 W
WThe Italian campaign of World War II, also called the Liberation of Italy, consisted of Allied and Axis operations in and around Italy, from 1943 to 1945. The Joint Allied Forces Headquarters (AFHQ) was operationally responsible for all Allied land forces in the Mediterranean theatre and it planned and led the invasion of Sicily in July 1943, followed in September by the invasion of the Italian mainland and the campaign in Italy until the surrender of the German Armed Forces in Italy in May 1945.
 W
WThe Trasimene Line was a German defensive line during the Italian Campaign of World War II. It was sometimes known as the Albert Line. The German Commander-in-Chief (C-in-C), Generalfeldmarschall Albert Kesselring, used the line to delay the Allied northward advance in Italy in mid June 1944 to buy time to withdraw troops to the Gothic Line and finalise the preparation of its defenses.
 W
WThe Allied invasion of Italy was the Allied amphibious landing on mainland Italy that took place on 3 September 1943 during the early stages of the Italian campaign of World War II. The operation was undertaken by General Sir Harold Alexander's 15th Army Group and followed the successful Allied Invasion of Sicily. The main invasion force landed around Salerno on 9 September on the western coast in Operation Avalanche, while two supporting operations took place in Calabria and Taranto.
 W
WThe Allied invasion of Italy, a phase of the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, took place on 3 September at Reggio di Calabria, and on 9 September 1943 at Taranto and Salerno. Allied naval forces landed American and Commonwealth troops on the beaches of southern Italy where they faced resistance from Axis forces.
 W
WThe Armistice of Cassibile was an armistice signed on 3 September 1943 by Walter Bedell Smith and Giuseppe Castellano and made public on 8 September between the Kingdom of Italy and the Allies during World War II. It was signed at a conference of generals from both sides in an Allied military camp at Cassibile, in Sicily, which had recently been occupied by the Allies. The armistice was approved by both King Victor Emmanuel III and Italian Prime Minister Pietro Badoglio. The armistice stipulated the surrender of Italy to the Allies.
 W
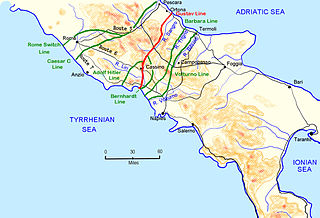
WDuring the Italian Campaign of World War II, the Barbara Line was a series of German military fortifications in Italy, some 10–20 mi (16–32 km) south of the Gustav Line, from Colli al Volturno to the Adriatic Coast in San Salvo and a similar distance north of the Volturno Line. Near the eastern coast, it ran along the line of the Trigno river. The line mostly consisted of fortified hilltop positions. The line was broken by the allied army in November 1943 following which the Axis forces withdrew to the defensible positions of the Winter Line.
 W
WThe Battle for Monte La Difensa, which took place between 3 December and 9 December 1943, occurred during Operation Raincoat, part of the Battle for the Bernhardt Line during the Italian Campaign in World War II.
 W
WThe Battle of Anzio was a battle of the Italian Campaign of World War II that took place from January 22, 1944 to June 5, 1944. The operation was opposed by German forces in the area of Anzio and Nettuno.
 W
WThe Bernhardt Line was a German defensive line in Italy during the Italian Campaign of World War II. Having reached the Bernhardt Line at the start of December 1943, it took until mid-January 1944 for the U.S. Fifth Army to fight their way to the next line of defences, the Gustav Line. The line was defended by XIV Panzer Corps, part of the German Tenth Army.
 W
WBig Fence was a secret navigational aid for US Army Air Force sorties from North Africa and Italy during World War II, ultimately located at the Castel del Monte in Apulia. It was operated by the 6649th Navigational Aids Squadron of the 341st Signal Company, XV Fighter Command, 15th Army Air Force.
 W
WThe Caesar Line was the last German line of defence in Italy before Rome during the Italian Campaign of the Second World War. It extended from the west coast near Ostia, over the Alban Hills south of Rome, from Valmontone to Avezzano and then to Pescara on the Adriatic coast. Behind the western half of the line was a subsidiary line, the Roman switch line which took a path north of Rome.
 W
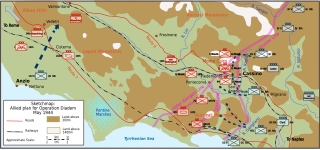
WOperation Diadem, also referred to as the Fourth Battle of Monte Cassino or, in Canada, the Battle of the Liri Valley, was an offensive operation undertaken by the Allies of World War II in May 1944, as part of the Italian Campaign of World War II. Diadem was supported by air attacks called Operation Strangle. The opposing force was the German 10th Army.
