 W
WRed Summer is the period from late winter through early autumn of 1919 during which white supremacist terrorism and racial riots took place in more than three dozen cities across the United States, as well as in one rural county in Arkansas. The term "Red Summer" was coined by civil rights activist and author James Weldon Johnson, who had been employed as a field secretary by the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) since 1916. In 1919, he organized peaceful protests against the racial violence which had occurred that summer.
 W
WThe 1919 Coatesville call to arms was when the black community of Coatesville, Pennsylvania formed a large armed group to prevent a rumoured lynching. Only later when the armed group had surrounded the jail to prevent the lynching did they learn that there was no suspect and no white lynch mob.
 W
WMiles Phifer and Robert Crosky were lynched in Montgomery, Alabama for allegedly assaulting a white woman.
 W
WThe 1919 Norfolk race riot occurred on July 21, 1919, when a homecoming celebration for African-American veterans of World War I was attacked in Norfolk, Virginia. At least two people were killed and six people were shot. City officials called in Marines and Navy personnel to restore order.
 W
WWhen they returned home from World War I, African-American veterans faced heavy discrimination. This article focuses on those African American veterans who were lynched after World War I.
 W
WThe Annapolis riot of 1919 took place on June 27, 1919, between midnight and 1 AM, in Annapolis, Maryland. A mob of African-American bluejackets from the U.S. Navy fought local Annapolis African-Americans.
 W
WThe Baltimore riots of 1919 were a series of riots connected to the Red Summer of 1919. As more and more African-Americans moved from the south to the industrial north they started to move into predominantly white neighborhoods. This change in the racial demographics of urban areas increased racial tension that occasionally boiled over into civil unrest.
 W
WThe Bisbee Riot, or the Battle of Brewery Gulch, occurred during the Red Summer on July 3, 1919, between the black Buffalo Soldiers of the 10th Cavalry and members of local police forces in Bisbee, Arizona. Following an incident between a military policeman and some of the Buffalo Soldiers, the situation escalated into a street battle in Bisbee's historic Brewery Gulch. At least eight people were seriously injured, and fifty soldiers were arrested, although the consequences of this skirmish were relatively minor compared to others during the summer of 1919.
 W
WIn the Boston Police Strike, Boston police officers went on strike on September 9, 1919. They sought recognition for their trade union and improvements in wages and working conditions. Police Commissioner Edwin Upton Curtis denied that police officers had any right to form a union, much less one affiliated with a larger organization like the American Federation of Labor (AFL), which some attribute to concerns that unionized police would not protect the interest of city official and business leaders. Attempts at reconciliation between the Commissioner and the police officers, particularly on the part of Boston's Mayor Andrew James Peters, failed.
 W
WThe Charleston riot of 1919 took place on the night of Saturday, May 10, between members of the US Navy and the local black population. They attacked black individuals, businesses, and homes killing six and injuring dozens.
 W
WThe Chicago race riot of 1919 was a violent racial conflict started by white Americans against black Americans that began on the South Side of Chicago, Illinois on July 27, and ended on August 3, 1919. During the riot, thirty-eight people died. Over the week, injuries attributed to the episodic confrontations stood at 537, with two-thirds of the injured being black and one-third white, while the approximately 1,000 to 2,000 who lost their homes were mostly black. It is considered the worst of the nearly 25 riots and civil disturbances in the United States during the "Red Summer" of 1919, so named because of the racial and labor related violence and fatalities across the nation. The prolonged conflict made it one of the worst riots in the history of Illinois.
 W
WCorbin, Kentucky race riot of 1919 was a race riot in 1919 in which a white mob forced nearly all the town's 200 black residents onto a freight train out of town, and a sundown town policy until the late 20th century.
 W
WThe Darby 1919 lynching attempt was the attempted lynching of Samuel Gorman in Darby, Pennsylvania on July 23, 1919. Samuel Gorman, a 17-year-old black man was sent to jail for the alleged murder of William E. Taylor.
 W
WThe Dublin, Georgia riot of 1919 were a series of violent racial riots between white and black members of Dublin, Georgia.
