinals who opposed Urban VI, and was the first antipope residing in Avignon, France. His election led to the Western Schism.
 W
WThe Comtat Venaissin, often called the Comtat for short, was a part of the Papal States (1274‒1791) in what is now the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of France.
 W
WGuillaume Court was a French Cistercian theologian and Cardinal.
 W
WBertrand de Déaulx was a French bishop, diplomat and Cardinal. He was born, perhaps around 1290, in Castrum de Blandiaco in the diocese of Uzès; or in Déaulx. He died in Avignon in 1355. Trained as a lawyer and teacher of law, he practiced in the papal courts, and became an arbitrator and diplomat for the Papacy. He had several assignments in Italy and one in Catalonia. He was responsible for the reorganization of the University of Montpellier and the granting of revised charters.
 W
WThe Declaration of Arbroath is the name usually given to a letter, dated 6 April 1320 at Arbroath, written by Scottish barons and addressed to Pope John XXII. It constituted King Robert I's response to his excommunication for disobeying the pope's demand in 1317 for a truce in the First War of Scottish Independence. The letter asserted the antiquity of the independence of the Kingdom of Scotland, denouncing English attempts to subjugate it.
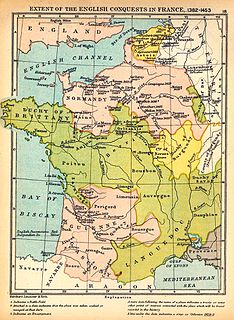 W
WDespenser's Crusade was a military expedition led by the English bishop Henry le Despenser in 1383 that aimed to assist the city of Ghent in its struggle against the supporters of Antipope Clement VII. It took place during the great Papal schism and the Hundred Years' War between England and France. While France supported Clement, whose court was based in Avignon, the English supported Pope Urban VI in Rome.
 W
WImbert du Puy was a French Cardinal of the fourteenth century. He was a nephew of Pope John XXII.
 W
WBérenger Fredoli was a French canon lawyer and Cardinal-Bishop of Frascati.
 W
WPope Gregory XI was head of the Catholic Church from 30 December 1370 to his death in 1378. He was the seventh and last Avignon pope and the most recent French pope. In 1377, Gregory XI returned the Papal court to Rome, ending nearly 70 years of papal residency in Avignon, France. His death shortly after was followed by the Western Schism involving two Avignon-based antipopes.
 W
WAnglic de Grimoard, also recorded as Angelic, was a French canon regular and a Cardinal. He was the younger brother of Pope Urban V.
 W
WPope Innocent VI, born Étienne Aubert, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 18 December 1352 to his death in 1362. He was the fifth Avignon pope and the only one with the pontifical name of "Innocent".
 W
WGaillard de La Mothe was a fourteenth-century prelate and Cardinal, of Gascon extraction. Gaillard was born towards the end of the 13th century, either in Toulouse or Bordeaux, and died in Avignon on 20 December 1356. He was the son of Amanieu Levieux de La Motte, seigneur de Langon et de Rochetaillé. His mother was Elips (Alix) de Got, daughter of Arnaud-Garsale de Got, brother of Bertrand de Got. He was therefore a nephew of Pope Clement V. Gaillard had a brother, Bertrand. Another uncle, his father's brother, Guillaume de la Mothe, was Bishop of Bazas from 1303-1313, when he was transferred to Saintes, and again from 1318 to 1319.
 W
WThe Liber sine nomine is a collection of nineteen personal letters written in Latin by the fourteenth century Italian poet and Renaissance humanist Petrarch. The letters being harshly critical of the Avignon papacy, they were withheld from the larger collection of his Epistolae familiares and assembled in a separate book. In this fashion, Petrarch reasoned, a reader could throw away this collection, and the other letters to friends could be preserved for posterity.
