 W
WThe Edict of Amboise, also known as the Edict of Pacification, was signed at the Château of Amboise on 19 March 1563 by Catherine de' Medici, acting as regent for her son Charles IX of France. The treaty officially ended the first phase of the French Wars of Religion. Moreover, the treaty restored peace to France by guaranteeing the Huguenots religious privileges and freedoms.
 W
WThe Treaty of Angoulême was signed on 10 August 1619 between Queen Marie de Medici and her son, King Louis XIII of France in Angoulême, France. The accord was negotiated by Cardinal Richelieu and it officially ended the civil war in France between supporters of Queen Marie and supporters of King Louis. Moreover, the agreement established lines of reconciliation between mother and son.
 W
WThe Treaty of Aranjuez was signed on June 3, 1777, between France and Spain. Based on the terms of the treaty, the two countries agreed to define the border of their respective colonies on the island of Santo Domingo in the Caribbean Sea which they shared ownership of. Spain made substantial gains in the upper Artibonite Valley in middle section of the island. The new border was to be marked by border stones. It was signed at Aranjuez Palace near Madrid in Spain. It was one of a number of diplomatic agreements signed at the palace in the eighteenth century and should not be confused with the 1779 Treaty of Aranjuez between the two states which led to Spain's entry into the American War of Independence.
 W
WThe Treaty of Aranjuez (1779) was signed on 12 April 1779 by France and Spain. Under its terms, Spain agreed to support France in its war with Britain, in return for French assistance in recovering the former Spanish possessions of Menorca, Gibraltar and the Floridas.
 W
WThe Treaty of Arras was signed at Arras on 23 December 1482 by King Louis XI of France and Archduke Maximilian I of Habsburg as heir of the Burgundian Netherlands in the course of the Burgundian succession crisis.
 W
WThe Treaty of Athis-sur-Orge was a peace treaty signed on 23 June 1305 between King Philip IV of France and Robert III of Flanders. The treaty was signed at Athis-sur-Orge after the Battle of Mons-en-Pévèle and concluded the Franco-Flemish War (1297-1305).
 W
WThe Treaty of Bärwalde, signed on 23 January 1631, was an agreement by France to provide Sweden financial support, following its intervention in the Thirty Years' War.
 W
WOn 7 November 921, the Treaty of Bonn, the text of which calls itself a "pact of friendship" (amicitia), was signed between Charles III of France and Henry I of Germany in a minimalist ceremony aboard a ship in the middle of the Rhine not far from Bonn. The use of the river, which was the border between their two kingdoms, as a neutral territory had extensive Carolingian precedents and was also used in classical antiquity and in contemporary Anglo-Saxon England.
 W
WThe Treaty of Chambord was an agreement signed on 15 January 1552 at the Château de Chambord between the Catholic King Henry II of France and three Protestant princes of the Holy Roman Empire led by Elector Maurice of Saxony. Based on the terms of the treaty, Maurice ceded the vicariate over the Three Bishoprics of Toul, Verdun, and Metz to France. In return, he was promised military and economic aid from Henry II in order to fight against the forces of Emperor Charles V of Habsburg.
 W
WThe 1698 Treaty of The Hague, also known as the 1698 Treaty of Den Haag or First Partition Treaty was the first of two attempts by France, Britain, and the Dutch Republic to achieve a diplomatic solution to the issues that led to the 1701–1714 War of the Spanish Succession.
 W
WThe Treaty of Dover, also known as the Secret Treaty of Dover, was a treaty between England and France signed at Dover on 1 June 1670. It required that Charles II of England would convert to the Roman Catholic Church at some future date and that he would assist Louis XIV with 60 warships and 4,000 soldiers to help in France's war of conquest against the Dutch Republic. In exchange, Charles would secretly receive a yearly pension of £230,000, as well as an extra sum of money when Charles informed the English people of his conversion, and France would send 6,000 French troops if there was ever a rebellion against Charles in England. The secret treaty was signed by Arlington, Arundell, Clifford, and Bellings for England and Colbert de Croissy for France. The two kings exchanged letters of ratification and kept secret the existence of the treaty. A public treaty of Dover was also negotiated, but it was a screen designed for propaganda purposes and to hide the religious dimension of the secret treaty. The Third Anglo-Dutch War was a direct consequence of this treaty. The actual treaty was published by historians a century later.
 W
WThe Eden Treaty was a treaty signed between Great Britain and France in 1786, named after the British negotiator William Eden, 1st Baron Auckland (1744–1814). It effectively ended, for a brief time, the economic war between France and the British and set up a system to reduce tariffs on goods from either country. It was spurred on in Britain by the secession of the thirteen American colonies, and the publication of Adam Smith's Wealth of Nations. British Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger was heavily influenced by the ideas of Smith, and was one of the key motivators of the treaty. Obstinancy in negotiations on the part of the British made the commercial agreement almost wholly beneficial to the British, and the unequal protection on certain industries ended up hurting the French economy. This treaty is often considered to be one of the grievances of the French people that sparked the French Revolution. The treaty collapsed in 1793, following claims in the National Convention that the Aliens Act 1793 breached the terms of the treaty and the outbreak of war in early February between Great Britain and France ended any chance of a compromise.