 W
WThe Hitler Line was a German defensive line in central Italy during the Second World War. The strong points of the line were at Aquino and Piedimonte. In May 1944, the line was renamed the Senger Line, after General von Senger und Etterlin, one of the generals commanding Axis forces in the area. This was done at Hitler's insistence, in order to minimise any propaganda significance should the line be penetrated.
 W
WThe 1st Special Service Force was an elite American–Canadian commando unit in World War II, under the command of the United States Fifth Army. The unit was organized in 1942 and trained at Fort William Henry Harrison near Helena, Montana in the United States. The Force served in the Aleutian Islands, and fought in Italy, and southern France before being disbanded in December 1944.
 W
WThe Four days of Naples refers to the popular ad hoc World War II uprising in Naples, Italy between September, 28-30 1943 against German occupying forces, immediately prior to the arrival in Naples of Allied forces on October 1st that same year.
 W
WThe French Expeditionary Corps, also known as the French Expeditionary Corps in Italy, was an expeditionary force of the French Liberation Army. Created in 1943, the corps fought in the Italian Campaign of World War II, under the command of General Alphonse Juin. Consisting of 112,000 men divided into four divisions, all but one of the divisions were colonial units, mostly Moroccans and Algerians drawn from the Army of Africa and led by French officers.
 W
WThe Gothic Line was a German defensive line of the Italian Campaign of World War II. It formed Field Marshal Albert Kesselring's last major line of defence along the summits of the northern part of the Apennine Mountains during the fighting retreat of the German forces in Italy against the Allied Armies in Italy, commanded by General Sir Harold Alexander.
 W
WThe Gothic Line was a German defensive line of the Italian Campaign of World War II. It formed Field Marshal Albert Kesselring's last major line of defence along the summits of the northern part of the Apennine Mountains during the fighting retreat of the German forces in Italy against the Allied Armies in Italy, commanded by General Sir Harold Alexander.
 W
WHamish Scott Henderson was a Scottish poet, songwriter, communist, intellectual and soldier.
 W
WThe Hitler Line was a German defensive line in central Italy during the Second World War. The strong points of the line were at Aquino and Piedimonte. In May 1944, the line was renamed the Senger Line, after General von Senger und Etterlin, one of the generals commanding Axis forces in the area. This was done at Hitler's insistence, in order to minimise any propaganda significance should the line be penetrated.
 W
WThe Allied invasion of Sicily, codenamed Operation Husky, was a major campaign of World War II, in which the Allies took the island of Sicily from the Axis powers. It began with a large amphibious and airborne operation, followed by a six-week land campaign, and initiated the Italian Campaign.
 W
WThe Italian Civil War was a civil war in Italy fought by the Italian Co-Belligerent Army and the Italian Resistance with the Allies of World War II against the Italian Fascists and Italian Social Republic and the German Army from 9 September 1943 to 2 May 1945.
 W
WMarocchinate is a term applied to the mass rape and killings committed during World War II after the Battle of Monte Cassino in Italy. These were committed mainly by the Moroccan Goumiers, colonial troops of the French Expeditionary Corps (FEC), commanded by General Alphonse Juin, and mostly targeted civilian women and girls in the rural areas between Naples and Rome, in Southern Lazio.
 W
WThe Moro River Campaign order of battle is a listing of the significant formations that were involved in the fighting during the Moro River Campaign in December 1943, part of the Italian Campaign of World War II.
 W
WThe Bernhardt Line was a German defensive line in Italy during the Italian Campaign of World War II. Having reached the Bernhardt Line at the start of December 1943, it took until mid-January 1944 for the U.S. Fifth Army to fight their way to the next line of defences, the Gustav Line. The line was defended by XIV Panzer Corps, part of the German Tenth Army.
 W
WThe Roman switch line was a German line of defense during World War II in Italy branching off the Caesar C line and running north of Rome towards coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea. The next line was Trasimene Line in central Italy which was intended to delay the Allies and allow the completion of the Gothic Line a major defensive works north of Florence.
 W
WOperation Avalanche was the codename for the Allied landings near the port of Salerno, executed on 9 September 1943, part of the Allied invasion of Italy. The Italians withdrew from the war the day before the invasion, but the Allies landed in an area defended by German troops. Planned under the name Top Hat, it was supported by the deception plan Operation Boardman.