 W
WGuy de Malsec was a French bishop and cardinal. He was born at the family's fief at Malsec (Maillesec), in the diocese of Tulle. He had two sisters, Berauda and Agnes, who both became nuns at the Monastery of Pruliano (Pruilly) in the diocese of Carcassone, and two nieces Heliota and Florence, who became nuns at the Monastery of S. Prassede in Avignon. He was a nephew of Pope Gregory XI, or perhaps a more distant relative. He was also a nephew of Pope Innocent VI. Guy was baptized in the church of S. Privatus, some 30 km southeast of Tulle. He played a part in the election of Benedict XIII of the Avignon Obedience in 1394, in his status as second most senior cardinal. He played an even more prominent role in Benedict's repudiation and deposition. Guy de Malsec was sometimes referred to as the 'Cardinal of Poitiers' (Pictavensis) or the 'Cardinal of Palestrina' (Penestrinus).
 W
WJean de Murat du Cros was a French cardinal of the Catholic Church. He became the Bishop of Limoges (1347–1371). He was a leader in what became the Great Schism within Western Christianity.
 W
WNicholas V, born Pietro Rainalducci was an antipope in Italy from 12 May 1328 to 25 July 1330 during the pontificate of Pope John XXII (1316–1334) at Avignon. He was the last antipope set up by a Holy Roman Emperor.
 W
WThe Palais des Papes is a historical palace located in Avignon, Southern France. It is one of the largest and most important medieval Gothic buildings in Europe. Once a fortress and palace, the papal residence was the seat of Western Christianity during the 14th century. Six papal conclaves were held in the Palais, leading to the elections of Benedict XII in 1334, Clement VI in 1342, Innocent VI in 1352, Urban V in 1362, Gregory XI in 1370 and Benedict XIII in 1394.
 W
WArnaud de Pellegrue was a cardinal-nephew of Pope Clement V, the first pope of the Avignon Papacy.
 W
WPierre Girard was born in the commune of Saint-Symphorien-sur-Coise, in the Department of Rhone, once in the ancient County of Forez. He died in Avignon on 9 November 1415. He was Bishop of Lodeve and then Bishop of Le Puy. He was a cardinal of the Avignon Obedience during the Great Western Schism, and was promoted to the Bishopric of Tusculum (Frascati). His principal work, however, was as a courtier and administrator at Avignon, and as a papal diplomat.
 W
WThe Fort Saint-André is a medieval fortress in the commune of Villeneuve-lès-Avignon in the Gard département of France, dating from the first half of the 14th century.
 W
WPasteur de Sarrats was a French Franciscan friar, bishop and Cardinal. He was born in the village of Aubenas in the Vivarais, or he took his monastic vows in the monastery of Aubenas. Pasteur may have had a brother. A bull of Benedict XII, dated 13 April 1337, grants the parish church of S. Martin de Valle Gorgia in the diocese of Viviers to Pierre de Serraescuderio, Canon of Viviers since 1333, who held a parish of S. Pierre de Melon in the diocese of Uzès. Pasteur died in Avignon in 1356.
 W
WTour Philippe-le-Bel is a medieval tower in Villeneuve-lès-Avignon which marked the French terminus of the Saint-Bénézet Bridge across the Rhone between the Kingdom of France and Papal territory of Avignon. It is named after the French king Philippe-le-Bel who was responsible for its construction.
 W
WPope Urban V, born Guillaume de Grimoard, was the head of the Catholic Church from 28 September 1362 until his death in 1370 and was also a member of the Order of Saint Benedict. He was the only Avignon pope to be beatified.
 W
WArnaud de Via was a French cardinal in the Roman Catholic Church. Arnaud's brother Jacques was also a cardinal and their mother was sister to pope John XXII.
 W
WThe Western Schism, also called Papal Schism, Great Occidental Schism and Schism of 1378, was a split within the Catholic Church lasting from 1378 to 1417 in which two men simultaneously claimed to be the true pope, and each excommunicated the other. Driven by authoritative politics rather than any theological disagreement, the schism was ended by the Council of Constance (1414–1418). For a time these rival claims to the papal throne damaged the reputation of the office.