 W
WThe Treaty of Fontainebleau was signed on 30 May 1631 during the Thirty Years' War, at the Palace of Fontainebleau. It was a pact of mutual assistance between Maximilian I, Elector of Bavaria, and France, for a period of eight years.
 W
WA Franco-Hungarian alliance was formed in October 1528 between King Francis I of France and King John Zápolya of Hungary.
 W
WThe Treaty of Hanover was a treaty of defensive alliance signed on 3 September 1725 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, the Electorate of Hanover, the Kingdom of France, and the Kingdom of Prussia. The alliance was formed to combat the power of the Austro-Spanish alliance founded at the Peace of Vienna months earlier in May 1725.
 W
WThe Convention of Klosterzeven was a convention signed on 10 September 1757 at Klosterzeven between France and the Electorate of Hanover during the Seven Years' War that led to Hanover's withdrawal from the war and partial occupation by French forces. It came in the wake of the Battle of Hastenbeck on 26 July in which Hanover had suffered a devastating defeat. Following the battle the Army of Observation had retreated northwards until it had reached Stade.
 W
WThe Treaty of London (1700) or Second Partition Treaty was the second of two attempts by France, Great Britain and the United Provinces, or Dutch Republic, to impose a diplomatic solution to the issues that resulted in the 1701-1714 War of the Spanish Succession.
 W
WThe Treaty of Lyon was signed on January 17, 1601 between France and Savoy, to bring an end to the Franco-Savoyard War of 1600–1601. Based on the terms of the treaty, Henry IV of France relinquished Saluzzo to Savoy, while Savoy kept Pont de Gresin, Valserine, and was required to pay France 150,000 livres. In return, Henry acquired Bugey, Valromey, Gex, and Bresse.
 W
WThe Pacte de Famille is one of three separate, but similar alliances between the Bourbon kings of France and Spain. As part of the settlement of the War of the Spanish Succession that brought the House of Bourbon of France to the throne of Spain. Spain and France made a series of agreements that did not unite the two thrones, but did cooperate on defined bases.
 W
WThe Treaty of Paris was a treaty between Louis IX of France and Henry III of England, agreed to on 4 December 1259, ending 100 years of conflicts between the Capetian and Plantagenet dynasties.
 W
WThe Persian embassy to Louis XIV caused a dramatic flurry at the court of Louis XIV in 1715, the year of the Sun King's death. Mohammed Reza Beg, or in French sources Méhémet Riza Beg, was a high-ranking official to the Persian governor of the Iravan (Erivan) province. He had been chosen by the Safavid Persian emperor Sultan Husayn for the mission and travelled with a grand entourage, as suitable to the diplomat of a mighty empire.
 W
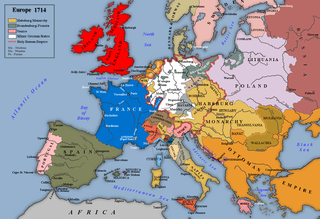
WThe Treaty of Rastatt was a peace treaty between France and Austria, concluded on 7 March 1714 in the Baden city of Rastatt, to put an end to state of war between them from the War of the Spanish Succession. The treaty followed the earlier Treaty of Utrecht of 11 April 1713, which ended hostilities between France and Spain, on the one hand, and Britain and the Dutch Republic, on the other hand. A third treaty at Baden, Switzerland was required to end the hostilities between France and the Holy Roman Empire.
 W
WThe Treaty or Peace of Saint-Germain-en-Laye of 19 June (OS) or 29 June (NS) 1679 was a peace treaty between France and the Electorate of Brandenburg. It restored to France's ally Sweden her dominions Bremen-Verden and Swedish Pomerania, lost to Brandenburg in the Scanian War. Sweden ratified the treaty on 28 July 1679.
 W
WThe Treaty of Senlis concerning the Burgundian succession was signed at Senlis, Oise in May 1493 between Maximilian I of Habsburg and King Charles VIII of France.
 W
WThe Siamese embassy to France in 1686 was the second such mission from the Kingdom of Siam. The embassy was sent by King Narai and led by ambassador Kosa Pan. This embassy was preceded by the First Siamese Embassy to France, composed of two Siamese ambassadors and Father Bénigne Vachet, who had left Siam for France on January 5, 1684.
 W
WThe Treaty of Tours was an attempted peace agreement between Henry VI of England and Charles VII of France, concluded by their envoys on 28 May 1444 in the closing years of the Hundred Years' War. The terms stipulated the marriage of Charles VII's niece, Margaret of Anjou, to Henry VI, and the creation of a truce of two years – later extended – between the kingdoms of England and France. In exchange for the marriage, Charles wanted the English-held area of Maine in northern France, just south of Normandy.