 W
WThe Elaine massacre occurred on September 30–October 1, 1919, at Hoop Spur in the vicinity of Elaine in rural Phillips County, Arkansas. Some records of the time state that eleven black men and five white men were killed. Estimates of deaths made in the immediate aftermath of the Elaine Massacre by eyewitnesses range from 50 to "more than a hundred". Walter Francis White, an NAACP attorney who visited Elaine, AR shortly after the incident stated "... twenty-five Negroes killed, although some place the Negro fatalities as high as one hundred". More recent estimates of the number of black people killed during this violence are higher than estimates provided by the eyewitnesses, recently ranging into the hundreds. The white mobs were aided by federal troops and terrorist organizations like the Ku Klux Klan. According to the Encyclopedia of Arkansas, "the Elaine Massacre was by far the deadliest racial confrontation in Arkansas history and possibly the bloodiest racial conflict in the history of the United States".
 W
WThe Ellenton Riot occurred in September of 1876. Author Mark M. Smith concluded that there was one white and up to 100 blacks killed, with several white people wounded.
 W
WThe Garfield Park riot of 1919 was a race riot that began in Garfield Park in Indianapolis, Indiana on July 14, 1919. Multiple people, including a seven-year-old girl, were wounded when gunfire broke out.
 W
WAfrican-American man, Jordan Jameson was lynched on November 11, 1919, in the town square of Magnolia, Columbia County, Arkansas. A large white mob seized Jameson after he allegedly shot the local sheriff. They tied him to a stake and burned him alive.
 W
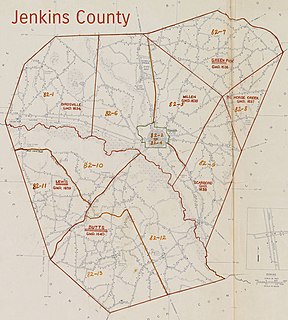
WThe Jenkins County riot of 1919 took place on Sunday, April 13, 1919, when a series of misunderstandings and out-of-control events spiralled into two white police officers being killed. In retaliation the local white community formed mobs and ravaged the black community, burning black community buildings and killing at least four people.
 W
WChilton Jennings was lynched on July 24, 1919, after being accused of attacking a white woman, Mrs. Virgie Haggard in Gilmer, Texas.
 W
WPaul Jones was lynched on November 2, 1919, after being accused of attacking a fifty-year-old white woman in Macon, Georgia.
 W
WThe Knoxville riot of 1919 was a race riot that took place in the American city of Knoxville, Tennessee, on August 30–31, 1919. The riot began when a lynch mob stormed the county jail in search of Maurice Mays, a biracial man who had been accused of murdering a white woman. Unable to find Mays, the rioters looted the jail and fought a pitched gun battle with the residents of a predominantly black neighborhood. The Tennessee National Guard, which at one point fired two machine guns indiscriminately into this neighborhood, eventually dispersed the rioters. At the end of August 1919 the Great Falls Daily Tribune reported four killed in a "race war riot" while the Washington Times reported "Scores dead." Other newspapers placed the death toll at just two, though eyewitness accounts suggest it was much higher.
 W
WThe Laurens County, Georgia race riot was an attack on the black community by white mobs in August of 1919. In the Haynes' report, as summarized in the New York Times, it is called the Ocmulgee, Georgia race riot.
 W
WThe Longview race riot was a series of violent incidents in Longview, Texas, between July 10 and July 12, 1919, when whites attacked black areas of town, killed one black man, and burned down several properties, including the houses of a black teacher and a doctor. It was one of the many race riots in 1919 in the United States during what became known as Red Summer, a period after World War I known for numerous riots occurring mostly in urban areas.
 W
WThe Macon, Mississippi, race riot took place on June 7, 1919, in Macon, Mississippi. Members of the white community were angry that some people were organizing to fight for better work conditions and so beat, whipped and then forced them into exile.
 W
WJim McMillan was lynched in Bibb County, Alabama on June 18, 1919.
 W
WOn Sunday, November 16, 1919, four African-Americans were lynched in Moberly, Missouri. Three were able to escape but one was shot to death.