 W
WThe Battle of San Pietro Infine was a major engagement from 8–17 December 1943, in the Italian Campaign of World War II involving Allied forces attacking from the south against heavily fortified positions of the German "Winter Line" in and around the town of San Pietro Infine, just south of Monte Cassino about halfway between Naples and Rome.
 W
WThe Second Battle of the Alps was a military campaign fought between combined German and Italian Social Republic forces, and the re-established French Republic led by Charles de Gaulle.
 W
WThe Hitler Line was a German defensive line in central Italy during the Second World War. The strong points of the line were at Aquino and Piedimonte. In May 1944, the line was renamed the Senger Line, after General von Senger und Etterlin, one of the generals commanding Axis forces in the area. This was done at Hitler's insistence, in order to minimise any propaganda significance should the line be penetrated.
 W
WThe Battle of Anzio was a battle of the Italian Campaign of World War II that took place from January 22, 1944 to June 5, 1944. The operation was opposed by German forces in the area of Anzio and Nettuno.
 W
WThe Allied invasion of Sicily, codenamed Operation Husky, was a major campaign of World War II, in which the Allies took the island of Sicily from the Axis powers. It began with a large amphibious and airborne operation, followed by a six-week land campaign, and initiated the Italian Campaign.
 W
WOperation Slapstick was the code name for a British landing from the sea at the Italian port of Taranto during the Second World War. The operation, one of three landings during the Allied invasion of Italy in September 1943, was undertaken by airborne troops of the British 1st Airborne Division, commanded by Major-General George Hopkinson.
 W
WThe spring 1945 offensive in Italy, codenamed Operation Grapeshot, was the final Allied attack during the Italian Campaign in the final stages of the Second World War. The attack into the Lombardy Plain by the 15th Allied Army Group started on 6 April 1945, ending on 2 May with the formal surrender of German forces in Italy.
 W
WOperation Strangle was a series of air interdiction operations during the Italian Campaign of World War II by the United States Fifteenth and Twelfth Air Forces to interdict German supply routes in Italy north of Rome from 19 March 1944 to 11 May 1944. Its aim was to prevent essential supplies from reaching German forces in Central Italy and compel a German withdrawal. The strategic goal of the air assault was to eliminate or greatly reduce the need for a ground assault on the region. The Allies failed in the overly ambitious objective of the campaign, namely the forced withdrawal of German forces from the Gustav Line, but the air interdiction seriously complicated the German conduct of defensive operations and played a major role in the success of the subsequent Allied ground assault Operation Diadem.
 W
WThunderbolt is a 1947 film directed by William Wyler and John Sturges which documented the American aerial operations of Operation Strangle in World War II, when flyers of the Twelfth Air Force based on Corsica successfully impeded Axis supply lines to the Gustav Line and Anzio beachhead. The film was originally shot in 16mm color by members of the Army Air Forces. The 12th Combat Camera Unit recorded the combat footage using cameras mounted on some of the P-47s and a B-25 medium bomber equipped as a camera ship to accompany the fighters.
 W
WThe Trasimene Line was a German defensive line during the Italian Campaign of World War II. It was sometimes known as the Albert Line. The German Commander-in-Chief (C-in-C), Generalfeldmarschall Albert Kesselring, used the line to delay the Allied northward advance in Italy in mid June 1944 to buy time to withdraw troops to the Gothic Line and finalise the preparation of its defenses.
 W
WThe Volturno Line was a German defensive position in Italy during the Italian Campaign of World War II.
 W
WThe Volturno Line was a German defensive position in Italy during the Italian Campaign of World War II.
 W
WThe Winter Line was a series of German and Italian military fortifications in Italy, constructed during World War II by Organisation Todt and commanded by Albert Kesselring. The series of three lines was designed to defend a western section of Italy, focused around the town of Monte Cassino, through which ran the important Highway 6 which led uninterrupted to Rome. The primary Gustav Line ran across Italy from just north of where the Garigliano River flows into the Tyrrhenian Sea in the west, through the Apennine Mountains to the mouth of the Sangro River on the Adriatic coast in the east. The two subsidiary lines, the Bernhardt Line and the Hitler Line ran much shorter distances from the Tyrrehnian sea to just North East of Cassino where they would merge into the Gustav Line. Relative to the Gustav Line, the Hitler Line stood to the North-West and the Bernhardt Line to the South-East of the primary defenses.