 W
WThe Treaty of Alliance or Franco-American Treaty was a defensive alliance between France and the United States of America, formed in the midst of the American Revolutionary War, which promised mutual military support in case fighting should break out between French and British forces, as the result of signing the previously concluded Treaty of Amity and Commerce. The alliance was planned to endure indefinitely into the future. Delegates of King Louis XVI of France and the Second Continental Congress, who represented the United States at this time, signed the two treaties along with a separate and secret clause dealing with future Spanish involvement, at the hôtel de Coislin in Paris on February 6, 1778. The Franco-American alliance would technically remain in effect until the 1800 Treaty of Mortefontaine, despite being annulled by the United States Congress in 1793 when George Washington gave his Neutrality Proclamation speech saying that America would stay neutral in the French Revolution.
 W
WThe Treaty of Amity and Commerce Between the United States and France, was the first of two treaties between the United States and France, signed on February 6, 1778, at the Hôtel de Coislin in Paris. Its sister treaty, the Treaty of Alliance were signed immediately thereafter. The Treaty of Amity and Commerce recognized the de facto independence of the United States and established a strictly commercial treaty between the two nations as an alternative to, and in direct defiance of, the British Acts of Trade and Navigation; the Treaty of Alliance, for mutual defense, was then signed "particularly in case Great Britain in Resentment of that connection and of the good correspondence which is the object of the [first] Treaty, should break the Peace with France, either by direct hostilities, or by hindering her commerce and navigation, in a manner contrary to the Rights of Nations, and the Peace subsisting between the two Crowns". These were the first treaties ever negotiated by the fledgling United States and signed in the midst of the American Revolutionary War. Due to later complications with the alliance treaty, America would not sign another military alliance until the Declaration by United Nations in 1942.
 W
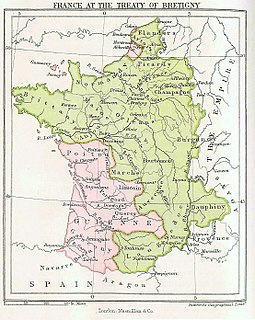
WThe Treaty of Brétigny was a treaty, drafted on 8 May 1360 and ratified on 24 October 1360, between King Edward III of England and King John II of France. In retrospect, it is seen as having marked the end of the first phase of the Hundred Years' War (1337–1453) as well as the height of English power on the Continent.
 W
WThe Caroline War was the second phase of the Hundred Years' War between France and England, following the Edwardian War. It was so-named after Charles V of France, who resumed the war nine years after the Treaty of Brétigny. The Kingdom of France dominated this phase of the war.
 W
WThe Treaty of Compiègne, signed on 10 June 1624, was a mutual defence alliance between the Kingdom of France and the Dutch Republic, for an initial period of three years.
 W
WThe Treaty of Lisbon was signed on 31 March 1667 by Portugal and France, which agreed to a ten-year defensive and offensive alliance against Spain. The treaty was driven by Louis XIV, who was preparing to seize the Spanish Netherlands. The Portuguese Restoration War, which had begun in 1640, was coming to an end. Ensuring that it continued would absorb Spanish resources and prevent Spain from sending reinforcements.
 W
WThe Treaty of London in 1518 was a non-aggression pact between the major European nations. The signatories were Burgundy, France, England, the Holy Roman Empire, the Netherlands, the Papal States and Spain, all of whom agreed not to attack one another and to come to the aid of any that were under attack.
 W
WThe Treaty of Orléans was a marriage treaty signed in 1275, that led to a short-lived personal union between the kingdoms of Navarre and France. It was signed by Philip III of France and his cousin Blanche of Artois, mother and regent to the two-year-old Joan I of Navarre. The original intent of the treaty was not to create a personal union, however, but to enable Philip to administer Navarre in Joan's name. Joan was also to marry either Philip's firstborn and heir apparent, Louis, or his second son, Philip. Pope Gregory X explicitly stated that he preferred a match with the younger son, as he probably wished to avoid merging Navarre with France. Louis died in 1276, however, leaving Philip as the only choice per the terms of the treaty.
 W
WThe Treaty of Turin (1696) was signed on 29 August 1696 by France and the Duchy of Savoy, ending Savoy's involvement in the Nine Years' War.
 W
WThe Treaty of Versailles was concluded on 15 May 1768 at Versailles between the Republic of Genoa and France. Genoa put Corsica in pledge to France.
 W
WThe Truce of Malestroit was signed on 19 January 1343 between Edward III of England and Philip VI of France, in the chapelle de la Madeleine in Malestroit. After the signing of this truce, the English sovereign and his troops left Bretagne for England.
 W
WThe Treaty of Versailles of 1787 was a treaty of alliance signed between the French king Louis XVI and the Vietnamese lord Nguyễn Ánh, the future Emperor Gia Long.
 W
WThe Treaty of Vossem was signed on 6 June 1673, between Frederick William, Elector Brandenburg and Louis XIV of France; England, then a French ally against the Dutch, was included as a party to the terms but not a signatory. It was ratified by both parties on 20 July.