 W
WThe Morgan County, West Virginia race riot of 1919 was caused by big business using African-American strikebreakers against striking white workers in Morgan County, West Virginia.
 W
WThe New London riots of 1919 were a series of racial riots between white and black Navy sailors and Marines stationed in New London and Groton, Connecticut.
 W
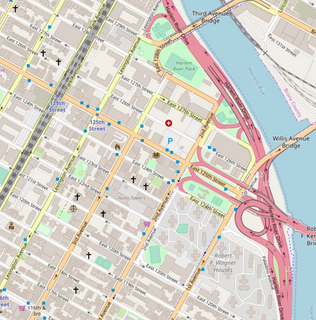
WThe New York race riots of 1919 developed with increasing racial tension and violent incidents in New York City. These riots were a part of the Red Summer, a series of violent terrorist attacks on black communities in many cities in the United States during the summer and early autumn of 1919. The New York race riots were caused by social tensions such as competition for jobs, politics, and racial tension. Many historians and scholars view these riots as the culmination of racial tensions which had been rising due to the migration of African Americans from the rural South to northern cities. Tensions developed partly due to the competition for jobs, which was worsened by the presence of African Americans workers who could replace striking White workers.
 W
WThe Newberry 1919 lynching attempt was the attempted lynching of Elisha Harper, Newberry, South Carolina on July 24, 1919. Harper was sent to jail for insulting a 14 year-old girl.
 W
WNewman O'Neal was the mayor of Hobson City, Alabama until he faced death threats and was assaulted forcing him to flee.
 W
WThe Omaha race riot occurred in Omaha, Nebraska, September 28–29, 1919. The race riot resulted in the lynching of Will Brown, a black civilian; the death of two white rioters; the injuries of many Omaha Police Department officers and civilians, including the attempted hanging of Mayor Edward Parsons Smith; and a public rampage by thousands of white rioters who set fire to the Douglas County Courthouse in downtown Omaha. It followed more than 20 race riots that occurred in major industrial cities of the United States during the Red Summer of 1919.
 W
WThe Port Arthur riot happened on July 15, 1919, in Port Arthur, Texas. Violence started after a group of white men objected to an African American smoking near a white woman on a street car. A "score" of whites and twice that number of African Americans battled in the streets leaving two seriously injured and dozens with minor injuries.
 W
WThe Putnam County, Georgia arson attack was an attack on the black community by white mobs in May of 1919.
 W
WThere were a number of Race riots in Philadelphia during the 1919 Red Summer.
 W
WThe Syracuse riot of 1919 were a violent racial attack that occurred when the management of the Globe Malleable Iron Works pitted striking white unionized workers against black strikebreakers in Syracuse, New York on July 31, 1919.
 W
WThe Washington race riot of 1919 was civil unrest in Washington, D.C. from July 19, 1919, to July 24, 1919. Starting July 19, white men, many in the United States Army, United States Navy, and United States Marine Corps, responded to the rumored arrest of a black man for rape of a white woman with four days of mob violence against black individuals and businesses. They rioted, randomly beat black people on the street, and pulled others off streetcars for attacks. When police refused to intervene, the black population fought back. The city closed saloons and theaters to discourage assemblies. Meanwhile, the four white-owned local papers, including the Washington Post, fanned the violence with incendiary headlines and calling in at least one instance for mobilization of a "clean-up" operation. After four days of police inaction, President Woodrow Wilson ordered 2,000 federal troops to regain control in the nation's capital. But a violent summer rainstorm had more of a dampening effect. When the violence ended, 15 people had died: at least 10 white people, including two police officers; and around 5 black people. Fifty people were seriously wounded and another 100 less severely wounded. It was one of the few times in 20th-century riots of whites against blacks that white fatalities outnumbered those of black people. The unrest was also one of the Red Summer riots in America.
 W
WBerry Washington was a black man who was lynched in Milan, Georgia, in 1919.
 W
WThe Whatley, Alabama race riot of 1919 was a riot, gun battle between the local Black and White community on August 1, 1919.
 W
WThe Wilmington, Delaware race riot of 1919 was a violent racial riot between white and black residents of Wilmington, Delaware on November 13, 1919.